VINCLOZOLIN
- CAS NO.:50471-44-8
- Empirical Formula: C12H9Cl2NO3
- Molecular Weight: 286.11
- MDL number: MFCD00055511
- EINECS: 256-599-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
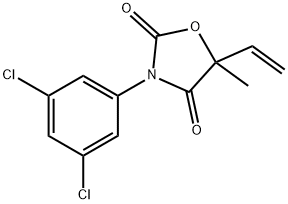
What is VINCLOZOLIN?
The Uses of VINCLOZOLIN
Vinclozolin is a non-systemic, contact fungicide that controls fruit rot, brown rot, mould and blight caused by Botrytis spp., Sclerotinia spp., Monilia spp., etc. in vines, fruits, vegetables, oilseed rape, ornamentals, hops, turf and strawberries. Vinclozolin exhibits both preventive and curative activities.
The Uses of VINCLOZOLIN
Agricultural fungicide.
What are the applications of Application
Vinclozolin is a fungicide with antiandrogenic properties
Definition
ChEBI: 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-ethenyl-5-methyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione is a member of the class of oxazolidinones that is 5-ethenyl-5-methyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione in which the imide hydrogen is replaced by a 3,5-dichlorophenyl group. It is a dicarboximide, a dichlorobenzene, an oxazolidinone and an olefinic compound.
General Description
Colorless crystals with slight aromatic odor. Used as a fungicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolysis rapidly occurs under alkaline conditions
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated dicarboximide. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Vinclozolin is a non-systemic fungicide which has been used on vines (such as grapes), strawberries, raspberries, chicory grown for Belgian endive, lettuce, kiwi, canola, succulent beans, and dry bulb onions. Import tolerances have been established to permit. Not approved for use in EU countries . Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
BAS-352-F®; BAS-35204-F®; CURALAN®; FLOTILLA®; FUMITE RONALIN®; MASCOT® contact turf fungicide; ORNALIN®[C]; POWERDRIVE®; RONILAN®; RONILAN-DF®; RONALINE-FL®; TOUCHE®; VINCHLOZOLINE®; VINCLOZOLINE®; VORLAND®
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion and inhalation. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx.
Metabolic pathway
The fungicides, chlozolinate, vinclozolin, and procymidone, are added to wine after fermentation and the degradation products are isolated and identified. Chlozolinate undergoes a rapid hydrolytic loss of the ethoxycarbonyl substituent to give an oxazolidine that further undergoes hydrolytic cleavage to give 3' ,5' -dichloro-2-hydroxypropanilide. The oxazolidine ring of vinclozolin undergoes a similar hydrolysis reaction to give the corresponding anilide, 3' ,5'-dichloro-2-hydroxy-2-methylbut-3-eneanilide. Both of these anilides are stable in wine for 150 days. A different degradation behavior is observed with procymidone and leads to the formation of 3,5- dichloroaniline, which, in turn, breaks down in wine.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the fungicide from Me2CO/H2O. Its solubility at 20o (w/w%) is 44 (Me2CO), 32 (CHCl3), 25 (EtOAc) and 10 (H2O). It irritates the eyes and skin. [GP 2,207,576 1973, Chem Abstr 79 137120 1973.]
Degradation
Vinclozolin (1) was rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline solution. The hydrolytic
DT50, values in pH 5, 7 and 9 solution at 25 °C were 45 days, 13.4
hours and 1.6 hours, respectively (Melkebeke et al., 1986). Szeto et al.
(1989a) and Villedieu et al. (1994, 1995) reported that the opening of
the oxazolidinedione ring by attack of the hydroxyl ion on the two
carbonyl groups is the primary hydrolysis mechanism to yield 2-{[3,5-
dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]-oxy}-2-methyl-3-butenoica cid (2) and 3'5'-
dichloro-2-hydroxy-2-methylbut-3-enanilide(3) as major products. The
formation of compound 3 was likely via the intermediate N-(2-hydroxy-
2-methyl-1-oxo-buten-3-yl)-3,5-dichlorophenyl-1-carbamic acid (4). 3,5-
Dichloroaniline (5) was reported as a minor hydrolysis product. The
proposed hydrolytic degradation pathway of vinclozolin is presented in
Scheme 1. Compound 3 was also reported as the primary degradation
product of vinclozolin in wine (pH 3-4, 30 °C) whereas 3,5-
dichloroaniline (5) was not detected in the wine samples (Cabras et al.,
1984; Pirisi et al., 1986).
The degradation rate of vinclozolin in aqueous solution at λ> 290 nm
was slower than at λ>230 nm; furthermore, the addition of humic
and fulvic acids catalysed the aqueous photodegradation reaction
(DT50 8 hours) to yield compound 5 and 3,5-dichlorophenyl isocyanate
(6) as primary degradation products (see Scheme 1; Hustert and
Moza, 1997). Schwack et al. (1995) reported the photolytic reactions of
vinclozolin in various organic solvents. Addition of the solvent molecules
to the vinyl moiety and dechlorination products were observed as major
photodegradation reactions.
Properties of VINCLOZOLIN
| Melting point: | 108℃ |
| Boiling point: | 131℃ (0.05mmHg) |
| Density | 1.51 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 1.3 x 10-4 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6100 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml,DMSO: 30 mg/ml,Ethanol: 30 mg/ml,Ethanol:PBS(pH 7.2) (1:1): 0.5 mg/ml |
| Water Solubility | 3.4 mg l-1 (20 °C) |
| form | neat |
| pka | -3.43±0.40(Predicted) |
| Merck | 13,10046 |
| BRN | 8331312 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Vinclozolin (50471-44-8) |
Safety information for VINCLOZOLIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H351:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for VINCLOZOLIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Vinclozolin CAS 50471-44-8View Details
Vinclozolin CAS 50471-44-8View Details
50471-44-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8