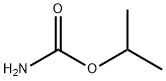
Propham
Synonym(s):IPC;Isopropyl phenylcarbamate
- CAS NO.:122-42-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 179.22
- MDL number: MFCD00026382
- EINECS: 204-542-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
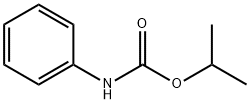
What is Propham?
Chemical properties
White to gray crystalline needles; odorless when pure. Mp 84C (technical grade). Soluble in alcohol, acetone, isopropyl alcohol; insoluble in water.
Chemical properties
Propham is a colorless crystalline solid.
The Uses of Propham
Herbicide, applied as a spray to the soil.
The Uses of Propham
Preemergence and postemergence herbicide used to control annual grass weeds in peas, beet crops, lucerne, clover, sugar beet, beans, lettuce, flax, safflowers and lentils.
The Uses of Propham
Inhibitor of plant metabolism
Definition
ChEBI: Propham is a carbamate ester that is the isopropyl ester of phenylcarbamic acid. It is a selective herbicide used for the control of annual grasses and some broad-leaf weeds and is also a growth regulator for control of sprouting in stored potatoes. It has a role as a herbicide and a plant growth retardant. It is a carbamate ester and a member of benzenes.
General Description
Colorless crystalline solid.
Reactivity Profile
Propham is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Moderately toxic herbicide; exhibited low tomoderate toxicity in experimental animalswhen administered by oral, intraperitoneal,intravenous, and subcutaneous routes; skinabsorption is slow; cholinesterase inhibitor;in human ingestion can cause carbamatepoisoning, which can be lethal when takenin large amount; probable lethal oral dosein adult human estimated to be larger thanother carbamate insecticides within the range35–50 g.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Moderately toxic experimentally by ingestion and possibly other routes. An experimental teratogen. Human mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. An herbicide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NO,. See also CARBAMATES.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation and application of this car- bamate/organonitrogen grass-control herbicide.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Rajagopal et al. (1989) reported that Achromobacter sp. and an Arthrobacter sp. utilized propham as a sole carbon source. Metabolites identified were Nphenylcarbamic acid, aniline, catechol, monoisopropyl carbonate, 2-propanol and carbon
dioxide (Rajagopal et al., 1989).
Soil. Readily degraded by soil microorganisms forming aniline and carbon dioxide
(Humburg et al., 1989). The reported half-life in soil is approximately 15 and 5 days at
16 and 29°C, respectively (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Groundwater. According to the U.S. EPA (1986) propham has a high potential to leach
to groundwater.
Plant. The major plant metabolite which was identified from soybean plants is isopropyl N-2-hydroxycarbanilate (Hartley and Kidd, 1987; Humburg et al., 1989).
Chemical/Physical. Hydrolysis of propham yields N-phenylcarbamic acid and 2-propanol. The acid is very unstable and is spontaneously decomposed to form aniline and
carbon dioxide (Still and Herrett, 1976). Emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides when heated
to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987).
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz- ardous material, Technical Name Required. UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Carbamates are incompatible with reduc- ing agents, strong acids, oxidizing acids, peroxides, and bases. Contact with active metals or nitrides cause the release of flammable, and potentially explosive, hydrogen gas. May react violently with bromine, ketones. Incompatible with azo dyes, caustics, ammonia, amines, boranes, hydrazines, strong
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recom- mendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following pack- age label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Propham
| Melting point: | 90°C |
| Boiling point: | 311.75°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0900 |
| refractive index | 1.4989 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.74±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Dark brown, blue-black |
| Water Solubility | 0.1g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,7908 |
| BRN | 2209666 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 122-42-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 12, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carbamic acid, phenyl-, 1-methylethyl ester(122-42-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propham (122-42-9) |
Safety information for Propham
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Propham
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Isopropyl N-phenylcarbamate 96% (GC) CAS 122-42-9View Details
Isopropyl N-phenylcarbamate 96% (GC) CAS 122-42-9View Details
122-42-9 -
 Propham CAS 122-42-9View Details
Propham CAS 122-42-9View Details
122-42-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8