viloxazine
- CAS NO.:46817-91-8
- Empirical Formula: C13H19NO3
- Molecular Weight: 237.29
- EINECS: 256-281-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
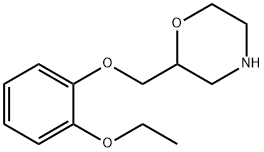
What is viloxazine?
Absorption
Viloxazine is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. The relative bioavailability of viloxazine extended-release relative to an immediate-release formulation was about 88%.
Viloxazine Cmax and AUC increase proportionally over a dosage range from 100 mg to 600 mg once daily. The Cmax ranges between 540 and 1600 ng/mL. Following administration of a single 200 mg dose, the median Tmax was approximately five hours, with a range of three to nine hours. Steady-state was reached after two days of once-daily administration, and no accumulation was observed. A high-fat meal decreases Cmax and AUC by about 9% and 8%, respectively, and delays Tmax by two hours.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of viloxazine was 2000 mg/kg in rats.
There is limited clinical experience with viloxazine overdose. According to case reports in the literature and postmarketing reports, doses ranging from 1000 mg to 6500 mg, which are 1.7 to 10.8 times the maximum recommended daily dose, resulted in overdose with drowsiness as the most reported symptom. Impaired consciousness, diminished reflexes, and increased heart rate have also been reported. There is no specific antidote for viloxazine overdose.
Originator
Vivalan,I.C.I. ,UK,1974
The Uses of viloxazine
Antidepressant.
Indications
Viloxazine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older.
Background
Viloxazine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. For decades, an immediate-release formulation of viloxazine has been used in Europe as an antidepressant. It was first approved in the UK in 1974; however, the immediate-release formulation was discontinued due to business reasons unrelated to drug safety and efficacy. In the US, viloxazine was assigned an orphan drug designation in 1984 under the brand name CATATROL: while this product was intended to treat cataplexy and narcolepsy, the drug was never approved for these therapeutic indications. In April 2021, an extended-release formulation of viloxazine under the brand name QELBREE was approved by the FDA for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Definition
ChEBI: 2-[(2-ethoxyphenoxy)methyl]morpholine is an aromatic ether.
Manufacturing Process
2-Ethoxyphenol is first reacted with epichlorohydrin to give 1,2-epoxy-3-(o-
ethoxyphenoxy)-propane.
A mixture of crude (83%) 1,2-epoxy-3-(o-ethoxyphenoxy)propane (19.4
grams), 70.5 grams 2-aminoethyl hydrogen sulfate, 40.0 grams sodium
hydroxide, 400 ml ethanol and 200 ml water is stirred at 60°C for 18 hours
and is then evaporated to dryness. The residue is dissolved in 200 ml water
and the mixture is extracted three times with 150 ml of diethyl ether each
time. The combined extracts are dried over magnesium sulfate and
evaporated to dryness, The crude product (21.5 grams) is dissolved in
isopropanol (20 ml), 10.5 ml concentrated aqueous hydrochloric acid and 75
ml ethyl acetate are added and the mixture is cooled. The mixture is filtered
and there is thus obtained as solid product 2-(o-ethoxyphenoxymethyl)
morpholine hydrochloride, MP 179° to 182°C (8.6 grams; 38% yield based on
total epoxide used), according to US Patent 3,712,890.
Therapeutic Function
Psychotropic
Pharmacokinetics
Viloxazine is a serotonin-norepinephrine modulating agent that has been used as a treatment for depression and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Although it is not a stimulant agent, viloxazine produces amphetamine-like CNS stimulant effects without a risk for drug abuse or dependence. Viloxazine does not produce sedative anticholinergic or adrenergic effects.
Metabolism
Viloxazine undergoes CYP2D6-mediated 5-hydroxylation to form 5-hydroxyviloxazine. This metabolite can be glucuronidated by UGT1A9 and UGT2B15 to form 5-hydroxyviloxazine glucuronide, which is the major metabolite detected in plasma. Viloxazine can also be glucuronidated to form Viloxazine N-carbamoyl glucuronide.
Properties of viloxazine
| Melting point: | 176-179 °C |
| Boiling point: | 379.83°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0942 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| pka | pKa 8.1 (Uncertain) |
Safety information for viloxazine
Computed Descriptors for viloxazine
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(2R)-2-[[[3-(4-MORPHOLINYLMETHYL)-2H-1-BENZOPYRAN-8-YL]OXY]METHYL]MORPHOLINE DIMETHANESULFONATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/205242-62-2.gif)
![2-[(2-ETHOXY-PHENOXY)-PHENYL-METHYL]-MORPHOLINE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID TERT-BUTYL ESTER](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure20/GIF/CB21009941.gif)

![(2RS,3RS)-6-[A-(2-ETHOXY-D5-PHENOXY)BENZYL]MORPHOLIN-3-ONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure21/GIF/CB0507549.gif)
![2-[(2-ethoxyphenoxy)methyl]morpholine hydrochloride](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/35604-67-2.gif)
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4