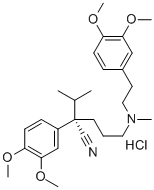
Verapamil hydrochloride
Synonym(s):(±)-Verapamil hydrochloride;5-[N-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenylethyl)methylamino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:23313-68-0
- Empirical Formula: C27H39ClN2O4
- Molecular Weight: 491.06
- MDL number: MFCD00055208
- EINECS: 245-579-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-05-07 14:42:03
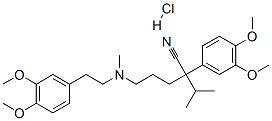
What is Verapamil hydrochloride?
Chemical properties
White Powder
The Uses of Verapamil hydrochloride
A calcium channel blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class IV)
The Uses of Verapamil hydrochloride
Calcium antagonists
brand name
Calan (Searle); Covera (Searle); Isoptin (FSC); Isoptin (Par); Verelan (Elan).
Clinical Use
Calcium-channel blocker:
Supraventricular arrhythmias
Angina
Hypertension
Cluster headaches (unlicensed)
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Veterinary experience with this agent is somewhat limited, but in dogs and cats verapamil may be useful for supraventricular tachycardias and, possibly, treatment of atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline and theophylline: enhanced effect of
aminophylline and theophylline.
Anaesthetics: increased hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of amiodaroneinduced bradycardia, AV block and myocardial
depression; increased risk of myocardial depression
and asystole with disopyramide and flecainide;
increased risk of bradycardia and myocardial
depression with dronedarone.
Antibacterials: metabolism increased by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin,
clarithromycin and telithromycin (increased risk of
toxicity).
Anticoagulants: possibly increases dabigatran
concentration - reduce dabigatran dose.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; concentration of imipramine and possibly
other trycyclics increased; concentration significantly
reduced by St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: effect probably reduced by
barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone; enhanced
effect of carbamazepine.
Antifungals: negative inotropic effect possibly
increased with itraconazole.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect,
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of postsynaptic alpha-blockers.
Antipsychotics: possibly increases concentration of
lurasidone.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
atazanavir and ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution.
Avanafil: concentration of avanafil increased.
Beta-blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect; risk of
asystole, severe hypotension and heart failure if coprescribed with beta-blockers.
Cardiac glycosides: increased levels of digoxin.
Increased AV block and bradycardia.
Ciclosporin: variable reports of decreased
nephrotoxicity and potentiated effect; may also
increase ciclosporin levels.
Colchicine: possibly increased risk of colchicine
toxicity - suspend or reduce colchicine, avoid
concomitant use in renal or hepatic failure.
Cytotoxics: possibly increased bosutinib,
doxorubicin, ibrutinib concentration - reduce dose
of bosutinib and ibrutinib; possibly increased risk
of bradycardia with crizotinib; concentration of
both drugs may be increased in combination with
everolimus - consider reducing everolimus dose;
concentration of olaparib possibly increased - avoid
or reduce olaparib dose.
Fingolimod: increased risk of bradycardia.
Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid
concomitant use.
Ivabradine: concentration of ivabradine increased -
avoid concomitant use.
Lenalidomide: possibly increases lenalidomide
concentration.
Lipid-lowering agents: increased myopathy with
atorvastatin and simvastatin - reduce dose of
atorvastatin, do not exceed 20 mg of simvastatin1
,
concentration of verapamil increased by atorvastatin;
concentration of lomitapide increased - avoid.
Sirolimus: concentration of both drugs increased.
Tacrolimus: may increase tacrolimus levels.
Metabolism
Verapamil undergoes considerable first pass loss and is
extensively metabolised in the liver. 12 metabolites have been
identified. Of these only norverapamil has any significant
activity (approximately 20
% that of the parent compound).
Norverapamil represents about 6
% of the dose eliminated
in urine and reaches steady-state plasma concentrations
approximately equal to those of verapamil. About 70
%
of a dose is excreted by the kidneys in the form of its
metabolites but about 16
% is excreted in the bile into the
faeces. Less than 4
% is excreted unchanged.
Purification Methods
The salt is purified by dissolving it in EtOH, filtering (if insoluble particles are present) and adding Et2O, filtering the salt, washing it with Et2O and drying it in vacuo. It has the following solubilities: hexane (0.001%), CH2Cl2 (~10%), MeOH (~10%), EtOH (20%) and H2O (8.3%). It has UV max at 232 and 278nm. The free base is a viscous yellow oil b 243-246o/0.01mm (n 25D 1.5448) and is almost insoluble in H2O but soluble in organic solvents. It is a Ca channel antagonist and is a coronary vasodilator. [Ramuz Helv Chim Acta 58 2050 1975, Harvey et al. Biochem J 257 95 1989.]
Properties of Verapamil hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 142 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | methanol: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23313-68-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Verapamil hydrochloride
Computed Descriptors for Verapamil hydrochloride
Abamectin manufacturer
Lakshmi Farmachem
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Verapamil hydrochloride 98%View Details
Verapamil hydrochloride 98%View Details -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4