Vardenafil
- CAS NO.:224785-90-4
- Empirical Formula: C23H32N6O4S
- Molecular Weight: 488.6
- MDL number: MFCD07773094
- EINECS: 607-088-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-11 20:33:26
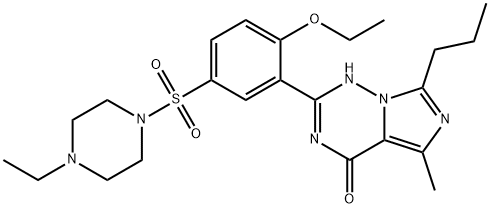
What is Vardenafil?
Absorption
Over the recommended dose range, vardenafil has a dose-proportional pharmacokinetics profile. In healthy male volunteers given a single oral dose of 20 mg of vardenafil, maximum plasma concentrations were reached between 30 minutes and 2 hours (median 60 minutes) after oral dosing in the fasted state, and 0.00018% of the dose was detected in semen 1.5 hours after dosing. Vardenafil has a bioavailability of approximately 15%. High-fat meals cause a Cmax reduction of 18%-50%; however, no changes were detected in AUC or Tmax.
Toxicity
Healthy male volunteers given a single dose of 120 mg of vardenafil experienced reversible back pain, myalgia and abnormal vision. Patients given vardenafil once daily over 4 weeks in single doses up to 80 mg and multiple doses up to 40 mg did not present serious adverse side effects. Cases of severe back pain were observed when 40 mg of vardenafil was administered twice daily; however patients did not present muscle or neurological toxicity. In cases of overdose, standard supportive measures should be taken as required. Renal dialysis is not expected to accelerate clearance as vardenafil is highly bound to plasma proteins and not significantly eliminated in the urine.
No carcinogenic effects were detected in rats and mice given vardenafil daily for 24 months. Vardenafil was not mutagenic or clastogenic, and did not have an effect in fertility in male and female rats given up to 100 mg/kg/day for 28 days prior to mating in males, and for 14 days prior to mating and through day 7 of gestation in females.
Description
Vardenafil is a new PDE5 inhibitor launched for oral treatment of male erectile dysfunction and it has significant structural similarity with sildenafil (Viagra?), which was the first PDE5 inhibitor introduced in 1998 for this indication. Vardenafil is synthesized in three steps starting with a cyclization reaction of 2-ethyoxybenzamidine with 2-butyramidopropionic acid and ethoxyallyl chloride to construct the imidazotriazine ring system, followed by sulfonation to the corresponding sulfonyl chloride and subsequent condensation with 1-ethylpiperazine. The potency of PDE5 inhibition by vardenafil (IC50=0.7 nM) is ~10 times greater than that of sildenafil (IC50=6.6 nM). Vardenafil is typically administered in single doses of 10 and 20 mg. The time to reach maximum plasma concentration is 0.75 h, which is slightly shorter than those of sildenafil (tmax=1.16 h) and tadalafil (tmax=2h), and the half-life is 4–5 h. Although it is almost completely absorbed following oral administration, the mean absolute bioavailability of a 10 mg dose is ~15%, resulting from extensive first pass metabolism. Vardenafil is metabolized in the liver primarily by CYP3A4 and is eliminated mainly in feces. In clinical studies, 10–20 mg doses of vardenafil was well tolerated and efficacious in patients with ED of various severities, including subjects with comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus or hypertension or hyperlipidemia. The side-effect profile of vardenafil is similar to that of sildenafil, with headache, flushing, dyspepsia and nasal congestion being the most common adverse events. Vardenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties, which can cause transient decrease in supine blood pressure; however, it does not appear to translate into clinical effects. The mean maximum decreases in supine systolic blood pressure following 20 and 40 mg vardenafil were 6.9 and 4.3 mmHg, respectively, when compared to placebo. However, single and multiple oral doses of vardenafil up to 40 mg produced no clinically relevant changes in the ECGs of normal male volunteers.
Originator
Bayer AG (Germany)
The Uses of Vardenafil
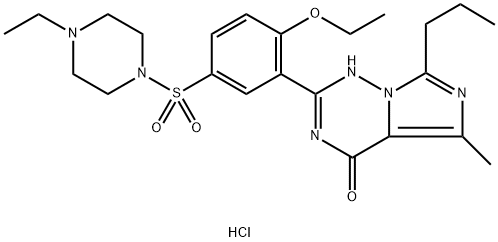
Vardenafil Hydrochloride Trihydrate (cas# 330808-88-3) has therapeutic applications and used in cosmetics and personal care products.
The Uses of Vardenafil
erectil dysfunction;PDE5 inhibitor
What are the applications of Application
Vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5)
Background
Vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) and an oral therapy for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. During sexual stimulation, nitric oxide (NO) is released from nerve endings and endothelial cells in the corpus cavernosum, activating the enzyme guanylate cyclase and increasing the synthesis of cGMP in the smooth muscle cells of the corpus cavernosum. PDE5 inhibitors, such as vardenafil, inhibit the degradation of cGMP and allow increased blood flow into the penis, resulting in an erection.. Compared to sildenafil and tadalafil, vardenafil is a more potent inhibitor of PDE5; however, its selectivity for other PDE isoforms is lower than the one detected for tadalafil.
The FDA approved the use of vardenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in 2003. Although other PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil and tadalafil have been associated with rare cases of acute liver injury, the use of vardenafil has not been linked to hepatotoxic effects. The use of vardenafil as a monotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension has also been evaluated.
Indications
Vardenafil is indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Definition
ChEBI: The sulfonamide resulting from formal condensation of the sulfo group of 4-ethoxy-3-(5-methyl-7-propylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(1H)-one-2-yl)benzenesulfonic acid and the secondary amino group of 4-ethylpiperazine.
brand name
Levitra
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
Vardenafil is a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), an enzyme responsible for the degradation of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum. The presence of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum leads to smooth muscle relaxation, an increased inflow of blood and an erection. Therefore, in patients with erectile dysfunction given vardenafil, normal sexual stimulation will increase cGMP levels in the corpus cavernosum. Without sexual stimulation and no cGMP production, vardenafil should not cause an erection.
Vardenafil should not be used in men for whom sexual activity is not recommended due to their underlying cardiovascular status. There is also a risk of developing prolonged erections that last longer than 4 hours, as well as priapism. In the event of a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes, patients should stop using vardenafil. Patients taking PDE5 inhibitors, such as vardenafil, may also develop sudden hearing loss and experience a prolonged QT interval.
Clinical Use
Treatment of erectile dysfunction
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alpha-blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect - avoid
for 6 hours after alpha-blockers (max dose 5 mg).
Antifungals: concentration increased by
ketoconazole, and itraconazole - avoid concomitant
use.
Antivirals: concentration increased by fosamprenavir,
indinavir and ritonavir- avoid with indinavir and
ritonavir; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid; avoid with telaprevir, use
tipranavir with caution.
Cobicistat: concentration of vardenafil possibly
increased - reduce dose of vardenafil.
Grapefruit juice: concentration possibly increased -
avoid concomitant use.
Nicorandil: possibly enhanced hypotensive effect -
avoid concomitant use.
Nitrates: possibly enhanced hypotensive effect -
avoid concomitant use.
Riociguat: enhanced hypotensive effect - avoid
concomitant use.
Metabolism
Vardenafil is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver, although CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms also contribute to its metabolism. The major circulating metabolite, M1 (N-desethylvardenafil), results from desethylation at the piperazine moiety of vardenafil, and has a plasma concentration of approximately 26% of that of the parent compound. M1 has a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to that of vardenafil and an in vitro inhibitory potency for PDE5 28% of that of vardenafil.
Metabolism
Vardenafil is metabolised in the liver primarily by
cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4 (the major route)
as well as CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms. The major
metabolite produced by desethylation of vardenafil also
has some activity.
Vardenafil is excreted as metabolites mainly in the faeces
(91 to 95
%), and to a lesser extent in the urine.
Properties of Vardenafil
| Melting point: | 230-235°C |
| Density | 1.37 |
| vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 71.34℃ |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | >22.5mg/mL in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 9.86±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 7mg/L at 20℃ |
Safety information for Vardenafil
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Vardenafil
| InChIKey | NOIHTGOGFDFCBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N12C(CCC)=NC(C)=C1C(=O)N=C(C1=CC(S(N3CCN(CC)CC3)(=O)=O)=CC=C1OCC)N2 |
Vardenafil manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
Rakshit Group of Companies (Rakshit Drugs Pvt Ltd)
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 224785-90-4 Vardenafil 98%View Details
224785-90-4 Vardenafil 98%View Details
224785-90-4 -
 Vardenafil 98%View Details
Vardenafil 98%View Details -
 Vardenafil 98%View Details
Vardenafil 98%View Details
224785-90-4 -
 Vardenafil 224785-90-4 98%View Details
Vardenafil 224785-90-4 98%View Details
224785-90-4 -
 Vardenafil HCl 97% CAS 224785-90-4View Details
Vardenafil HCl 97% CAS 224785-90-4View Details
224785-90-4 -
 Vardenafil dihydrochloride solution CAS 224785-90-4View Details
Vardenafil dihydrochloride solution CAS 224785-90-4View Details
224785-90-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1