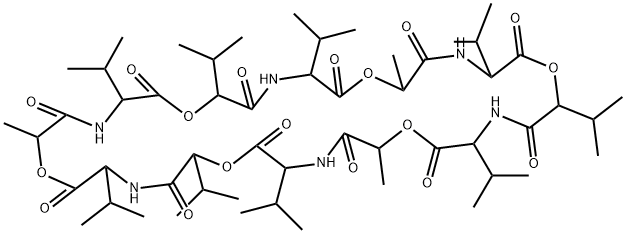
VALINOMYCIN
Synonym(s):Cyclo(L -Val-D -HyIva-D -Val-L -Lac-)3: HyIva = α-Hydroxyisovaleric acid, Lac = Lactic acid;Valinomycin;Valinomycin, Streptomyces fulvissimus - CAS 2001-95-8 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:2001-95-8
- Empirical Formula: C54H90N6O18
- Molecular Weight: 1111.32
- MDL number: MFCD00005114
- EINECS: 217-896-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
What is VALINOMYCIN?
Description
Valinomycin (2001-95-8) is a selective K+ ionophore capable of transporting potassium ions through lipid membranes.1 Valinomycin can induce apoptosis in cells by causing a rapid loss of mitochondrial membrane potential via potassium efflux.2,3
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
The Uses of VALINOMYCIN
Valinomycin is a hydrophobic cyclodepsipeptide with potent antitumour activity. Valinomycin is a highly selective potassium ionophore and this action leads to a diverse range of profound cell membrane effects. More recently, valinomycin has found application as a biosensor to detect to detect potassium efflux.
The Uses of VALINOMYCIN
antibiotic; LD50 (rat, po) 4 mg/kg
The Uses of VALINOMYCIN
K+-selective ionophoric cyclodepsipeptide; potassium ionophore which uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, induces apoptosis in murine thymocytes, inhibits NGF-induced neuronal differentiation and anta gonizes ET-induced vasoconstriction. Used as insecticide, nematocide.
The Uses of VALINOMYCIN
Valinomycin is a hydrophobic cyclodepsipeptide with potent antitumor activity. Valinomycin is a highly selective potassium ionophore and this action leads to a diverse range of profound cell membrane effects. More recently, valinomycin has found application as a biosensor to detect to detect potassium efflux.
The Uses of VALINOMYCIN
Insecticide, nematocide, Patterson, Wright, US 3520973 (1970 to Am. Cyanamid).
What are the applications of Application
Valinomycin is a potassium ionophore shown to induce cell death
Definition
ChEBI: A twelve-membered cyclodepsipeptide composed of three repeating D-alpha-hydroxyisovaleryl-D-valyl-L-lactoyl-L-valyl units joined in sequence. An antibiotic found in severa Streptomyces strains.
General Description
Shiny crystalline solid. Used as an insecticide and nematocide. Not registered as a pesticide in the U.S.
Reactivity Profile
VALINOMYCIN is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
VALINOMYCIN is highly toxic orally.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, VALINOMYCIN emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
Biological Activity
Selective K + ionophore (K 0.5 values are 48, 73, 75, 93 and 246 mM for K + , Rb + , Cs + , Na + and Li + respectively) that transports K + across biological and artificial lipid membranes. Inhibits Ca 2+ -ATPase activity and induces apoptosis through mitochondrial membrane depolarization, caspase-3 activation and phosphatidylserine translocation in vitro .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Valinomycin affects the ion transport behavior of mitochondrial systems.
in vitro
valinomycin caused substantial cho cells death within 12 h of treatment. several apoptotic events were identified in valinomycin-treated cho cells, including caspase-3 activation, phosphatidylserine (ps) membrane translocation, and mitochondrial membrane depolarization during the first few hours of treatment. k+ efflux was reduced by elevating extracellular k+ concentrations [2].
in vivo
valinomycin is irritant in the case of eye and skin contact. inhalation of valinomycin can cause breathing disturbances and even loss of conscious. lethal doses (ld50) for mouse and rabbit is 2.5 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg respectively. valinomycin also shows to provoke lots of chronic effects, including damage of the central and peripheral nervous system, eyes, lens and cornea [1].
storage
Store at -20°C
Purification Methods
Recrystallise valinomycin from dibutyl ether or Et2O. It is dimorphic: modification A crystallises from n-octane, and modification B crystallises from EtOH/H2O. It is soluble in pet ether, CHCl3, AcOH, BuOAc and Me2CO. [Smith et al. J Am Chem Soc 97 7242 1975, UV, IR and NMR see Brocknmann & Schmidt-Kastner Chem Ber 88 57 1955, Beilstein 27 I 9728. 17 IV 9728.]
References
1) Pressman, (1976) Biological applications of ionophores; Annu. Rev. Biochem., 45 501 2) Furlong et al., (1998) Induction of apoptosis by valinomycin: mitochondrial permeability transition causes intracellular acidification; Cell Death Diff., 5 214 3) Inai et al. (1997) Valinomycin induces apoptosis of ascites hepatoma cells (AH-130) in relation to mitochondrial membrane potential; Cell Struc. Funct., 22 555
Properties of VALINOMYCIN
| Melting point: | 187-190 °C |
| Boiling point: | 821.74°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 +31.0° (c = 1.6 in benzene) |
| Density | 1.060 |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 87℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥10 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 11.32±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +32±2°, c = 1.6% in benzene |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO at 10mg/ml. Insoluble in water |
| Merck | 13,9976 |
| BRN | 78657 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Valinomycin (2001-95-8) |
Safety information for VALINOMYCIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for VALINOMYCIN
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Valinomycin CAS 2001-95-8View Details
Valinomycin CAS 2001-95-8View Details
2001-95-8 -
 Potassium ionophore I CAS 2001-95-8View Details
Potassium ionophore I CAS 2001-95-8View Details
2001-95-8 -
 Valinomycin CAS 2001-95-8View Details
Valinomycin CAS 2001-95-8View Details
2001-95-8 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
