Validamycin
- CAS NO.:37248-47-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H35NO13
- Molecular Weight: 497.49
- MDL number: MFCD09028089
- EINECS: 609-372-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
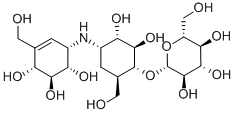
What is Validamycin?
Description
Validamycin A is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. limoneus nov. var (30). Structure revised (31). Colorless, odorless, hygroscopic powder. V.p. Negligible at room temperature. Solubility: Readily soluble in water, soluble in methanol, dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. Slightly soluble in ethanol and acetone. Sparingly soluble in diethyl ether and ethyl acetate. pKa 6.0 Stability [α]24D + 110? (water).
The Uses of Validamycin
Validamycin A is the major analogue of a family of cyclitol disaccharides isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. limoneus by researchers at Takeda in 1970. Although commonly regarded as an aminoglycoside, validamycin shares little in common with conventional aminoglycosides such as streptomycin and gentamicin. Validamycin A is a potent antifungal agent and is used to control fungi in crop production. Validamycin A acts as a potent inhibitor of trehalase, an important enzyme in carbohydrate storage and ultilisation in fungi.
The Uses of Validamycin
Validamycin A is used for the control of Rhizoctonia diseases in rice (sheath blight), potatoes, vegetables, strawberries, tobacco and other crops.
The Uses of Validamycin
Validamycin A (>70%) Hydrochloride Salt is a metabolite of Validamycin A (>70%) (V943430) which is an antibiotic fungicide that inhibits trehalase activity in plants, insects, and fungi.
What are the applications of Application
Validamycin A is is an antibiotic fungicide that inhibits trehalase activity in plants, insects, and fungi.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of validamycins that is (1R,2S,3S,4S,6R)-4-amino-6-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane-1,2,3-triol in which the hydroxy group at position 1 has been converted to its beta-D-glucoside and in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a (1R,4R,5R,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)cycloh x-2-en-1-yl group. It is the major validamycin produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus.
What are the applications of Application
Validamycin was found in the culture broth of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. limoneus by Takeda Chemicals Industries in 1971 in the course of screening for substances active against sheath blight in the rice plant. It consists of five components. The major component, validamycin A, was found to be the major contributor to the activity. Validamycin is active against a variety of phytopathogenic fungi, especiallyPellicularia sasakii, and it has been used to protect rice plants against sheath blight.
Pharmacology
Validamycin A specifically inhibits trehalase in R. solani AG-1 in a competitive manner between validoxylamine A (the possible active form of validamycin A) and the substrate, trehalose (33). Because trehalose is a storage carbohydrate in some fungi, trehalase is suggested to play an essential role for the digestion of trehalose to D-glucose and for its transportation to the hyphal tips (34).
Metabolic pathway
Validamycin A is an effective fungistatic (as opposed to fungicidal) antibiotic which has a very low toxicity to mammals and fish. This is presumably a consequence of its selective mode of action, the inhibition of trehalase. It is readily degraded under environmental conditions.
Degradation
Validamycin A is stable at room temperature in neutral or alkaline media but is unstable in acidic media.
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >20 g/kg. Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5 g/kg. Nonirritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 mg/L air. NOEL: In 90-d feeding trials, rats receiving 1 g/kg of diet and mice receiving 2 g/kg of diet showed no ill-effects. In 2-y feeding trials, NOEL for rats was 40.4 mg/kg daily. Toxicity Class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) IV.
Properties of Validamycin
| Melting point: | 130-135°C |
| Boiling point: | 813.7±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D24 +110° (c = 1 in water or pyridine), +92° (c = 1 in DMF) |
| Density | 1.69±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | Neglible at room temperature |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 2 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/ml |
| Water Solubility | Readily soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 6.0(at 25℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Validamycin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H227:Flammable liquids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Validamycin
Validamycin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 37248-47-8 Validamycin A 98%View Details
37248-47-8 Validamycin A 98%View Details
37248-47-8 -
 Validamycin A 98% (HPLC) CAS 37248-47-8View Details
Validamycin A 98% (HPLC) CAS 37248-47-8View Details
37248-47-8 -
 Validamycin A CAS 37248-47-8View Details
Validamycin A CAS 37248-47-8View Details
37248-47-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1