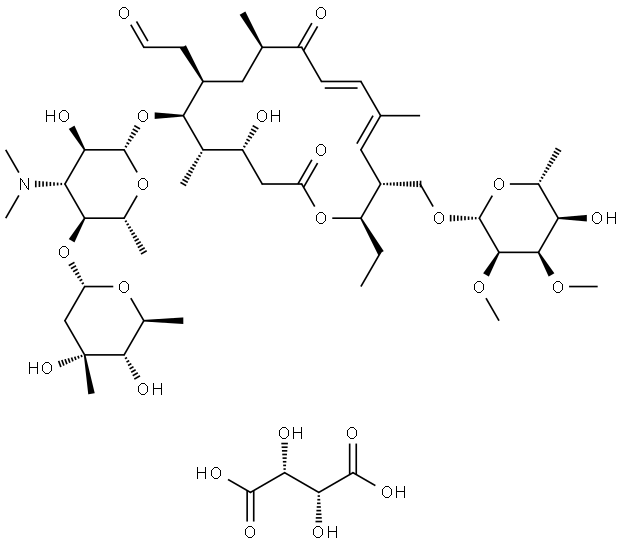
Tylvalosin tartrate
- CAS NO.:63428-13-7
- Empirical Formula: C57H93NO25
- Molecular Weight: 1192.35
- MDL number: MFCD31656805
- EINECS: 256-145-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-22 13:59:06
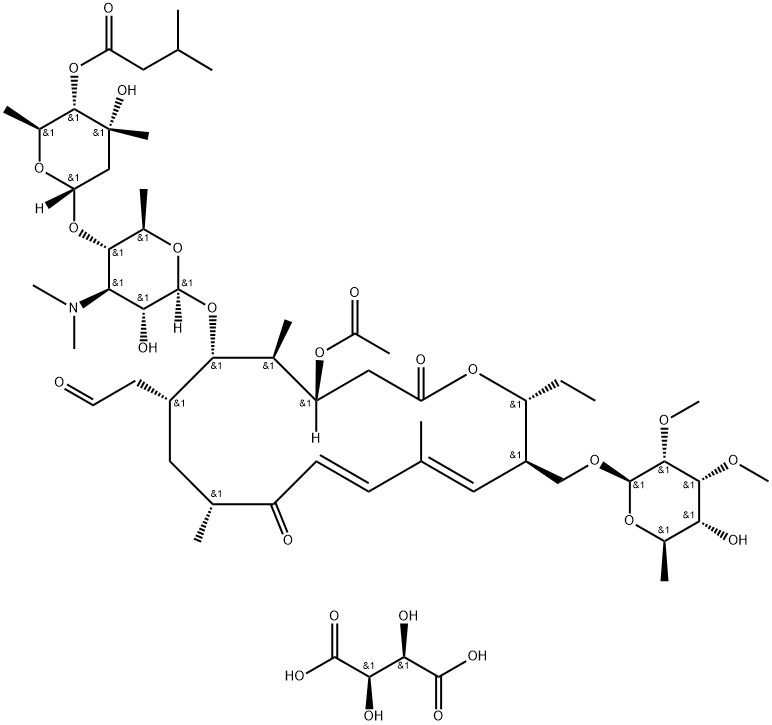
What is Tylvalosin tartrate?
The Uses of Tylvalosin tartrate
Tylvalosin Tartrate is an impurity of Tylvalosin (T898210); Tylvalosin is an anti-bacterial agent that is shown through study as a good inhibitor of gram-positive bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
Tylvalosin tartrate is a macrolide antibiotic with antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and some Gram-negative organisms and mycoplasma. It acts by inhibiting protein synthesis in the bacterial cell. Macrolide antibiotics are metabolites or semi-synthetic derivatives of metabolites of soil organisms obtained by fermentation. They have differently-sized lactone rings and are essential due to the dimethylamino group. Tylvalosin has a sixteen-membered ring. Macrolides interfere with protein synthesis by reversibly binding to the 50S ribosome subunit.
Pharmacology
Tylvalosin tartrate is rapidly absorbed after oral administration of Aivlosin. After administration of the recommended dose, lung concentrations of 0.060–0.066 μg/ml were found at 2 and 12 hours post-treatment. The parent compound is widely distributed in the tissues, with the highest concentrations found in the lungs, bile, intestinal mucosa, spleen, kidney, and liver. There is evidence that the concentration of macrolides is higher at the site of infection than in plasma, particularly in neutrophils, alveolar macrophages, and alveolar epithelial cells. In vitro metabolism studies have confirmed that the parent compound is rapidly metabolised to 3-O-acetyltylosin. In a trial with 14C-labeled Aivlosin administered at 2.125 mg/kg to pigs for 7 days, over 70% of the dose was excreted in the feces, with urinary excretion accounting for 3 to 4% of the dose.
in vitro
Tylvalosin tartrate (10 μg/mL; 0.5, 1 h) increases caspase-3 cleavage in porcine neutrophils, leading to DNA fragmentation during apoptosis.Tylvalosin tartrate (0.1-10 μg/mL; 0.5 h) Promote endocytosis of porcine neutrophils by macrophages without changing phagocytosis.
Properties of Tylvalosin tartrate
| Melting point: | 208 - 211°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Tylvalosin tartrate
Computed Descriptors for Tylvalosin tartrate
| InChIKey | OLLSDNUHBJHKJS-YZBHKUDENA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole N-Boc-L-proline methyl ester 2-(BOC-Amino)4-picoline 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazoleRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Acetylisovaleryltylosin tartrate 95% CAS 63428-13-7View Details
Acetylisovaleryltylosin tartrate 95% CAS 63428-13-7View Details
63428-13-7 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5