TUTIN
Synonym(s):
- CAS NO.:2571-22-4
- Empirical Formula: C15H18O6
- Molecular Weight: 294.3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-25 18:01:11
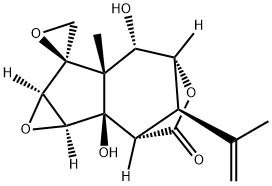
What is TUTIN?
Description
Tutin is a tetracyclic organic molecule with nine chiral centers. It exists in nature in six species of the tutu plant (genus Coriara) that grows in New Zealand. It is extremely toxic.
Tutin and its fellow toxin coriamyrtin1 were first described in 1901 by Thomas Hill Easterfield at Victoria College and Bernard Cracroft Aston at the New Zealand Department of Agriculture (both in Wellington). These compounds, along with a third tutu ingredient, picrotoxinin2, were responsible for poisoned honey that began to afflict New Zealanders in the 19th century.
Honeybees (Apis mellifera) don’t get it from the tutu plant’s pollen or nectar; the toxins are present only in the green plant parts. So how do tutin and its cousins get into honey? According to New Zealand’s Ministry for Primary Industries, “Passion vine hopper insects [Scolypopa australis] feed on tutu plants and produce honeydew which contains tutin. When bees collect this honeydew, the honey they make can contain tutin.”
Tutin’s toxicity results from its ability to inhibit glycine receptors in spinal neurons. Glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter; when it is inhibited, individuals can exhibit hypersalivation, agitation, seizures, exhaustion, coma, and respiratory distress. These signs are often preceded by nausea, blurred vision, and memory deficit. As of 2017, no specific antidote had been developed; recommended treatment is diazepam or barbiturates to control seizures and maintenance of respiratory function.
In 2016, the Ministry for Primary Industries issued an extensive guide for beekeepers, packers, and exporters to comply with New Zealand’s food standard for tutin in honey.
1. CAS Reg. No. 2571-86-0.
2. CAS Reg. No. 17617-45-7.
The Uses of TUTIN
Coriaria Lactone can be used in biological study for effects of tutin and its derivatives on GAD and GABA-T in Pseudelatia separata tested as novel active ingredients for pest control. It is also utilized in agricultural use for anti-feedant activities and effects of tutin and its derivatives on mythimna separata and its physiological parameters.
Definition
ChEBI: Tutin is a gamma-lactone.
Properties of TUTIN
| Melting point: | 209-212°; mp 204-205° (Wakamatsu) |
| Boiling point: | 356.07°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 +9.25° (alc); D17 +13.9° (c = 0.75, methanol) |
| Density | 1.1975 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4359 (estimate) |
| solubility | soluble; specific solubility not reported |
| appearance | colorless crystals |
| pka | 12.83±0.70(Predicted) |
Safety information for TUTIN
Computed Descriptors for TUTIN
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![1-Oxaspiro[2.8]undecane](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/185-90-0.gif)
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1