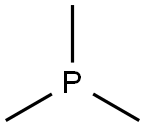
Triphenylphosphine
Synonym(s):Phosphorus triphenyl;Phosphorustriphenyl;Triphenylphosphine
- CAS NO.:603-35-0
- Empirical Formula: C18H15P
- Molecular Weight: 262.29
- MDL number: MFCD00003043
- EINECS: 210-036-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:35
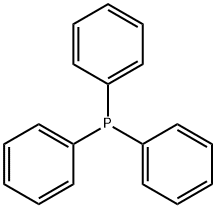
What is Triphenylphosphine?
Description
Triphenylphosphine is often used as a reducing agent, leading to the formation of triphenylphosphine oxide. The reaction is driven by the formation of the thermodynamically favored P=O bond of triphenylphosphine oxide. Triphenylphosphine oxide is a side-product that can be difficult to separate from desired product. Triphenylphosphine oxide is often removed through chromatography. When exposed to air, triphenylphosphine slowly oxidizes to triphenylphosphine oxide.
Description
First prepared by Pfeiffer and Sauvage in 1904, triphenylphosphine’s first important use in organic synthesis was in the Wittig reaction (1954) that converts aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Triphenylphosphine is also used in the Suzuki, Mitsunobu, and Appel reactions, and as a transition-metal ligand in olefin polymerizations.
Chemical properties
Triphenylphosphine is a white to light tan flaked solid. Insoluble inwater; slightly soluble in alcohol; soluble in benzene, acetone, carbon tetrachloride. Combustible.
The Uses of Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is used in the synthesis of Chlorambucil with cytotoxicity in breast and pancreatic cancers. Also used in the preparation of α-Tocopherol analogues for monitoring antioxidant status.
The Uses of Triphenylphosphine

To a solution of A (400 mg, 1.54 mmol), B (621 mg, 3.09 mmol), and PPh3 (610 mg, 2.32 mmol) in THF (5.5 mL) at RT was added DEAD (404 mg, 2.32 mmol) in THF (0.5 mL). After 90 min, silica gel was added and the mixture was concentrated and purified on a flash column (25% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product. [545 mg, 80%]
Production Methods
Triphenylphosphine is one of the most widely used phosphorus-containing reagents in organic synthesis for many types of transformations such as the Mitsunobu, the Wittig, and the Staudinger reaction. Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium.
PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl
Definition
ChEBI: Triphenylphosphine is a member of the class of tertiary phosphines that is phosphane in which the three hydrogens are replaced by phenyl groups. It has a role as a reducing agent. It is a member of benzenes and a tertiary phosphine.
What are the applications of Application
Triphenylphosphine is used in the following ways:
(1) Used as a pharmaceutical intermediate in the synthesis of Chlorambucil, Vitamin D2, Vitamin A, Clindamycin and other drugs.
(2) As a chemical reagent, used as sensitiser, heat stabiliser, light stabiliser, antioxidant, flame retardant, anti-static agent, rubber anti-ozone agent and analytical reagent.
(3) For the manufacture of tocopherol analogues using to monitor antioxidant status
(4) The Wittig reaction, which converts aldehydes and ketones to alkenes, was Ph3P’s first significant use in organic synthesis.
(5) Used as transition metal ligands in olefin polymerisation reactions and Suzuki, Mitsunobu, and Appel reactions.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 35, p. 625, 1994 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)75855-2
General Description
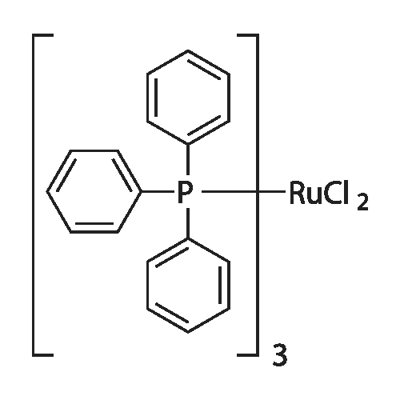
Rhodium and triphenylphosphine catalyst system has been used for the hydroformylation of soybean, safflower and linseed oils and their methyl esters. Polymer supported triphenylphosphine has been reported to efficiently catalyze the γ-addition of pronucleophiles to alkynoate. Triphenylphosphine reacts with hydrated ruthenium trichloride in methanol to afford [RuCl2(PPh3)4], [RuCl2(PPh3)3] and [RuCl3(PPh3)2CH3OH]. It participates in the Heck reaction of 4-bromoanisole and ethyl acrylate in ionic liquids.
Reactivity Profile
Triphenylphosphine reacts vigorously with oxidizing materials. .
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: Toxic; when heated to decomposition, emits highly toxic fumes of phosphine and POx.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by inhalation. A skin and eye irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Slight explosion hazard in the form of vapor when exposed to flame. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use dry chemical, fog, CO2. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of phosphne and POx. See also PHOSPHINE and PHENOL.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from hexane, MeOH, diethyl ether, CH2Cl2/hexane or 95% EtOH. Dry it at 65o/<1mm over CaSO4 or P2O5. Chromatograph it through alumina using (4:1) *benzene/CHCl3 as eluent. [Blau & Espenson et al. J Am Chem Soc 108 1962 1986, Buchanan et al. J Am Chem Soc 108 1537 1986, Randolph & Wrighton J Am Chem Soc 108 3366 1986, Asali et al. J Am Chem Soc 109 5386 1987.] It has also been crystallised twice from pet ether and 5 times from Et2O/EtOH to give m 80.5o. Alternatively, dissolve it in conc HCl, and upon dilution with H2O it separates because it is weakly basic, it is then crystallised from EtOH/Et2O. It recrystallises unchanged from AcOH. [Forward et al. J Chem Soc Suppl. p121 1949, Muller et al. J Am Chem Soc 78 3557 1956.] 3Ph3P.4HCl crystallises out when HCl gas is bubbled through an Et2O solution, it has m 70-73o, but recrystallises very slowly and is deliquescent. The hydriodide, made by adding Ph3P to hydriodic acid, is not hygroscopic and decomposes at ~100o. The chlorate (1:1) salt has m 165-167o, but decomposes slowly at 100o. All salts hydrolyse in H2O to give Ph3P [IR, UV: Sheldon & Tyree J Am Chem Soc 80 2117 1958, pK: Henderson & Streuli J Am Chem Soc 82 5791 1960, Kosolapoff, Organophosphorus Compounds, Wiley 1950]. [Beilstein 16 IV 951.] § Available commercially on a polystyrene or polyethyleneglycol support.
Properties of Triphenylphosphine
| Melting point: | 79-81 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 377 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.132 |
| vapor density | 9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 5 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6358 |
| Flash point: | 181 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble0.00017 g/L at 22°C |
| form | Crystals, Crystalline Powder or Flakes |
| appearance | White solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.132 |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 8: reacts rapidly with moisture, water, protic solvents |
| Merck | 14,9743 |
| BRN | 610776 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 603-35-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphine, triphenyl-(603-35-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Triphenylphosphine (603-35-0) |
Safety information for Triphenylphosphine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Triphenylphosphine
| InChIKey | RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Triphenylphosphine manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Triphenylphosphine 98%View Details
Triphenylphosphine 98%View Details -
 Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
603-35-0 -
 Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
603-35-0 -
 Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
Triphenylphosphine CAS 603-35-0View Details
603-35-0 -
 Triphenyl Phosphine Pellets CASView Details
Triphenyl Phosphine Pellets CASView Details -
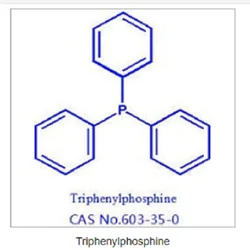 Triphenylphosphine Cas No. 603-35-0View Details
Triphenylphosphine Cas No. 603-35-0View Details
603-35-0 -
 Triphenylphosphine (CAS NO-603-35-0)View Details
Triphenylphosphine (CAS NO-603-35-0)View Details
603-35-0 -
 TRIPHENYL PHOSPHINEView Details
TRIPHENYL PHOSPHINEView Details
603-35-0
