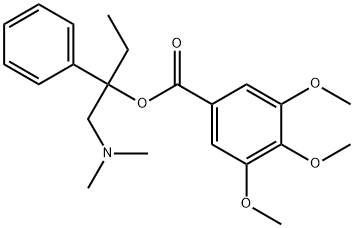
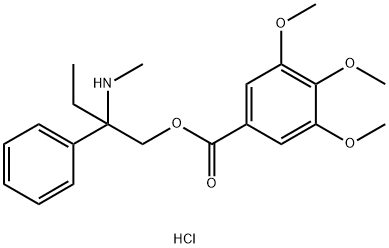
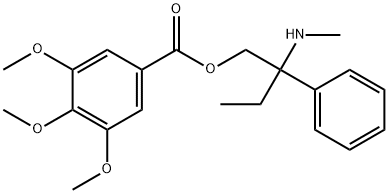
Trimebutine
Synonym(s):3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoic acid 2-(dimethylamino)-2-phenylbutyl ester
- CAS NO.:39133-31-8
- Empirical Formula: C22H29NO5
- Molecular Weight: 387.47
- MDL number: MFCD00133873
- EINECS: 254-309-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
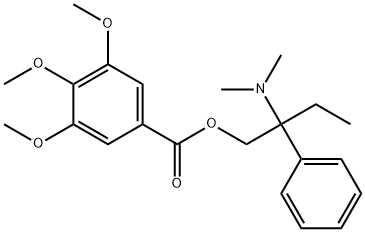
What is Trimebutine?
Absorption
The free base form or salt form of trimebutine are rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with the peak plasma concentration reached after 1 hour of ingestion . The time to reach peak plasma concentration following a single oral dose of 200mg trimebutine is 0.80 hours .
Toxicity
Common gastrointestinal adverse effects include dry mouth, foul taste, diarrhea, dyspepsia, epigastric pain, nausea and constipation. Some CNS effects include drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, hot/cold sensations and headaches. In case of overdosage, gastric lavage is recommended. Oral LD50 in mouse and rats is >5000 mg/kg and 2500 mg/kg in rabbits, respectively. Trimebutine is not reported to display teratogenic, mutagenic or carcinogenic potential .
The Uses of Trimebutine
Trimebutine is an agonist of peripheral mu, kappa and delta opiate receptors, used as spasmolytic agent for treatment of both acute and chronic abdominal pain.
The Uses of Trimebutine
Trimebutine is an opioid receptor agonist and an antispasmodic agent (1,2). It is used to treat acute and chronic abdominal pain.
Indications
Indicated for symptomatic treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and treatment of postoperative paralytic ileus following abdominal surgery.
Background
Trimebutine is a spasmolytic agent that regulates intestinal and colonic motility and relieves abdominal pain with antimuscarinic and weak mu opioid agonist effects. It is marketed for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and lower gastrointestinal tract motility disorders, with IBS being one of the most common multifactorial GI disorders . It is used to restore normal bowel function and is commonly present in pharmaceutical mixtures as trimebutine maleate salt form. Trimebutine is not a FDA-approved drug, but it is available in Canada and several other international countries.
What are the applications of Application
Trimebutine base is An opioid receptor agonist
Definition
ChEBI: 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid [2-(dimethylamino)-2-phenylbutyl] ester is a trihydroxybenzoic acid.
Pharmacokinetics
Trimebutine is a spasmolytic agent that acts directly on smooth muscle to modulate gastric motility. It shows a "dual function" that stimulates or inhibits spontaneous contractions depending on the concentration and prior contractile activity in the preparation. Targeting ion conductance that regulates GI motility, trimebutine inhibits the inward calcium currents and calcium-dependent potassium currents in a concentration-dependent manner . At lower concentrations (1-10uM), trimebutine depolarizes the resting membrane potential without affecting the amplitude of contractions, which is thought to be mediated by inhibition of outward potassium currents. It is also shown to activate T-type Ca2+ channel and increase gastric emptying, intestinal and colonic contractility . At higher concentrations (100-300uM), reduced amplitude of spontaneous contractions and action potentials is thought to be mediated by inhibition of L-type Ca2+ channels and inward calcium current . Trimebutine mediates a local anesthetic action by acting as a weak agonist at mu opioid receptors.
Metabolism
Trimebutine undergoes extensive hepatic first-pass metabolism. Nortrimebutine, or N-monodesmethyltrimebutine, is the main metabolite that retains pharmacological activity on the colon. This metabolite can undergo second N-demethylation to form N-didesmethyltrimebutine. Other main urinary metabolites (2-amino, 2-methylamino or 2-dimethylamino-2-phenylbutan-1-ol) can be formed via hydrolysis of the ester bond of desmethylated metabolites or initial hydrolysis of the ester bond of trimebutine followed by sequential N-demethylation . Trimebutine is also prone to sulphate and/or glucuronic acid conjugation .
Properties of Trimebutine
| Melting point: | 78-80°C |
| Boiling point: | 513.42°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1998 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5614 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 7.29±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 10g/L |
| Merck | 14,9699 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 39133-31-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Trimebutine
Computed Descriptors for Trimebutine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 39133-31-8 TRIMEBUTINE 0.787% GRANULES 98%View Details
39133-31-8 TRIMEBUTINE 0.787% GRANULES 98%View Details
39133-31-8 -
 Trimebutine CAS 39133-31-8View Details
Trimebutine CAS 39133-31-8View Details
39133-31-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
