Trifluoperazine
- CAS NO.:117-89-5
- Empirical Formula: C21H24F3N3S
- Molecular Weight: 407.5
- MDL number: MFCD00242601
- EINECS: 204-219-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
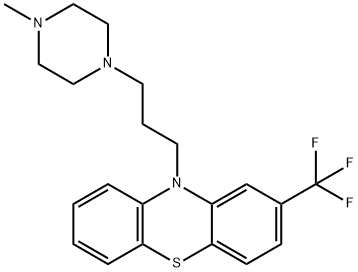
What is Trifluoperazine?
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include agitation, coma, convulsions, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, extreme sleepiness, fever, intestinal blockage, irregular heart rate, low blood pressure, and restlessness.
Originator
Stelazine,SKF,US,1958
The Uses of Trifluoperazine
Trifluoperazine is one of the most active antipsychotic drugs. A moderate stimulatory effect accompanies the neuroleptic effect. Trifluoperazine is unique in that, patients instead of the usual stiffness and weakness characteristic of phenothazine derivatives, become more lively. This drug has a strong anticonvulsant activity. It is widely used in psychiatry for treating schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
The Uses of Trifluoperazine
Antipsychotic.
The Uses of Trifluoperazine
10-[3-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine is a psychoactive drug.
Indications
For the treatment of anxiety disorders, depressive symptoms secondary to anxiety and agitation.
Background
A phenothiazine with actions similar to chlorpromazine. It is used as an antipsychotic and an antiemetic.
Definition
ChEBI: Trifluoperazine is a member of the class of phenothiazines that is phenothiazine having a trifluoromethyl subsitituent at the 2-position and a 3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl group at the N-10 position. It has a role as a dopaminergic antagonist, an antiemetic, an EC 1.8.1.12 (trypanothione-disulfide reductase) inhibitor, an EC 5.3.3.5 (cholestenol Delta-isomerase) inhibitor, a calmodulin antagonist and a phenothiazine antipsychotic drug. It is a N-alkylpiperazine, a N-methylpiperazine, a member of phenothiazines and an organofluorine compound.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 17.2 grams of 2-trifluoromethylphenothiazine, 3.1 grams of sodamide and 14 grams of 1-(3'-chloropropyl)-4-methylpiperazine in 200 ml of xylene is heated at reflux for 2 hours. The salts are extracted into 150 ml of water. The xylene layer is then extracted with several portions of dilute hydrochloric acid. The acid extracts are combined and neutralized with ammonium hydroxide solution. The product, 10-[3'-(4''-methyl-1''- piperazinyl)-propyl]-2-trifluoromethylphenothiazine, is taken into benzene and purified by vacuum distillation, BP 202° to 210°C at 0.6 mm.
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Pharmacokinetics
Trifluoperazine is a trifluoro-methyl phenothiazine derivative intended for the management of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Trifluoperazine has not been shown effective in the management of behaviorial complications in patients with mental retardation.
Clinical Use
Schizophrenia and other psychoses
Anxiety
Severe nausea and vomiting
Synthesis
Trifluoperazine, 2-trifluoromethyl-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl) propyl]- phenothazine (6.1.5), is synthesized in the manner described above of alkylation using 2- trifluoromethylphenothazin-4-methyl-1-piperazinylpropylchloride [11,17–20].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative
effects with opioids; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with methadone.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with anti-arrhythmics that prolong
the QT interval, e.g. procainamide, disopyramide,
dronedarone and amiodarone - avoid with
amiodarone and dronedarone.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with delamanid and moxifloxacin -
avoid with moxifloxacin.
Antidepressants: increased level of tricyclics; possibly
increased risk of antimuscarinic side effects; risk
of ventricular arrhythmias with citalopram and
escitalopram - avoid; possible increased risk of
convulsions with vortioxetine.
Antiepileptics: antagonism (convulsive threshold
lowered).
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether/lumefantrine
and piperaquine with artenimol.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with droperidol and pimozide - avoid;
possible increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with risperidone.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased with
ritonavir; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: increased sedative effects.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias.
Beta-blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with arsenic trioxide.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Lithium: increased risk of extrapyramidal side effects
and possibly neurotoxicity.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
Trifluoperazine undergoes extensive first pass metabolism. The major metabolite is the possibly active N-oxide; other metabolites include the sulfoxide and the 7-hydroxy derivative.
Elimination occurs in the bile and urine.
Properties of Trifluoperazine
| Melting point: | 232°C |
| Boiling point: | bp0.6 202-210° |
| Density | 1.2060 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 8.05±0.04(H2O
t = 20 0.5
I not reported
but pKa
was stated
to be
independent
of I.) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 12.23mg/L(24 ºC) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Trifluoperazine(117-89-5) |
Safety information for Trifluoperazine
Computed Descriptors for Trifluoperazine
Trifluoperazine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

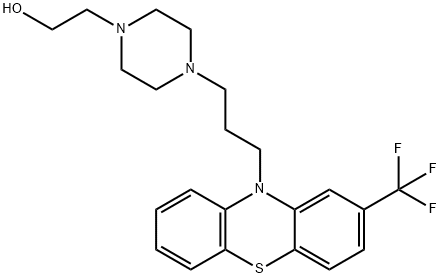
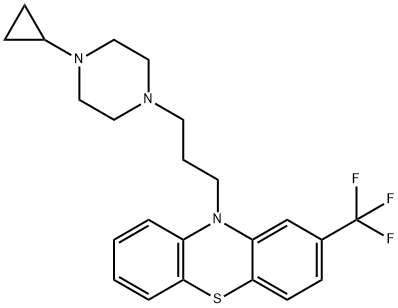
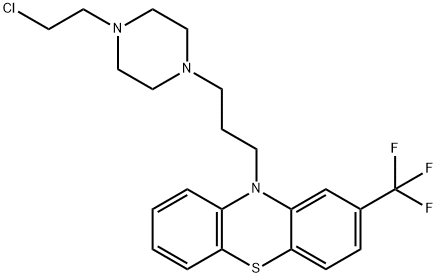
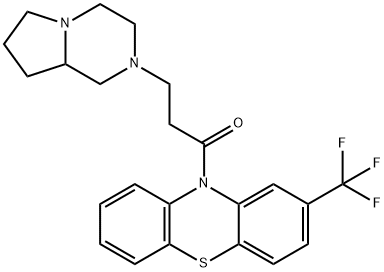
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
