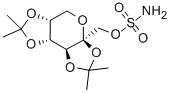
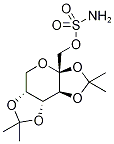
Topiramate
Synonym(s):2,3:4,5-Bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-36-D -fructo-pyranose sulfamate;McN 4853;RWJ 17021;Topamax;Topiramate
- CAS NO.:97240-79-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H21NO8S
- Molecular Weight: 339.36
- MDL number: MFCD00865320
- EINECS: 619-263-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
What is Topiramate?
Absorption
After a 400mg dose in one clinical trial, topiramate reached maximal concentrations within 1.8-4.3 hours and ranged from 1.73-28.7 ug/mL. Food did not significantly affect the extent of absorption, despite delaying time to peak concentration. In patients with normal creatinine clearance, steady state concentrations are reached within 4 days. The bioavailability of topiramate in tablet form is about 80% compared to a topiramate solution.
Toxicity
The LD50 of intraperitoneal topiramate in the rat is above 1500 mg/kg.
Overdose information
In a study of 4 healthy adult women taking topiramate, the severity of clinical effects following an overdose ranged from asymptomatic to severe, with no deaths reported. According to the FDA prescribing information for topiramate, an overdose may cause hypotension, severe metabolic acidosis, coma, abdominal pain, visual disturbances, convulsions, drowsiness, speech abnormalities, impaired mentation and coordination, stupor, agitation, dizziness, as well as depression.
In the case of a recent ingestion of topiramate, the stomach contents should be emptied through the induction of emesis or gastric lavage. Offer supportive treatment, including activated charcoal and hemodialysis.
Description
Topiramate, a novel sulfamate-substituted D-fructose derivative, was launched in the United Kingdom as an adjunct therapy for use in partial seizures with or without secondary generalized seizures in adult patients inadequately controlled on conventional antiepileptics. Topiramate is structurally distinct from other available antiepileptics and functions through a unique combination of several mechanisms. It appears to act by blocking voltage-sensitive sodium channels to raise the action potential threshold and block the spread of seizure, enhancing GABA activity at postsynaptic GABA receptors and reducing glutamate activity at postsynaptic AMPAtype receptors, and is also a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Topiramate is orally active with rapid absorption, high bioavailability, and long duration of action. Excellent efficacy has been reported as an add-on therapy in epilepsy and it is also being evaluated as a monotherapy.
Chemical properties
White-to-Off-White Crystalline Powder
Originator
Johnson & Johnson (U.S.A.)
The Uses of Topiramate
Topiramate may be used as a pharmaceutical reference standard for the quantification of the analyte in pharmaceutical formulations using high-performance liquid chromatography technique and spectrophotometric technique.
The Uses of Topiramate
Used as an anticonvulsant
The Uses of Topiramate
anticonvulsant, antimigraine, GABA-A agonist, AMP/kinate glutamate receptor antagonist, carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
The Uses of Topiramate
Used for the treatment and control of partial seizures and severe tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures and also for the prevention of migraine headaches. In children it is also used for treatment of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Qsymia? is indicated for the treat
Background
Topiramate is a anti-epileptic drug used to manage seizures and prevent migraines. It was initially approved by the FDA in 1996. In 2004, topiramate was approved for the prevention of migraine in adults. Since 2012, the extended-release formulation has been approved in combination with phentermine for chronic weight management therapy in adults.
Characteristics that distinguish topiramate from other antiepileptic drugs are a monosaccharide chemical structure containing a sulfamate, and 40% of its mass accounted for by oxygen. Interestingly, topiramate was discovered by chance when attempts were made to formulate a novel antidiabetic drug.
Indications
Topiramate is indicated for the following conditions: 1)Monotherapy for partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures for patients 2 years of age and above 2)Adjunctive therapy for partial onset seizures or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures for both adult and pediatric patients above 2 years old 3)Adjunctive therapy for seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients above 2 years of age 4)Prophylaxis of migraine in children 12 years of age and older and adults.
Topiramate is also used off-label as an adjunct therapy for weight management and for mood disorders.
What are the applications of Application
Topiramate is a GluR5 kainate receptor antagonist which also inhibits Nav channels, L-type Ca2+ channels, and carbonic anhydrase
Definition
ChEBI: A hexose derivative that is 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-beta-D-fructopyranose in which the hydroxy group has been converted to the corresponding sulfamate ester. It blocks voltage-dependent sodium channe s and is used as an antiepileptic and for the prevention of migraine.
Manufacturing Process
To a cold solution (-4°C) of 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-β-fructopyranose (75
g, 0.29 mol) in DMF (725 ml) was added 50% oily sodium hydride (16.34 g,0.34 mol). After stirring for 90 min, sulfamoyl chloride (54.9 g, 0.48 mol) was
added and the stirring continued for an additional 3.5 h at that temperature.
The reaction mixture was poured into cold water and extracted with toluene.
The organic layer was dried (Na2SO4) and the solvents removed under
vacuum to give a syrup which crystallized immediately. Recrystallization from
ethylacetate/hexane gave pure 2,3:4,5-bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-β-D_x0002_fructopyranose sulfamate, melting point 125°-126°C.
brand name
Topamax
Therapeutic Function
Anticonvulsant
Biological Functions
Topiramate is most useful in patients with generalized tonic–clonic seizures and those with partial complex seizures. Topiramate causes a higher incidence of CNSrelated side effects (primarily cognitive slowing and confusion) than other AEDs. It does not appear to cause a significant incidence of rashes or other hypersensitivity reactions; however, a significantly higher incidence of kidney stones has been observed in persons receiving topiramate than in a similar untreated population.
General Description
TPM is a sulphamate-substituted monosaccharide, a derivativeof the naturally occurring sugar D-fructose thatexhibits broad and potent AED actions at both glutamateand GABA receptors.19 It has good oral bioavailability of85% to 95%, most likely resulting from its structural similarityto D-glucose. Thus, it may be actively transportedinto the brain by the D-glucose transporter. (Recall thatD-fructose and D-glucose have identical stereochemistry atmany of their chiral centers.) Only about 20% of the drugis eliminated by hepatic metabolism (CYP2C19), the remainingdrug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys.57 Thesulphamate ester is hydrolyzed by sulfatases to the correspondingprimary alcohol, which is further oxidized to thecorresponding carboxylic acid. Even though there are noreports of significant interactions between TPM and otherAEDs, TPM is said to have a weak carbonic anhydrase inhibitoryactivity because of the presence of the sulphamatemoiety. Thus, concomitant use of TPM with other carbonicanhydrase inhibitors should be avoided.57 The exact mechanismof actions are still unknown, but TPM appears toblock glutamate release, antagonize glutamate kainicacid/AMPA receptors, and increase GABAergic transmissionby binding to a site distinct from BZDs or barbiturateson the GABAA receptor complex.
Biological Activity
Anticonvulsant. Antagonizes GluR5 kainate receptors (IC 50 = 0.46 μ M), acts as a positive allosteric modulator of GABA A receptor-mediated currents, inhibits Na v channels (IC 50 = 48.9 μ M) and inhibits L-type Ca 2+ channels. Also inhibits carbonic anhydrase (CA) (K i values are 0.1 and 0.2 μ M at rat CA II and CA IV respectively), which lowers intracellular neuronal pH.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Kainate GluR5 receptor antagonist; anticonvulsant.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action for topiramate is unknown, but several actions are thought to contribute to its AED activity. It blocks repetitive firing by acting on sodium channels, may enhance GABAA-mediated chloride flux, and appears to be an antagonist at the AMPA and KA receptors, thus blocking the effect of glutamate. In addition, recent evidence suggests inhibition of L-type calcium currents.
Pharmacokinetics
Topiramate prevents the occurrence of seizures and prevents migraine symptoms by reducing neural pathway excitability. It is important to note that this drug may cause metabolic acidosis, mood changes, suicidal thoughts and attempts, as well as kidney stones. When topiramate is combined with valproic acid, it is known to cause hypothermia.
Pharmacokinetics
Topiramate is rapidly absorbed, with at least an 80 to 95% oral bioavailability that is unaffected by food. Following an oral dose
of topiramate, peak plasma concentration is reached in 1 to 4 hours, exhibiting linear pharmacokinetics. Protein binding is
minimal (<20%), and the usual elimination half-life is 20 to 30 hours, allowing a twice-daily dosing regimen. In the absence of
enzyme-inducing drugs, approximately 70 to 80% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, with the remainder as
metabolites resulting from oxidation and hydrolysis. Enzyme-inducing AEDs alter the pharmacokinetics of topiramate by
reducing its plasma levels and increasing its rate of elimination.
In children from 4 to 17 years of age, topiramate exhibits linear pharmacokinetics, with a 50% increase in clearance rate
compared to adults. Topiramate may require up to a 50% dose reduction in patients with renal insufficiency, and a replacement dose may be needed after renal dialysis. Topiramate has demonstrated teratogenicity in animal studies.
Clinical Use
Topiramate is a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide derived from fructose with a broad spectrum of AED activity. It is approved for monotherapy or as an adjunct drug for partial or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients older than 10 years, as adjunct therapy in children aged from 2 to 10 years with partial-onset seizures, and in persons older than 2 years with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Topiramate also is approved for the prophylaxis of migraine headaches.
Side Effects
Common CNS side effects associated with topiramate therapy include drowsiness, dizziness, impaired concentration and
memory, speech and language difficulties, and confusion. These effects develop during the first weeks of therapy and may
decline over time. Acute closed-angle glaucoma caused by topiramate requires immediate evaluation. Only rare hepatic or
bone marrow effects have been noted thus far; however, an increased incidence of renal stones is troublesome and probably
related to the drug's activity as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, reducing citrate excretion and increasing urinary pH. Use of
additional carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, a ketogenic diet, or a family history of nephrolithiasis may be considered as
contraindications for using topiramate.
Topiramate is not devoid of potential interaction properties: It induces CYP3A4 and inhibits CYP2C19, thus significantly increasing plasma phenytoin levels. Topiramate also may decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptives.
Synthesis
Ziconitide is the synthetic form of the conotoxin ω-conopeptide MVIIA .
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Topiramate may be useful for treating seizures in dogs, particularly partial seizure activity. It may also be of benefit in treating cats, but little information is available.
in vitro
in principal neurons of the rat basolateral amygdala, low concentrations of topiramate selectively inhibited pharmacologically isolated excitatory synaptic currents mediated by kainate receptors with the glur5 subunit with an ic50 value of 0.5 μm. topiramate also partially depressed predominantly ampa-receptor-mediated epscs with lower efficacy [1]. in dissociated neocortical slices, low concentrations of tpm (25–30 μm) slightly inhibited the persistent fraction of na+ current and reduced the na+-dependent long-lasting action potential shoulders evoked in layer v pyramidal neurons after ca2+ and k+ current blockade. tpm (100 μm) had no effects on the voltage dependence of activation but induced a leftward shift of the steady-state inaf inactivation curve [3].
in vivo
tpm treatment significantly improved the 24-h neurological deficit scores (high dose, 1.17 ± 0.41; low dose, 1.75 ± 0.5; p < 0.05 for both doses). the percentage of infarct volume (low dose, 22.9 ± 8.9%, p = 0.002; high dose 7.6 ± 3.4%, p < 0.001) reduced when compared with the controls (infarct size, 54.2 ± 9.0%; neurobehavior score, 2. 67 ± 0.52). higher dose of tpm induced more neuroprotection than that of lower dose (p < 0.05). in a rat model of focal ischemia, treatment with tpm 2 h after mca embolization resulted in neuroprotective effect in a dose- and use-dependent manner [2]. topiramate (25-100 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently elevated the threshold for clonic seizures induced by infusion of a selective agonist of glur5 kainate receptors atpa [4]. topiramate (i.p) effectively suppressed acute seizures induced by perinatal hypoxia in a dose-dependent manner with an ed50 of 2.1 mg/kg [5]. topiramate (20 and 40 mg/kg i.p.) dose-dependently inhibited both tonic and absence-like seizures. in dba/2 mice, topiramate inhibited sound-induced seizures with ed50 of 8.6 mg/kg (p.o) [6].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antidepressants: antagonism of anticonvulsant
effect; avoid with St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: concentration reduced by
fosphenytoin, phenytoin, carbamazepine and possibly
phenobarbital; increases fosphenytoin and phenytoin
concentration; reduces concentration of perampanel;
hyperammonaemia and CNS toxicity reported with
valproate.
Antimalarials: mefloquine antagonises
anticonvulsant effect.
Antipsychotics: anticonvulsant effect antagonised.
Oestrogens and progestogens: reduced contraceptive
effect.
Orlistat: possibly increased risk of convulsions.
Ulipristal: reduced contraceptive effect - avoid.
Metabolism
The metabolites of topiramate are not known to be active. The metabolism of topiramate is characterized by reactions of glucuronidation, hydroxylation and hydrolysis that lead to the production of six minor metabolites. Some of topiramate's metabolites include 2,3-desisopropylidene topiramate, 4,5-desisopropylidene topiramate, 9-hydroxy topiramate, and 10-hydroxy topiramate.
Metabolism
Topiramate is not extensively metabolised (~20
%) in
healthy volunteers. It is metabolised up to 50
% in patients
receiving enzyme-inducing drugs. Six metabolites formed
through hydroxylation, hydrolysis and glucuronidation
have been identified but have little activity. It is eliminated
chiefly in urine, as unchanged drug and metabolites.
storage
+4°C
References
[1] gryder d s, rogawski m a. selective antagonism of glur5 kainate-receptor-mediated synaptic currents by topiramate in rat basolateral amygdala neurons[j]. the journal of neuroscience, 2003, 23(18): 7069-7074.
[2] yang y, shuaib a, li q, et al. neuroprotection by delayed administration of topiramate in a rat model of middle cerebral artery embolization[j]. brain research, 1998, 804(2): 169-176.
[3] taverna s, sancini g, mantegazza m, et al. inhibition of transient and persistent na+ current fractions by the new anticonvulsant topiramate[j]. journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics, 1999, 288(3): 960-968.
[4] kaminski r m, banerjee m, rogawski m a. topiramate selectively protects against seizures induced by atpa, a glur5 kainate receptor agonist[j]. neuropharmacology, 2004, 46(8): 1097-1104.
[5] koh s, jensen f e. topiramate blocks perinatal hypoxia‐induced seizures in rat pups[j]. annals of neurology, 2001, 50(3): 366-372.
[6] nakamura j, tamura s, kanda t, et al. inhibition by topiramate of seizures in spontaneously epileptic rats and dba/2 mice[j]. european journal of pharmacology, 1994, 254(1-2): 83-89.
Properties of Topiramate
| Melting point: | 125°C |
| Boiling point: | 438.7±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D23 -34.0° (c = 0.4 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.336±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ~44 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 9.22±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 9.705g/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 14,9547 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | .beta.-D-Fructopyranose, 2,3:4,5-bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-, 1-sulfamate (97240-79-4) |
Safety information for Topiramate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Topiramate
Topiramate manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 -
 97240-79-4 Topiramate 98%View Details
97240-79-4 Topiramate 98%View Details
97240-79-4 -
 Topiramate 97240-79-4 98%View Details
Topiramate 97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 -
 Topiramate CAS 97240-79-4View Details
Topiramate CAS 97240-79-4View Details
97240-79-4 -
 97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 -
 97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 98%View Details
97240-79-4 -
 Topiramate 98% (HPLC) CAS 97240-79-4View Details
Topiramate 98% (HPLC) CAS 97240-79-4View Details
97240-79-4 -
 Topiramate 95.00% CAS 97240-79-4View Details
Topiramate 95.00% CAS 97240-79-4View Details
97240-79-4
