Tin(II) fluoride
Synonym(s):SNF2;Stannous fluoride;BRM;Difluorostannylene;MRD16
- CAS NO.:7783-47-3
- Empirical Formula: F2Sn
- Molecular Weight: 156.71
- MDL number: MFCD00042540
- EINECS: 231-999-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02

What is Tin(II) fluoride?
Absorption
Tin is retained in the demineralized organic matrix to some extent, diffuses through the phosphorylated non-collagenous proteins in the dentine called phosphophoryn and accumulates in the underlying mineralized tissue.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 value in rats is 360mg/kg and the dermal LD50 value is >2000mg/kg. Repeated or prolonged dermal contact can cause irritant symptoms such as reddening of the skin, blisters, or dermatitis.
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
Chemical properties
Stannous fluoride is a white crystalline solid with a bitter, salty taste.
The Uses of Tin(II) fluoride
Tin(II) fluoride is used in the prevention of dental caries. It is an active ingredient in toothpastes.
The Uses of Tin(II) fluoride
Dental caries prophylactic.
The Uses of Tin(II) fluoride
Stannous fluoride (SnF2) is used as a toothpaste additive to help prevent tooth decay.
Background
Stannous Fluoride, or Tn(II) Fluoride, is a compound commonly used in toothpastes for the prevention of gingivitis, dental infections, cavities, and to relieve dental hypersensitivity. Although similar in function and activity to Sodium Fluoride (NaF), the conventionally added ingredient in toothpastes, stannous fluoride has been shown to be more effective at stopping and reversing dental lesions . It manages and prevents dental caries and gingivitis by promoting enamel mineralization , reducing gingival inflammation and bleeding through its potential broad-spectrum antibiotic effect and modulation of the microbial composition of the dental biofilm . It is an FDA-approved over-the-counter product.
Indications
Indicated for use to relieve dental hypersensitivity, increase enamel production, prevent gingivitis and cavities, and control periodontal infections.
Definition
ChEBI: Stannous fluoride is an inorganic fluoride salt.
General Description
White crystalline solid. Sinks and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Tin(II) fluoride, a strong reducing agent, is incompatible with oxidizers. Avoid contact with acids - HF fumes may be produced [USCG, 1999].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, strong irritant to skin and tissue.
Health Hazard
EYES: Severe irritation - corrosive, irreversible. SKIN: Corrosive on abraded skin, no effect on intact skin.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmacokinetics
Stannous fluoride mediates both bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties and provides an anti-erosive action on tooth enamel.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable carcinogen. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of F-. See also TIN COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Stannous fluoride is used in dental caries (tooth decay); as an ingredient of cavity-preventing toothpastes.
Metabolism
Not Available
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2923 Corrosive solids, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, 6.1Poisonous material, Technical Name Required
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Reacts with acids, forming hydrogen fluoride fumes. Reacts violently with chlorine and metal nitrates. Reacts with metals releasing flammable hydrogen gas.
Properties of Tin(II) fluoride
| Melting point: | 215°C |
| Boiling point: | 850°C |
| Density | 4.57 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | soluble in H2O; insoluble in ethanol, ethyl ether,chloroform |
| form | Powder, Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 4.57 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in potassium hydroxide and potassium fluoride. Insoluble in water, ethanol, ether and chloroform. |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8784 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; IDLH 250 mg/m3; TWA 2 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Non-flammable. Avoid contact with water or oxidizing agents. Moisture-sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-47-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tin difluoride(7783-47-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tin fluoride (SnF2) (7783-47-3) |
Safety information for Tin(II) fluoride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Tin(II) fluoride
| InChIKey | ANOBYBYXJXCGBS-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
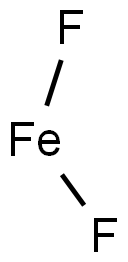

You may like
-
 7783-47-3 Stannous Fluoride / Tin(II) fluoride 98%View Details
7783-47-3 Stannous Fluoride / Tin(II) fluoride 98%View Details
7783-47-3 -
 7783-47-3 98%View Details
7783-47-3 98%View Details
7783-47-3 -
 Tin(II) fluoride 98%View Details
Tin(II) fluoride 98%View Details
7783-47-3 -
 Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
7783-47-3 -
 Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
7783-47-3 -
 Tin(II) fluoride 99% CAS 7783-47-3View Details
Tin(II) fluoride 99% CAS 7783-47-3View Details
7783-47-3 -
 Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
Tin(II) fluoride CAS 7783-47-3View Details
7783-47-3 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
