Timolol
- CAS NO.:26839-75-8
- Empirical Formula: C13H24N4O3S
- Molecular Weight: 316.42
- MDL number: MFCD00864565
- EINECS: 248-032-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
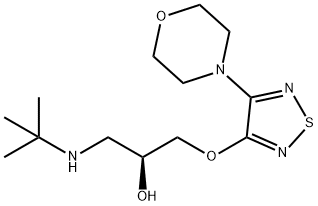
What is Timolol?
Absorption
The systemic bioavailability of the ophthalmic eyedrop in one study of healthy volunteers was 78.0 ± 24.5% , indicating that caution must be observed when this drug is administered, as it may be significantly absorbed and have various systemic effects. Another study measured the bioavailability of timolol eyedrops to be 60% in healthy volunteers.
The peak concentration of ophthalmic timolol in plasma, Cmax was about 1.14 ng/ml in most subjects within 15 minutes following the administration of timolol by the ophthalmic route. The mean area under the curve (AUC) was about 6.46 ng/ml per hour after intravenous injection and about 4.78 ng/ml per hour following eyedrop administration.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 for timolol maleate is 1028 mg/kg in the rat and 1137 mg/kg in the mouse.
Symptoms of timolol overdose may include dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, bradycardia, in addition to bronchospasm. Sometimes, an overdose may lead to cardiac arrest. An overdose of timolol can be reversed with dialysis, however, patients with renal failure may not respond as well to dialysis treatment.
Originator
Blocadren,MSD,UK,1974
The Uses of Timolol
Timolol is a β-adrenergic blocker most commonly used to treat raised blood pressure; used to treat angina (pain from inadequate oxygen supply to the heart muscle); treatment of so me disturbances of heart rhythm; used to prevent migraine headaches; drops treat some types of glaucoma (raised pressure within the eye).
The Uses of Timolol
Betimol(Sanofi Winthrop).
The Uses of Timolol
Timolol is a nonselective β-adrenoblocker that prevents action of catecholamines. When used locally in the form of eye drops, intraocular pressure decreases. It is used for chronic open-angle glaucoma as well as closed-angle glaucoma.
Indications
Ophthalmic timolol is indicated for the treatment of increased intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. The oral form of this drug is used to treat high blood pressure. In certain cases, timolol is used in the prevention of migraine headaches.
Background
Timolol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist given in an eye drop solution to reduce intraocular pressure, or pressure in the eyes. It is also used in tablet form as a drug to treat hypertension. Timolol was first approved by the FDA in 1978. This drug is marketed by several manufacturers and is an effective agent for the management of conditions such as open-angle glaucoma and hypertension.
Definition
ChEBI: (S)-timolol (anhydrous) is the (S)-(-) (more active) enantiomer of timolol. A beta-adrenergic antagonist, both the hemihydrate and the maleate salt are used in the mangement of glaucoma, hypertension, angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, and for the prevention of migraine. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug, an antihypertensive agent, an anti-arrhythmia drug and a beta-adrenergic antagonist. It is a conjugate base of a (S)-timolol(1+). It is an enantiomer of a (R)-timolol.
Manufacturing Process
Step A: Preparation of 3-tert-Butylamino-2-Oxopropanol - To an aqueous
solution of tert-butylamine (1 mol) at ambient temperature, there is added
slowly and with vigorous stirring 2 mols bromoacetol. The reaction mixture is
allowed to stand at ambient temperature for about 5 hours whereupon it is
made basic by the addition of sodium hydroxide.
The reaction mixture then is extracted with ether, the excess amine is
removed from the ethereal solution under reduced pressure and the ether
then removed by evaporation to give 3-tert-butylamino-2-oxopropanol.
Step B: A solution of the 3-tert-butylamino-2-oxopropanol in a mixture of
pyridine hydrochloride and pyridine is treated with p-toluenesulfonylchloride.
The mixture is stirred for 1/2 hour at 25° to 30°C and then poured into cold water. The solution is treated with potassium carbonate and the pyridine
evaporated in vacuo at a temperature between 55° and 60°C. The aqueous
residue is treated with potassium carbonate and the mixture extracted with
methylene chloride. Evaporation of the dried extract provides 1-
toluenesulfonyloxy-2-oxo-3-tert-butylaminopropane.
Step C: Preparation of 3-Morpholino-4-(3-tert-Butylamino-2-Oxopropoxy)-
1,2,5-Thiadiazole - The 1-toluenesulfonyloxy-2-oxo-3-tert-butylaminopropane,
prepared as described in Step B, (11 mols) is added to 0.80 N methanolic
sodium methoxide (15 ml) at 0°C. The mixture is stirred for 15 minutes at 0°
to 5°C, treated with 3-morpholino-4-hydroxy-1,2,5-thiadiazole (4.29 grams)
and then refluxed for 16 hours. The solvent is evaporated in vacuo and the
residue is treated with excess potassium carbonate to provide 3-morpholino-
4-(3-butylamino-2-oxopropoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazole.
Step D: Chemical Reduction Preparation of 3-Morpholino-4-(3-tert_x0002_Butylamino-2-Hydroxypropoxy)-1,2,5-Thiadiazole - The 3-morpholino-4-(3-
tert-butylamino-2-oxopropoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazole (0.01 mol) is dissolved in
isopropanol (10 ml). To the solution is added sodium borohydride in portions
until the initial evolution of heat and gas subsides. The excess sodium
borohydride is destroyed by addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid until
the mixture remains acidic. The precipitate of sodium chloride is removed,
ether is added, and the solution is concentrated to crystallization. The solid
material is removed by filtration and dried thus providing 3-morpholino-4-(3-
tert-butylamino-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazole, MP 161° to 163°C (as
hydrochloride).
Alternative Step D: Reduction with a Reductate - Sucrose (1 kg) is dissolved
in water (9 liters) in a 20-liter bottle equipped with a gas trap. Baker's yeast
(Saccharomyces cerevisiae, 1 kg) is made into a paste with water (1 liter) and
added to the sucrose solution with stirring. After lively evolution of gas begins
(within 1 to 3 hours), 3-morpholino-4-(3-tert-butylamino-2-oxopropoxy)-
1,2,5-thiadiazole hydrogen maleate [1.35 mols, prepared by reaction of the 3-
morpholino-4-(3-tert-butylamino-2-oxopropoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazole with an
equimolar quantity of maleic acid in tetrahydrofuran]. The mixture is allowed
to stand until fermentation subsides, after which the bottle is kept in a 32°C
incubator until all fermentation has ended (in approximately 1 to 3 days). The
yeast is filtered off with addition of diatomaceous earth and the filtrate is
evaporated to dryness to give S-3-morpholino-4β-tert-butylamino-2-
hydroxypropoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazole, MP 195° to 198°C (as hydrogen maleate),
according to US Patent 3,619,370.
Step E: The base may be converted to the maleate by maleic acid
Therapeutic Function
Antiarrhythmic, Antiglaucoma
Contact allergens
Timolol was implicated in allergic contact dermatitis due to beta-blocker agents in eyedrops.
Pharmacokinetics
Timolol, when administered by the ophthalmic route, rapidly reduces intraocular pressure. When administered in the tablet form, it reduces blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output, and decreases sympathetic activity.. This drug has a fast onset of action, usually occurring within 20 minutes of the administration of an ophthalmic dose. Timolol maleate can exert pharmacological actions for as long as 24 hours if given in the 0.5% or 0.25% doses.
Metabolism
Timolol is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 2D6 enzyme, with minor contributions from CYP2C19. 15-20% of a dose undergoes first-pass metabolism. Despite its relatively low first pass metabolism, timolol is 90% metabolized. Four metabolites of timolol have been identified, with a hydroxy metabolite being the most predominant.
Metabolism
Timolol (Timoptic) is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma levels occur 2 to 4 hours after oral administration; the plasma halflife of timolol is approximately 5.5 hours.The extensive tissue distribution of timolol into lung, liver, and kidney is similar to that of other -blockers. Approximately 70% of the drug is excreted in the urine within 24 hours, mostly as highly polar unconjugated metabolites. Only 6% of an administered dose is recovered in the feces. Although timolol is approved for the topical treatment of elevated intraocular pressure, there is limited information about its pharmacokinetics following administration by this route.The drug apparently can reach the systemic circulation after intraocular instillation, but plasma levels are only about 7% of those achieved in the aqueous humor.
Properties of Timolol
| Melting point: | 71.5-72.5 °C |
| Boiling point: | 487.2±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.224±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | pKa ~9.2(H2O
t = 25.0) (Uncertain) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26839-75-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Propanol, 1-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-3-[[4-(4-morpholinyl)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]oxy]-, (2S)- (26839-75-8) |
Safety information for Timolol
Computed Descriptors for Timolol
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
