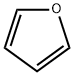
Thiophene
Synonym(s):Thiophene;CYP3A;Thiofuran;Thiole;HLP
- CAS NO.:110-02-1
- Empirical Formula: C4H4S
- Molecular Weight: 84.14
- MDL number: MFCD00005413
- EINECS: 203-729-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-27 17:16:38

What is Thiophene?
Chemical properties
Thiophene is a colourless to pale yellow liquid that has an odor similar to benzene. It is a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring containing four carbon atoms and one sulfur atom. The ring system is also known as a thienyl ring. It occurs as an impurity in commercial benzene and is used as a solvent and in organic syntheses.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless liquid with an aromatic odor resembling benzene. An odor threshold concentration of 0.056 ppbv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of Thiophene
Thiophene is used as a building block of various organic molecules and pharmaceuticals providing functional properties.
The Uses of Thiophene
Solvent similar to benzene, but suitable for lower and higher temps; manufacture of resins from thiophene-phenol mixtures and formaldehyde; manufacture of dyes and pharmaceuticals.
The Uses of Thiophene
Thiophene is an important building block in dyes, agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals synthesis. It is involved in the chloroalkylation reactions in 2,5-positions. It is also used to prepare butane by reduction with raney nickel, 2-vinylthiophene, dithienyl, and 2-halo thiophenes by reacting with halogens.
Definition
ChEBI: Thiophene is a monocyclic heteroarene that is furan in which the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur. It has a role as a non-polar solvent. It is a mancude organic heteromonocyclic parent, a member of thiophenes, a monocyclic heteroarene and a volatile organic compound.
Production Methods
Thiophene is present in coal tar and is recovered in the benzene distillation fraction (up to about 0.5% of the benzene present). Its removal from benzene is accomplished by mixing with concentrated sulfuric acid, soluble thiophene sulfonic acid being formed. Thiophene gives a characteristic blue coloration with isatin in concentrated sulfuric acid. The basic nomenclature of the thiophene ring system and its derivatives is indicated by the following: the sulfur atom is number 1, positions 2 and 5 are equivalent in the parent ring, as are the 3 and 4 positions.
General Description
Thiophene appears as a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Insoluble in water and slightly denser than water. Flash point 30 °F. Vapors heavier than air. Irritates the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Used to make pharmaceuticals and dyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Thiophene reacts violently with strong oxidizing agents and concentrated nitric acid causing fire and explosion hazards [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 899]. A mixture of Thiophene and N-nitrosoacetanilide exploded at 0°C [Ber., 1887, 30, 367].
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation and subcutaneous routes. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Explosive reaction with N-nitrosoacetanilide. Violent or explosive reaction with nitric acid. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of SOx.
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. A rate constant 9.70 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the reaction of thiophene and OH radicals in the atmosphere at room temperature (Atkinson, 1985). Thiophene also reacts with NO3 radicals in the atmosphere at rate constants ranging from 3.2 x 10-14 (Atkinson et al., 1985) to 3.93 x 10-14 cm3/molecule?sec (Atkinson, 1991).
Purification Methods
The simplest purification procedure is to dry thiophen with solid KOH, or reflux it with sodium, and fractionally distil it through a glass-helices-packed column. More extensive treatments include an initial wash with aqueous HCl, then water, drying with CaSO4 or KOH, and passage through columns of activated silica gel or alumina. Fawcett and Rasmussen [J Am Chem Soc 67 1705 1945] washed thiophene successively with 7M HCl, 4M NaOH, and distilled water, dried with CaCl2 and fractionally distilled it. *Benzene was removed by fractional crystallisation by partial freezing, and the thiophene was degassed and sealed in Pyrex flasks. [Also a method is described for recovering the thiophene from the *benzene-enriched portion.] [Beilstein 17 H 29, 17 I 17, 17 II 35, 17 III/IV 234, 17/1 V 297.]
Properties of Thiophene
| Melting point: | -38 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 84 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 40 mm Hg ( 12.5 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | -9 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with carbon tetrachloride, heptane, pyrimidine, dioxane, toluene, and many organic
solvents (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992) |
| form | powder |
| color | Clear |
| Specific Gravity | 1.06 |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in propylene glycol. alliaceous garlic |
| Odor Threshold | 0.00056ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.5-12.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,9353 |
| BRN | 103222 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.33 and 2.70 in distilled water and seawater, respectively (Przyjazny et al., 1983) |
| Dielectric constant | 9.3(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, nitrates. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-02-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiophene(110-02-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiophene (110-02-1) |
Safety information for Thiophene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Thiophene
Thiophene manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 110-02-1 THIOPHENE 99%View Details
110-02-1 THIOPHENE 99%View Details
110-02-1 -
 110-02-1 THIOPHENE 99%View Details
110-02-1 THIOPHENE 99%View Details
110-02-1 -
 Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1 -
 Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1 -
 Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1 -
 THIOPHENE Extra Pure CAS 110-02-1View Details
THIOPHENE Extra Pure CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1 -
 Thiophene 98.00% CAS 110-02-1View Details
Thiophene 98.00% CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1 -
 Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
Thiophene CAS 110-02-1View Details
110-02-1
