TETRODOTOXIN
- CAS NO.:4368-28-9
- Empirical Formula: C11H17N3O8
- Molecular Weight: 319.27
- MDL number: MFCD00213719
- EINECS: 224-458-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
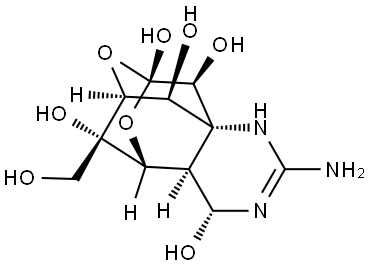
What is TETRODOTOXIN?
Description
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a selective sodium channel blocker nonprotein heat-stable toxin. The mechanism of toxicity is through the blockage of fast voltage-gated sodium channels. The consumption of toxic amounts of TTX results primarily in neurologic and gastrointestinal signs and symptoms. TTX is widely distributed in marine taxa such as pufferfish and porcupine fish (suborders of the Tetraodontiformes order), salamanders of the family Salamandridae, Central American frogs (genus Atelopus), shellfish, starfish, crabs, and some species of ribbonworm and octopus. However, in terrestrial taxa, it is limited to a single class of vertebrates (Amphibia). TTX is now known to be produced not by puffer but by bacteria, and reaches various species of animals via food chain.
Chemical properties
white powder
The Uses of TETRODOTOXIN
Tetrodotoxin is a highly selective, reversible sodium channel blocker.
The Uses of TETRODOTOXIN
TTX is an extremely popular chemical tool in the physiological and pharmacological laboratories since discovery of its channel blocking action in the early 1960s. Some potential therapeutic uses include suppressing pain in cancer patients, preventing ischemic damage of the brain that follows stroke, relieving the symptoms of withdrawal in opiate addicts, and using it as anesthetic agent.
Definition
ChEBI: A quinazoline alkaloid that is a marine toxin isolated from fish such as puffer fish. It has been shown to exhibit potential neutotoxicity due to its ability to block voltage-gated sodium channels.
Biological Activity
Selective inhibitor of Na + channel conductance. Binding is reversible and of high affinity (K d = 1-10 nM). Blocks in a use-dependent manner.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Nox.
storage
-20°C (desiccate)
Toxicity evaluation
TTX is a selective sodium channel blocker that can block nerve and muscle conductions; action potentials are blocked while resting membrane potentials and resting membrane resistance are not affected. TTX blocks axonal transmission by lowering the conductance of sodium at nodes of Ranvier. Vomiting occurs because the toxin can act directly at or near the chemoreceptor trigger zone. Respiratory depression is caused by either a specific action of tetrodotoxin on the brain’s respiratory center or because paralysis of respiratory nerves and muscles occurs.
Properties of TETRODOTOXIN
| Melting point: | 280 °C (decomp) |
| Boiling point: | 458.31°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 -8.64° (c = 8.55 in dil acetic acid) |
| Density | 1.3768 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: stable at pH 4-5 if stored frozensoluble |
| form | powder |
| pka | 8.76 (water); 9.4 (50% alc) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 13,9318 |
| Stability: | Acid Sensitive, Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4368-28-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrodotoxin (4368-28-9) |
Safety information for TETRODOTOXIN
Computed Descriptors for TETRODOTOXIN
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1