Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
Synonym(s):Bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide;Bis(dimethylthiocarbamyl) disulfide;Tetramethylthiuram disulfide;Thiram
- CAS NO.:137-26-8
- Empirical Formula: C6H12N2S4
- Molecular Weight: 240.43
- MDL number: MFCD00008325
- EINECS: 205-286-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02

What is Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide?
Description
Tetramethylthiuram disulfide is a rubber chemieal, an accelerator of vulcanization. It represents the most commonly positive allergen contained in the "thiuram mix". The most frequent occupational categories are the metal industry, homemakers, health services and laboratories, building industries, and shoemakers.
Chemical properties
white to almost white powder
Chemical properties
Thiram is a colorless to yellow, crystalline solid. Characteristic odor. Commercial pesticide products may be dyed blue.
Physical properties
Colorless to white to cream-colored crystals. May darken on exposure to air or light.
The Uses of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
Tetramethylthiuram disulfide is used as fungicide; bacteriostat; pesticide; rubber vulcanization accelerator; scabicide; seed disinfectant; animal repellent; insecticide; lube-oil additive; wood preservative; in antiseptic sprays; in the blending of lubrieant oils; used against Botrytis, rusts and downy mildews; seed dressing against "damping off' and verticillium wilt; ethanol antagonist and deterrent in mixtures of the methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl derivatives; antioxidant in polyolefin plastics; peptizing agent in polysulphide elastomers; in soaps and rodent repellents; nut, fruit, and mushroom disinfectant.
The Uses of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
antianginal
The Uses of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
Thiram is an ectoparasiticide. Thiram is used in agriculture to prevent fungal diseases in seed and crops. Thiram has other applications ranging from use as a topical bactericide to animal repellent.
The Uses of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
Rubber accelerator; vulcanizer; seed disinfectant; fungicide; bacteriostat in soap; animal repellent.
The Uses of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
Thiram is a protective fungicide applied to foliage to control Botrytis spp. on grapes, soft fruit, lettuce, vegetables and ornamentals. It also controls rust on ornamentals, scab and storage diseases on apple and pear and leaf curl and Monilia on stone fruit. It is used in seed treatments alone or in combination with added insecticides or fungicides to control damping off diseases such as Pythium spp., and other diseases like Fusarium spp. of maize, cotton, cereals, legumes, vegetables and ornamentals.
Background
Thiram may be used in dermatology as a scabicide . Thiram is mainly used as a fungicide for plants and treatment for seeds, however, this use is being investigated for safety in many markets including Canada .
Definition
ChEBI: An organic disulfide that results from the formal oxidative dimerisation of N,N-dimethyldithiocarbamic acid. It is widely used as a fungicidal seed treatment.
General Description
A liquid solution of a white crystalline solid. Primary hazard is to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Easily penetrates the soil to contaminates groundwater and waterways.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Decomposes in acidic media to give toxic products. Decomposes to an extent on prolonged exposure to heat, air or moisture.
Reactivity Profile
TMTD is incompatible with oxidizing materials and strong acids. Also incompatible with strong alkalis and nitrating agents .
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, irritant to skin and eyes. Body weight and hematologic effects. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust may cause respiratory irritation. Liquid irritates eyes and skin and may cause allergic eczema in sensitive individuals. Ingestion causes nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, all of which may be persistent; paralysis may develop.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating oxides of sulfur are formed. Carbon disulfide may be formed from unburned material.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Rodenticide: Thiram is used as a fungicide to prevent crop damage in the field and to prevent crops from deterioration in storage or transport. Thiram is also used as a seed, nut, fruit, and mushroom disinfectant from a variety of fungal diseases. In addition, it is used as an animal repellent to protect fruit trees and ornamentals from damage by rabbits, rodents, and deer. Thiram has been used in the treatment of human scabies, as a sun screen, and as a bactericide applied directly to the skin or incorporated into soap. Thiram is used as a rubber accelerator and vulcanizer and as a bacteriostat for edible oils and fats. It is also used as a rodent repellent, wood preservative, and may be used in the blending of lubricant oils. Registered for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
AAPIROL®; AATACK®; AATIRAM®; ACCELERATOR T®; ACCELERATOR THIURAM®; ACCEL TMT®; AGROSOL POUR-ON®; ANLES®; ARASAN®[C]; ATIRAM®; ATTACK®; AULES®; CHIPCO THIRAM 75®; CRYLCOAT®; CUNITEX®; CYURAM DS®; DELSAN®; EBECRYL®; EKAGOM TB®; EVERSHIELD T SEED PROTECTORANT®; FALITIRAM®; FERMIDE®; FERNACOL®; FERNASAN®; FERNIDE®; FLO PRO T SEED PROTECTANT®; FMC 2070®[C]; FORMALSOL®; HERMAL®; HERYL®; HEXATHIR®; HY-VIC®; KODIAK T®; KREGASAN®; LIQUID MOLY-CO-THI®; MERCURAM®; METIURAC®; MOLY-T®; NA2771®; NOBECUTAN®; NOMERSAN®; NORMERSAN®; OPTIMA®; PANORAM 75®; POLYRAM ULTRA®; POMARSOL®; POMARSOL FORTE®; POMASOL®; PRO-GRO®; PURALIN®; RAXIL®; REZIFILM®; ROOTONE®; ROYAL TMTD®; RTUBAYTAN- THIRAM®; RTU FLOWABLE SOYBEAN FUNGICIDE®; SADOPLON®; SOLUCRYL®; SPOTRETE®; SPOTRETE-F®; SQ 1489®; SRANANSF- X®; TERSAN 75®[C]; TERSANTETRAMETHYL DIURANE SULFIDE®; TETRAPOM®; TETRASIPTON®; THIANOSAN®; THILLATE®; THIMAR®; THIMER®; THIOKNOCK®; THIOSAN®; THIOSCABIN®; THIOTEX®; THIOTOX®; THIRAM 75®; THIRAM 80®; THIRAMAD®; THIRAM B®; THIRAMPA®; THIRASAN®; THIULIN®; THIULIX®; THIURAD®; THIURAMIN®; THIURAMYL®; THYLATE®; TIRAMPA®; TITAN FL®; TRAMETAN®; TRIDIPAM®; TRIPOMOL®; TUADS®; TUEX®; TULISAN®; UCECOAT®; UCECRYL®; UVECRYL®; VANCIDA TM-95®; VANCIDE TM®; VITAFLO 280®; VITAVAX® Thiram; VITAVAX-T®; VUAGT-1-4®; VULCAFOR TMTD®; VULKACIT MTIC®; VULKACIT THIURAM®; VULKACIT THIURAM/C®
Contact allergens
TITD is a rubber vulcanization accelerator
Contact allergens
This rubber chemical, accelerator of vulcanization, represents the most commonly positive allergen contained in “thiuram mix.” The most frequent occupational categories are the metal industry, homemakers, health services and laboratories, the building industry, and shoemakers. It is also widely used as a fungicide, belonging to the dithiocarbamate group of carrots, bulbs, and woods, and as an insecticide. Thiram is the agricultural name for thiuram.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic and teratogenic data. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported, Affects human pulmonary system. A rmld allergen and irritant. Acute poisoning in experimental animals produced liver, hdney, and brain damage. Dangerous in a fire; see NITROGEN MONOXIDE and SULFUR DIOXIDE.
Potential Exposure
Thiram is a dithiocarbamate. Some thiurams have been used as rubber components: thiram is used as a rubber accelerator and vulcanizer; a seed, nut, fruit, and mushroom disinfectant; a bacteriostat for edible oils and fats; and as an ingredient in suntan and antiseptic sprays and soaps. It is also used as a fungicide, rodent repellent; wood preservative; and may be used in the blending of lubricant oils.
Carcinogenicity
Thiram also was not carcinogenic in rats
by gavage or in mice by single subcutaneous
injection. In skin painting studies in mice
thiram had tumor-initiating and -promoting
activity but was not a complete carcinogen.
Thiram was genotoxic to insects, plants,
fungi, and bacteria: it induced sister chromatid
exchange and unscheduled DNA synthesis in
cultured human cells. Despite established
genotoxicity in vitro, it showed no clastogenic
and/or aneugenic activity in vivo after oral
administration to mice at the maximum tolerated
dose.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In both soils and water, chemical and biological mediated reactions can
transform thiram to compounds containing the mercaptan group (Alexander, 1981).
Odeyemi and Alexander (1977) isolated three strains of Rhizobium sp. that degraded
thiram. One of these strains, Rhizobium meliloti, metabolized thiram to yield dimethy-
lamine (DMA) and carbon disul?de which formed spontaneously from dimethyldithiocar-
bamate (DMDT). The conversion of DMDT to DMA and carbon disul?de occurred via
enzymatic and nonenzymatic mechanisms (Odeyemi and Alexander, 1977).
When thiram (100 ppm) was inoculated with activated sludge (30 ppm) at 25°C and
pH 7.0 for two weeks, 30% degraded. Metabolites included methionine, elemental sulfur,
formaldehyde, dimethyldithiocarbamate-α-aminobutyric acid and the corresponding keto
aci
To a non-autoclaved alluvial sandy loam (pH 7.3) fortified and inoculated with the
bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 40 and 86% degradation were observed after 4 and
24 days, respectively. In autoclaved soil, thiram degradation was not affected. Degradat
Soil. Decomposes in soils to carbon disul?de and dimethylamine (Sisler and Cox,
1954; Kaars Sijpesteijn et al., 1977). When a spodosol (pH 3.8) pretreated with thiram
was incubated for 24 days at 30°C and relative humidity of 60–90%, dimethylamine formed
as the major product. Minor degradative products included nitrite ions (nitration reduction)
and dimethylnitrosamine (Ayanaba et al., 1973).
Plant. Major plant metabolites are ethylene thiourea, thiram monosul?de, ethylene
thiram disul?de and sulfur (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Metabolic pathway
Dialkyldithiocarbamates chelate copper and inhibit pyruvate dehydrogenase. It is likely that the mode of action of chelators is principally through their effect on lipoamide containing dehydrogenases (Corbett et al., 1984). Thiram generates dimethyldithiocarbamic acid by being cleaved in acidic conditions and in biological media. The acid is conjugated with glucose and alanine in plants and with glucuronic acid in mammals. Dimethyldithiocarbamic acid is further degraded to dimethylamine and CS2. An extensive review of the properties of dithiocarbamate pesticides was published by the World Health Organisation (WHO, 1988) from which much of the following information is taken.
Metabolism
Not Available
Shipping
UN2771 Thiocarbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise thiram (three times) from boiling CHCl3, then recrystallise it from boiling CHCl3 by adding EtOH dropwise to initiate crystallisation, and allow it to cool. Finally it is precipitated from cold CHCl3 by adding EtOH (which retains the monosulfide in solution). [Ferington & Tobolsky J Am Chem Soc 77 4510 1955, Beilstein 4 IV 242.]
Degradation
Thiram is decomposed in acidic media. It deteriorates on prolonged
exposure to heat, air or moisture. DT50 values are estimated as 128 days,
18 days and 9 hours at pH 4, 7 and 9, respectively (PM). The dimethyldithiocarbamate
(2) is stable in alkaline media but unstable in acidic
conditions, decomposing to dimethylamine and carbon disulfide. In
water, the dimethyldithiocarbamate can be oxidatively degraded to a
number of products. The rate of degradation depends on pH and the
type of any cations that might be present. The rate of decomposition and
production of CS2 is decreased by cations in the following order Na+ >
Zn2+> Fe3+> Cu2+. Thiram was completely degraded in sewage water in
12 days.
An ethanolic solution of unlabelled thiram (4 g l-1) was exposed to UV
light for 48 hours. The reaction tube was encircled by low pressure Hg
lamps that gave more than 85% of their total radiation at 253.7 nm. Pure
nitrogen was bubbled through the solutions. Photo-oxidation studies were
done similarly except that oxygen was bubbled through the solution.
In further experiments, irradiation was by visible light from a tungsten
lamp and again oxygen was bubbled through the solution. The outlet
gases from the UV study were condensed in a cold trap and analysed
by GC-MS. Traces of carbon disulfide and dimethylamine were
identified. The reaction mixture was also analysed by GC-MS and
three products were identified as tetramethyl hydrazine (3), N,N-dimethylthioformamide
(4) and tetramethylthiourea (5). The identity of
the latter was confirmed by IR and NMR. The reaction mixture was concentrated
and applied to TLC plates and sulfur and tetramethylthiourea
(5) were identified as the main products of photolysis. The same
products with the addition of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide were
produced by UV light and oxygen. Oxidation of thiram in the presence
of visible light together with Rose Bengal as a photosensitiser also gave the same products in almost identical yields. The results confirm that
C-S and S-S bond fissions are primary photochemical steps with
dithiocarbamates.
Toxicity evaluation
Thiram cytotoxicity appears to result from its potential to disrupt cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress. In cultured human skin fibroblast, thiram results in an increase in oxidative markers such as lipid peroxidation and oxidation of reduced glutathione and decrease in other endogenous antioxidant. Toxic effects of thiram have been described in humans and animal model systems ranging from liver injury, testicular toxicity, ophthalmological changes, and development of micronuclei in bone marrow. However, the mechanisms of these effects are not characterized and inconsistent across various studies.
Incompatibilities
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine,fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from strong alkaline materials, strong acids, strong bases and nitrating agents.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Thiram can be dissolved in alcohol or other flammable solvent and burned in an incinerator with an afterburner and scrubber.
Properties of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
| Melting point: | 156-158 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 129 °C (20 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.43 |
| vapor pressure | 8 x 10-6 mmHg at 20 °C (NIOSH, 1997) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 89°C |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (argon) |
| solubility | 0.0184g/l |
| form | solid |
| pka | 0.87±0.50(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 16.5 mg/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9371 |
| BRN | 1725821 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 0.5 mg/m3, IDLH 100 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: 0.5
mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 mg/m3. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 137-26-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiram(137-26-8) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 53) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiram (137-26-8) |
Safety information for Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
| InChIKey | KUAZQDVKQLNFPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide manufacturer
Super Crop Safe Limited
Related products of tetrahydrofuran
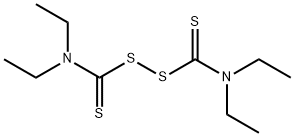
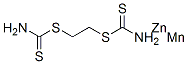
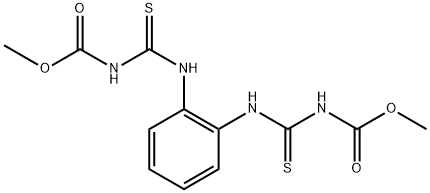
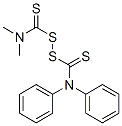


You may like
-
 137-26-8 Thiram 99%View Details
137-26-8 Thiram 99%View Details
137-26-8 -
 137-26-8 99%View Details
137-26-8 99%View Details
137-26-8 -
 Thiram 99%View Details
Thiram 99%View Details
137-26-8 -
 137-26-8 Thiram 98%View Details
137-26-8 Thiram 98%View Details
137-26-8 -
 137-26-8 98%View Details
137-26-8 98%View Details
137-26-8 -
 Tetramethylthiuram disulphide, 97% CAS 137-26-8View Details
Tetramethylthiuram disulphide, 97% CAS 137-26-8View Details
137-26-8 -
 37951-47-6 3'-Benzyloxy propiophenone, 98% 99%View Details
37951-47-6 3'-Benzyloxy propiophenone, 98% 99%View Details
37951-47-6 -
 3'-Methoxypropiophenone, 99% 37951-49-8 99%View Details
3'-Methoxypropiophenone, 99% 37951-49-8 99%View Details
37951-49-8