Disulfiram
Synonym(s):Disulfiram;TETD;Tetraethylthiuram disulfide;DRAM;DRAM1
- CAS NO.:97-77-8
- Empirical Formula: C10H20N2S4
- Molecular Weight: 296.54
- MDL number: MFCD00009048
- EINECS: 202-607-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
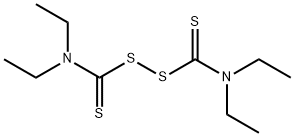
What is Disulfiram?
Absorption
Disulfiram is absorbed slowly from the gastrointestinal tract (80 to 90% of oral dose).
Toxicity
LD50=8.6g/kg (orally in rats). Symptoms of overdose include irritation, slight drowsiness, unpleasant taste, mild GI disturbances, and orthostatic hypotension.
Description
Disulfiram was first synthesized in the 1800s to improve the manufacturing process of rubber. A physician working in a rubber factory plant first observed in 1937 that factory workers who were exposed to disulfiram were intolerant to ethanol. In the 1940s, two scientists rediscovered the disulfiram– ethanol effects while researching antiparasitic therapies. This finding eventually led to the approval of the medication to be used as an ethanol deterrent by the Food and Drug Administration in 1951.
Chemical properties
yellow-white crystals or grey powder
Originator
Esperal,Millot Solac,France,1950
The Uses of Disulfiram
Disulfiram is a copper and zinc chelator and an irreversible inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase (IC50 = 0.1 mM) that has been indicated for the treatment of alcohol dependence. It also inhibits the copper-dependent enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase, which prevents the breakdown of dopamine and has been considered as a treatment for cocaine dependence. When in complex with copper, disulfiram has been shown to inhibit purified 20S proteasome (IC50 = 7.5 μM) and 26S proteasome (IC50 = 20 μM) from MDA-MB-0231 breast cancer cells. Because disulfiram targets the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, it has been investigated as an anti-cancer agent. Furthermore, at 250 nM it has been shown to induce reactive oxygen species, to activate JNK and p38 pathways, and to inhibit NF-κB activity, which suppresses self-renewal in cancer stem cells.
The Uses of Disulfiram
It is used as rubber accelerator; vulcanizer; seed disinfectant; fungicide; alcohol deterrent.
The Uses of Disulfiram
Alcohol deterrent;Dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor;For the treatment and management of chronic alcoholism.
Background
A carbamate derivative used as an alcohol deterrent. It is a relatively nontoxic substance when administered alone, but markedly alters the intermediary metabolism of alcohol. When alcohol is ingested after administration of disulfiram, blood acetaldehyde concentrations are increased, followed by flushing, systemic vasodilation, respiratory difficulties, nausea, hypotension, and other symptoms (acetaldehyde syndrome). It acts by inhibiting aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Indications
For the treatment and management of chronic alcoholism
What are the applications of Application
Disulfiram is an ALDH and tumor cell growth inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: An organic disulfide that results from the formal oxidative dimerisation of N,N-diethyldithiocarbamic acid. A multi-enzyme inhibitor that is used in alcohol aversion therapy and also exhibits anticancer properties.
Manufacturing Process
Disulfiram may be made by the reaction of diethyl amine with carbon disulfide in the presence of sodium hydroxide. The (C2H5)2NCSSNa intermediate is oxidatively coupled using hydrogen peroxide to give disulfiram.
brand name
Antabuse (Odyssey) .
Therapeutic Function
Alcohol deterrent
General Description
Odorless or almost odorless white or almost white to tan powder. Unpleasant taste with metallic or garlic aftertaste. pH of a solution obtained by shaking 1 g with 30 mL of water is 6 to 8.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Disulfiram is sensitive to light. Disulfiram is incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizers and nitrosating agents (e.g. N-Nitrosodiphenylamine). .
Hazard
Toxic symptoms when ingested with alcohol; animal teratogen. Vasodilation and nausea. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Disulfiram affects the central
nervous system, thyroid, and skin; in combination
with alcohol it causes an “Antabusealcohol”
syndrome.
Small doses of disulfiram reportedly can
cause effects on thyroid iodine uptake and
thyroid gland hypertrophy. It may also
produce dermatitis and acneform rashes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Disulfiram are not available; however, Disulfiram is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biological Activity
Inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase that displays antialcoholism activity. Shown to reversibly stimulated Ca 2+ -ATPase activity and inhibit V-ATPase (EC 50 = 26 μ M). Also inhibits expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and displays anti-invasive activity.
Contact allergens
TETD is a rubber accelerator of the thiuram group, contained in “thiuram mix.” It can cross-react with other thiurams, especially TMTD. TETD is used to aid those trying to break their dependence on alcohol. The disulfiram-alcohol reaction is not allergic but due to the accumulation of toxic levels of acetaldehyde. The implanted drug can, however, lead to local or generalized dermatitis, for example ingested disulfiram, mainly in previously rubber-sensitized patients. As an adjunctive treatment of alcoholism, it caused occupational contact dermatitis in a nurse.
Pharmacokinetics
Disulfiram produces a sensitivity to alcohol which results in a highly unpleasant reaction when the patient under treatment ingests even small amounts of alcohol. Disulfiram blocks the oxidation of alcohol at the acetaldehyde stage during alcohol metabolism following disulfiram intake, the concentration of acetaldehyde occurring in the blood may be 5 to 10 times higher than that found during metabolism of the same amount of alcohol alone. Accumulation of acetaldehyde in the blood produces a complex of highly unpleasant symptoms referred to hereinafter as the disulfiram-alcohol reaction. This reaction, which is proportional to the dosage of both disulfiram and alcohol, will persist as long as alcohol is being metabolized. Disulfiram does not appear to influence the rate of alcohol elimination from the body. Prolonged administration of disulfiram does not produce tolerance; the longer a patient remains on therapy, the more exquisitely sensitive he becomes to alcohol.
Clinical Use
Adjunct in the treatment of chronic alcohol dependence
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. An experimental poison by intraperitoneal route. Toxic symptoms when accompanied by ingestion of alcohol. Human systemic effects by ingestion: jaundtce, joint changes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. See also THIRAM.
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Drug, Tumorigen, Mutagen; ReproductiveEffector; Human Data; Hormone, Primary Irritant. Somethiurams have been used as rubber components. Disulfiramis used as an accelerator in compounding natural, styrenebutadiene, and Neoprene? rubbers as a rubber acceleratorand vulcanizer; as a seed disinfectant and fungicide; in therapy; as an alcohol deterrent; in adhesives.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alcohol: risk of severe disulfiram reaction.
Anticoagulants: enhanced anticoagulant effect with
coumarins.
Antiepileptics: inhibition of metabolism of
fosphenytoin and phenytoin (increased risk of
toxicity).
Paraldehyde: increased risk of toxicity with
paraldehyde.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note: For alcohol/disulfiram or ethylene dibromide/disulfiram reaction, remove the person from exposure. Begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility.
Carcinogenicity
In a lifetime carcinogenicity bioassay,
disulfiram was not carcinogenic in either rats
or mice when fed in the diet. The highest
doses were 600 ppm in rats and 2000ppm in
mice.
Increased fetal resorptions, but no teratogenic
effects, were seen in rats exposed at
100mg/kg/day from day 3 of gestation. A weak
genotoxic response was observed in mice
treated in vivo as evidenced by an increase in
sister chromatid exchanges in bone marrow
and spermatogonial cells.9
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime-
weighted average (TLV-TWA) is
2mg/m3.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
Disulfiram is rapidly reduced to diethyldithiocarbamate,
mainly by the glutathione reductase system in
erythrocytes; reduction may also occur in the liver.
Diethyldithiocarbamate is metabolised in the liver to its
glucuronide and methyl ester and to diethylamine, carbon
disulfide, and sulfate ions. Metabolites are excreted mainly
in the urine; carbon disulfide is exhaled in the breath.
storage
+4°C
Shipping
Toxic solids, flammable, organic, n.o.s. requiresa shipping label of “POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS.”They fall into Hazard Class 6.1.
Toxicity evaluation
Disulfiram has multiple mechanisms of toxicity. Its most welldefined action is inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase, which thereby diminishes the breakdown of acetaldehyde. Accumulation of carbon disulfide, a disulfiram metabolite, as well as inhibition of dopamine-b-hydroxylase has also been associated with its toxicity in particular related to use for cocaine dependence.
Properties of Disulfiram
| Melting point: | 69-71 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 117°C |
| Density | 1.27 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 117°C/17mm |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.004g/l |
| pka | 0.86±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Crystals, Crystalline Powder or Granules |
| color | Light yellow |
| Odor | lt. gray powd., sl. odor |
| Water Solubility | 0.02 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 14,3364 |
| BRN | 1712560 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 2 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidants. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 97-77-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 12, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Disulfiram(97-77-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Disulfiram (97-77-8) |
Safety information for Disulfiram
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Disulfiram
| InChIKey | AUZONCFQVSMFAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Disulfiram manufacturer
Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd
East Coast Organics
Unidrug Innovative Pharma Technologies Ltd
REXIN Laboratories (Redson Group)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Disulfiram 98%View Details
Disulfiram 98%View Details
97-77-8 -
 97-77-8 Disulfiram 99%View Details
97-77-8 Disulfiram 99%View Details
97-77-8 -
 Disulfiram 99%View Details
Disulfiram 99%View Details
97-77-8 -
 Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide CAS 97-77-8View Details
Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide CAS 97-77-8View Details
97-77-8 -
 97-77-8 98%View Details
97-77-8 98%View Details
97-77-8 -
 97-77-8 98%View Details
97-77-8 98%View Details
97-77-8 -
 Disulfiram 95% CAS 97-77-8View Details
Disulfiram 95% CAS 97-77-8View Details
97-77-8 -
 Disulfiram CAS 97-77-8View Details
Disulfiram CAS 97-77-8View Details
97-77-8