Tetramethrin
- CAS NO.:7696-12-0
- Empirical Formula: C19H25NO4
- Molecular Weight: 331.41
- MDL number: MFCD00084635
- EINECS: 231-711-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:41
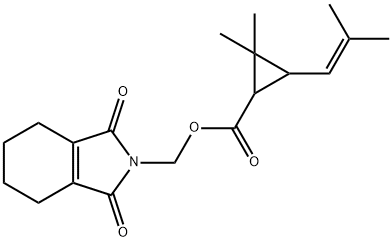
What is Tetramethrin?
Description
Form: Colorless crystals with slight pyrethrum-like odor
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
The Uses of Tetramethrin
Tetramethrin is used to control flies, wasps, cockroaches and other insects in public health, home and garden situations.
The Uses of Tetramethrin
Tetramethrin is a synthetic pyrethroid pesticide used in large-scale commercial agricultural applications as well as in consumer products for domestic purposes.
The Uses of Tetramethrin
Insecticide.
Definition
ChEBI: Tetramethrin is a phthalimide insecticide, a member of maleimides and a cyclopropanecarboxylate ester. It has a role as a pyrethroid ester insecticide. It is functionally related to a chrysanthemic acid.
General Description
Colorless crystals with slight odor. Non corrosive. Used as an insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolysis occurs with strong acid or base.
Reactivity Profile
A pyrethroid. Tetramethrin is an ester and nitrile. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide: Tetramethrin is often formulated as an aerosol and used primarily for indoor pest control or in mosquito coils. It is also used in shampoos to control fleas and ticks on pets. It is often formulated with other insecticides and synergists. Not approved for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
FMC 9260®; ENT-27339; EVERCIDE INTERMEDIATE® 2265 (tetramethrin + fenvalerate); MULTICIDE®; NEO-PYNAMIN®; NEOPYNAMINE®; NEOPYNAMIN FORTE®; NIAGARA®-9260; NIA®- 9260; PHTHALTHRIN®; SP-1103; SUMITOMO® SP-1103
Metabolic pathway
Tetramethrin was the second synthetic pyrethroid to be produced commercially (1964). The compound has a rapid knock-down action and a reasonable killing activity which is enhanced by use with synergists. It is usually used with piperonyl butoxide and in the presence of other insecticides. It has two chiral centres, both in the acid group, and therefore is a 1 RS-cis-trans mixture. A(1R)-rich product containing cis- and trans-isomers in the ratio 20:80 is also used in public health; this is named dtetramethrin. The two products will not be distinguished here because metabolic studies have been performed with various combinations of isomers. Most published information relates to its mode of action in insects and its metabolism in rodents. This is a reflection of its limited outdoor and field use.
Degradation
Tetramethrin is a stable chemical but it is base labile and it is also sensitive
to strong acids. It is hydrolysed to (1RS)-cis-trans-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-
methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropanecarboxylic acid (chrysanthemic acid, 2)
and tetrahydrophthalimide (4). It is oxidised by m-chloroperbenzoic acid
to form epoxy-tetramethrin (5) which is ring-opened to the diol (6) in
dilute aqueous acid (Smith and Casida, 1981). This reaction has been
postulated as initiating the opening of the cyclopropane ring with the
ultimate formation of CO 2 in biological systems (see below). Another
biomimetic reaction of tetramethrin and its ester cleavage product 4 is
Michael addition of thiols to the double bond. Glutathionyl-tetramethrin
(7) is formed by incubation of the constituents in buffered aqueous
methanol (Smith et al., 1982). Its formation on incubation with mouse liver
microsomes is probably non-enzymatic. At the time of this discovery
there appeared to be no equivalent reaction in vivo but the more recent
discovery of sulfonate metabolites (see below) demonstrates its role.
The chrysanthemic acid esters are very sensitive to photodegradation,
being subject to ring-opening initiated by the formation of epoxides such
as 5 (Ruzo et al., 1982) as described under bioallethrin and phenothrin.
Isomerisation was observed only in de-oxygenated benzene solution
because photo-oxidative degradation predominated under most conditions.
Many products were seen in oxygenated benzene solution and in a
thin film in sunlight.
These chemical and photochemical reactions are summarised in
Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for rats: >5,000 mg/kg
Properties of Tetramethrin
| Melting point: | 60-80°C |
| Boiling point: | 468.68°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | d2020 1.108 |
| vapor pressure | 0.94×10-3 Pa (30 °C) |
| refractive index | nD21.5 1.5175 |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 1.83 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| pka | -2.55±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-white to light yellow |
| Merck | 13,9296 |
| BRN | 8807938 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7696-12-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tetramethrin(7696-12-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetramethrin (7696-12-0) |
Safety information for Tetramethrin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H351:Carcinogenicity H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Tetramethrin
Tetramethrin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Tetramethrin 95% (total isomers) CAS 7696-12-0View Details
Tetramethrin 95% (total isomers) CAS 7696-12-0View Details
7696-12-0 -
 Tetramethrin CAS 7696-12-0View Details
Tetramethrin CAS 7696-12-0View Details
7696-12-0 -
 Tetramethrin CAS 7696-12-0View Details
Tetramethrin CAS 7696-12-0View Details
7696-12-0 -
 TetramethrinView Details
TetramethrinView Details
7696-12-0 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
