Terbinafine
- CAS NO.:91161-71-6
- Empirical Formula: C21H25N
- Molecular Weight: 291.43
- MDL number: MFCD00242672
- EINECS: 618-706-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
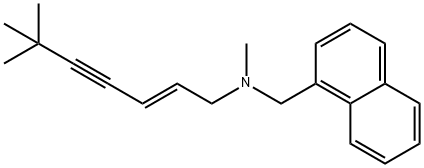
What is Terbinafine?
Absorption
Oral terbinafine is >70% absorbed but only 40% bioavailable after first pass metabolism, reaching a Cmax of 1μg/mL with a Tmax of 2 hours an an AUC of 4.56μg*h/mL. Over the course of a week, 1% topical terbinafine's Cmax increases from 949-1049ng/cm2 and the AUC increases from 9694-13,492ng/cm2/h.
Toxicity
The subcutaneous LD50 in rats and mice is >2g/kg. The TDLO for women is 210mg/kg/6W.
Overdose data with terbinafine is rare, however symptoms are expected to be nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, rash, frequent urination, and headache. Treat overdose with activated charcoal as well as symptomatic and supportive therapy.
Originator
Lamisil,Novartis,UK
The Uses of Terbinafine
Terbinafine (Lamisil) is a second-generation allylamine that is related to naftifine; however, it is 10 to 100 times more potent in vitro. It is fungicidal, whereas griseofulvin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and other azole derivatives are all fungistatic. Because it is fungicidal, duration of therapy is shorter, and relapse rates are less than with other oral or topical therapies. Terbinafine acts by inhibiting squalene epoxidase and thereby decreasing synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. It is highly lipophilic and concentrates in the stratum corneum, sebum, and hair follicles. Slightly better cure rates are attained with b.i.d. than with daily dosing.

Background
Terbinafine hydrochloride (Lamisil) is a synthetic allylamine antifungal. It is highly lipophilic in nature and tends to accumulate in skin, nails, and fatty tissues. Like other allylamines, terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting the fungal squalene monooxygenase (also called squalene epoxidase), an enzyme that is part of the fungal cell wall synthesis pathway.
Terbinafine hydrochloride was granted FDA approval on 30 December 1992.
Indications
Terbinafine hydrochloride is indicated to treat fungal skin and nail infections caused by Trichophyton species, Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum, and Tinea species. Terbinafine hydrochloride also treats yeast infections of the skin caused by Candida species and Malassezia furfur.
Definition
ChEBI: A tertiary amine that is N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine in which the amino hydrogen is replaced by a 3-(tertbutylethynyl)allyl group. An antifungal agent administered orally (generally as the hydrochloride salt) for the t eatment of skin and nail infections.
Indications
Terbinafine (Lamisil) is a second-generation allylamine that is related to
naftifine; however, it is 10 to 100 times more potent in vitro. It is fungicidal,
whereas griseofulvin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and other azole derivatives
are all fungistatic. Because it is fungicidal, duration of therapy is shorter, and
relapse rates are less than with other oral or topical therapies.
Terbinafine acts by inhibiting squalene epoxidase and thereby decreasing
synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes.
It is highly lipophilic and concentrates in the stratum corneum, sebum, and
hair follicles. Slightly better cure rates are attained with b.i.d. than with daily
dosing.
Manufacturing Process
To an ice-cooled solution of N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine
hydrochloride (2.1 g) in methanol (40 ml) and water (10 ml) was added
sodium hydroxide powder (2 g) followed by dropwise addition of
epichlorohydrin (8 ml). The mixture was heated at 60°C for 3 h, then cooled
to room temperature. Volatile materials were removed in vacuo and the
residue was taken up in ethyl acetate and washed with water. The organic
phase was collected, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and evaporated to
dryness. The crude mixture was purified by flash chromatrography on silica
gel (grade 9385, Merck, 230-400 mesh, 60 A) using a solvent gradient of a
mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate (95:5, 90:10 and 85:15) as eluent,
affording the N-methyl-N-naphthylmethyl-2,3-epoxypropane (1.85 g, 81.5%)
as an oil.
To a solution of 3,3-dimethylbutyne (2.95 ml) in dry THF (50 ml) at -78°C
was added a 2.5 M solution of n-BuLi in hexane (10 ml) dropwise. The
mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature over 15 min and stirred at
that temparature for a further 15 min, then was cooled back to -78°C and
BF3OEt2 (3 ml) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred for 15 min and
1.8 g of N-methyl-N-naphthylmethyl-2,3-epoxypropane, dissolved in THF (10
ml), was added dropwise. After stirring at -78°C for 2 h, saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution (15 ml) was added, and the reaction mixture was allowed
to warm to room temperature. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate
(2 times 25 ml), and the combined organic fractions was dried over sodium
sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by flash
chromatrography on silica gel (grade 9385, Merck, 230-400 mesh, 60 a) using
a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate (85:15) as eluent, thereby affording
the N-methyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)-2-hydroxy-heptan-4-ynyl-1-amine as an
oil (1.95 g, 79%).
To an ice-cooled solution of N-methyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)-2-hydroxyheptan-
4-ynyl-1-amine (155 mg) in THF (10 ml) was added Et3N (0.35 ml)
followed by methanesulfonyl chloride (0.075 ml). The resulting mixture was
stirred at 0°C for 3 h, then filtered. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo,
dissolved in toluene (10 ml) and 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU)
(0.37 ml) was added. The resulting mixture was heated at 80°C for 4 h,
cooled to room temperature then poured onto a silica gel column and eluted
with hexane (100%) followed by a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate
(95:5). Thus, a mixture of E- and Z-isomers of N-methyl-N-(1-
naphthylmethyl)-6,6-dimethylhept-2-en-4-ynyl)-1-amine were obtained in a
ratio of 2:5 (95 mg, 66%).
Therapeutic Function
Antifungal
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 29, p. 1509, 1988 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)80338-X
Antimicrobial activity
Terbinafine is active against a wide range of pathogenic fungi, including dermatophytes (Epidermophyton, Microsporum and Trichophyton spp.), various Candida spp., Aspergillus spp., some dimorphic fungi (Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum and Sporothrix schenckii) and many dematiaceous fungi.
Acquired resistance
Resistance has not been reported.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A synthetic allylamine available as the hydrochloride for oral and topical administration.
Pharmacokinetics
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal that inhibits squalene epoxidase (also known as squalene monooxygenase) to prevent the formation of ergosterol and cause an accumulation of squalene, weakening the cell wall of fungal cells. Terbinafine distributes into tissues and has a long terminal elimination half life, so the duration of action is long. Overdose with terbinafine is rare, even above the therapeutic dose, so the therapeutic index is wide. Patients taking oral terbinafine should have liver function tests performed prior to treatment to reduce the risk of liver injury.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: 70–80%
Cmax 250 mg oral: c. 1 mg/L after 2 h
Plasma half-life: c. 17 h
Volume of distribution: 1000 L
Plasma protein binding: >99%
Blood concentrations increase in proportion to dosage. It is
lipophilic and is rapidly and extensively distributed to body
tissues. It reaches the stratum corneum by diffusion through
the dermis and epidermis, and secretion in sebum. Diffusion
from the nail bed is the major factor in its rapid penetration
of nails. It is metabolized by the liver and the inactive metabolites
are mostly excreted in the urine. The elimination half-life
is prolonged in patients with hepatic or renal impairment.
Clinical Use
Terbinafine hydrochloride can be used in Tinea pedis, tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea capitis, Onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes.
Side Effects
These include abdominal discomfort, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, headache, impairment of taste, rash and urticaria. Serious skin reactions, including Stevens– Johnson syndrome, and rare hepatotoxic reactions, including jaundice, cholestasis and hepatitis, are occasionally encountered.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration reduced by rifampicin.
Metabolism
Terbinafine can be deaminated to 1-naphthaldehyde by CYP2C9, 2B6, 2C8, 1A2, 3A4, and 2C19. 1-naphthaldehyde is then oxidized to 1-naphthoic acid or reduced to 1-naphthalenemethanol.
Terbinafine can also be hydroxylated by CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C8, 2B6, and 2C19 to hydroxyterbinafine. Hydroxyterbinafine is then oxidized to carboxyterbinafine or N-demethylated by CYP3A4, 2B6, 1A2, 2C9, 2C8, and 2C19 to desmethylhydroxyterbinafine.
Terbinafine can be N-demethylated to desmethylterbinafine. Desmethylterbinafine is then dihydroxylated to a desmethyldihydrodiol or hydroxylated to desmethylhydroxyterbinafine.
Finally, terbinafine can be dihydroxylated to a dihydrodiol which is then N-demethylated to a desmethyldihydrodiol.
Metabolism
Terbinafine undergoes extensive first pass loss. It is hepatically metabolised to two major inactive metabolites, 80% of which are renally excreted.
Properties of Terbinafine
| Melting point: | 203-205 °C |
| Boiling point: | 417.9±33.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.007±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | soluble in Methanol |
| form | powder to crystal |
| pka | 6.92±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91161-71-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Terbinafine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Terbinafine
Terbinafine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 91161-71-6 Terbinafine 98%View Details
91161-71-6 Terbinafine 98%View Details
91161-71-6 -
 91161-71-6 99%View Details
91161-71-6 99%View Details
91161-71-6 -
 Terbinafine 98%View Details
Terbinafine 98%View Details -
 91161-71-6 Terbinafine 98%View Details
91161-71-6 Terbinafine 98%View Details
91161-71-6 -
 91161-71-6 98%View Details
91161-71-6 98%View Details
91161-71-6 -
 91161-71-6 Terbinafine 99%View Details
91161-71-6 Terbinafine 99%View Details
91161-71-6 -
 Terbinafine CAS 91161-71-6View Details
Terbinafine CAS 91161-71-6View Details
91161-71-6 -
 Terbinafine 98% (HPLC) CAS 91161-71-6View Details
Terbinafine 98% (HPLC) CAS 91161-71-6View Details
91161-71-6
