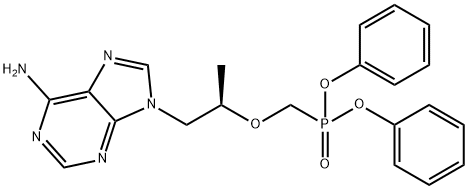
Tenofovir Alafenamide
- CAS NO.:379270-37-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H29N6O5P
- Molecular Weight: 476.47
- MDL number: MFCD23843796
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 11:34:44

What is Tenofovir Alafenamide?
Absorption
As compared to the parent molecule, tenofovir, tenofovir alafenamide presents a lipophilic group that masks the negative charge of the parent moiety which improves its oral bioavailability.
Tenofovir alafenamide is highly stable in plasma and, after administration of this prodrug, there is a low concentration of tenofovir in plasma. After oral administration, tenofovir alafenamide is rapidly absorbed by the gut. When a single dose is administered, a peak concentration of 16 ng/ml of the parent compound, corresponding to about 73% of the dose, is observed after 2 hours with an AUC of 270 ng*h/mL. Once inside the body, tenofovir alafenamide enters hepatocytes by passive diffusion regulated by the organic anion transporters 1B1 and 1B3 for its activation.
Administration of tenofovir alafenamide concomitantly with a high-fat meal results in an increase of about 65% in its internal exposure.
Toxicity
The LD50 of tenofovir alafenamide has not been reported. In cases of overdose, continuous monitoring of vital signs is required as the adverse effects in high doses has not been evaluated. However, in case of overdose, tenofovir is efficiently removed by hemodialysis with an extraction coefficient of 54%.
Carcinogenic reports have only been performed with tenofovir disoproxil and it is important to consider that tenofovir alafenamide does not present a high systemic exposure. However, long-term exposure with 10-fold dosages of tenofovir disoproxil was reported to produce liver adenomas in females. Tenofovir alafenamide was not reported to present mutagenic potential and it did not present effects on fertility.
Description
Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate is an oral phosphonoamidate prodrug of the reverse transcriptase inhibitor tenofovir. It was approved by the USFDA for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease. Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate was discovered and developed by Gilead as a potentially safer form of the previously approved tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread).
The Uses of Tenofovir Alafenamide
Tenofovir Alafenamide is a prodrug of Tenofovir (T018500), which is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor used to treat HIV and Hepatitis B. Antiviral.
Indications
Tenofovir alafenamide is indicated for the treatment of hepatitis B virus infection in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with compensated liver disease.
In combination with emtricitabine and other antiretrovirals, it is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adolescent and adult patients with a weight higher than 35 kg. This combination is also indicated to prevent HIV-1 infections in high risk adolescent and adult patients, excluding patients at risk from receptive vaginal sex. When combined with antiretrovirals other than protease inhibitors that require a CYP3A inhibitor, it can be used to treat pediatric patients weighing 25-35 kg.
In the combination product with emtricitabine and bictegravir, tenofovir alafenamide is considered a complete treatment regimen for HIV-1 infections for treatment-naive patients or patients virologically suppressed for at least three months with no history of treatment failure.
Additionally, the combination product including elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide and the combination product including emtricitabine, rilpivirine and tenofovir alafenamide can be used in the treatment of HIV-1 infection in patients older than 12 years with no previous antiretroviral therapy history or who are virologically suppressed for at least 6 months with no history of treatment failure.
The combination product including darunavir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults without prior antiretroviral therapy or in patients virologically suppressed for 6 months and no reported resistance to darunavir or tenofovir.
Background
Tenofovir alafenamide is a novel tenofovir prodrug developed in order to improve renal safety when compared to the counterpart tenofovir disoproxil. Both of these prodrugs were first created to cover the polar phosphonic acid group on tenofovir by using a novel oxycarbonyloxymethyl linkers to improve the oral bioavailability and intestinal diffusion. Tenofovir alafenamide is an alanine ester form characterized for presenting low systemic levels but high intracellular concentration. It has been reported to produce a large antiviral efficacy at doses ten times lower than tenofovir disoproxil. Tenofovir alafenamide is indicated to treat chronic hepatitis B, treat HIV-1, and prevent HIV-1 infections.
Tenofovir alafenamide was developed by Gilead Sciences Inc and granted FDA approval on 5 November 2015.
Definition
ChEBI: An L-alanine derivative that is isopropyl L-alaninate in which one of the amino hydrogens is replaced by an (S)-({[(2R)-1-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)( henoxy)phosphoryl group. A prodrug for tenofovir, it is used (as the fumarate salt) in combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Tenofovir alafenamide has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of hepatitis B viral replication.
Tenofovir alafenamide presents a better renal tolerance when compared with the counterpart tenofovir disoproxil. This improved safety profile seems to be related to a lower plasma concentration of tenofovir.
In clinical trials, tenofovir alafenamide was shown to present 5-fold more potent antiviral activity against HIV-1 when compared to tenofovir disoproxil.
Synthesis
A multikilogram synthesis of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate was described in a Gilead patent. Additional process improvements on specific steps of the Gilead process have been reported on 100 g scale, and these will be noted throughout the description of the synthesis. The synthesis was initiated with the alkylation of adenine (72) with (R)-propylene carbonate (73) to give hydroxypropyl adenine 74 in 75% yield. It should be noted that sodium hydroxide can be replaced by potassium bases with increased yields on 100 g scale.27 Alkylation of 74 with diethyl p-toluenesulfonyloxymethylphosphonate (75) gave intermediate 76, which was not isolated. Hydrolysis of the phosphonate esters with trimethylsilyl bromide followed by recrystallization from water gave phosphonic acid 77 in 50% yield. Interestingly, replacing Mg(Ot-Bu)2 with PhMgCl/t-BuOH led to improved yields for the alkylation step (74 ?ú 76) on a 100 g scale. Additionally, the authors note that conditions for hydrolyzing the phosphonate ester can be modified using HCl or HBr for improved yields on smaller scale. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) coupling of 77 with phenol produced phosphonate 78 in 51% yield. This step was also reported to proceed in higher yield on smaller scale by changing the solvent to cyclopentylmethyl ether. Monophosphonate ester 78 was treated with thionyl chloride followed by L-alanine isopropyl ester (79) and triethylamine to give tenofovir alafenamide rac-80 as a mixture of phosphonate diastereomers in 47% yield. The diastereomers were separated using simulated moving bed chromatography to give the desired diastereomer ent-80 in 47% yield and 99% diastereomeric purity. The diastereomers could also be separated using a crystallization-induced dynamic resolution of rac-80. Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (VI) was prepared from ent-80 and fumaric acid in 83% yield.

Metabolism
To be activated, tenofovir alafenamide is required to be hydrolyzed to the parent compound tenofovir by the activity of cathepsin A or carboxylesterase 1. Tenofovir alafenamide presents significant plasma stability and hence, its activation is performed inside the target cells.
After activation, tenofovir is further processed and after 1-2 days, it is detected in plasma almost completely transformed to uric acid.
Properties of Tenofovir Alafenamide
| Melting point: | >119°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 640.4±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.39±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C(protect from light) |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.21±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Tenofovir Alafenamide
Computed Descriptors for Tenofovir Alafenamide
| InChIKey | LDEKQSIMHVQZJK-QTJFZWIYNA-N |
| SMILES | C(OC(C)C)(=O)[C@H](C)NP(CO[C@H](C)CN1C2=C(N=C1)C(N)=NC=N2)(OC1=CC=CC=C1)=O |&1:6,12,r| |
Tenofovir Alafenamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
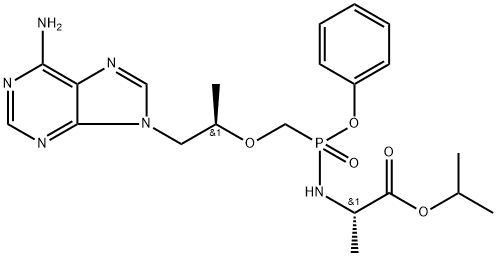
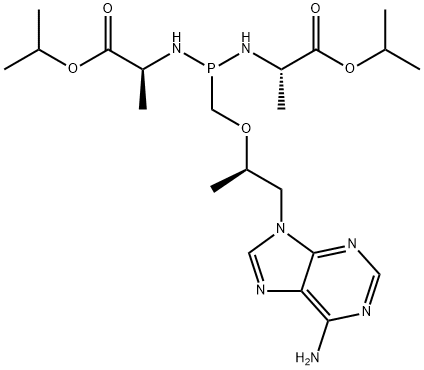
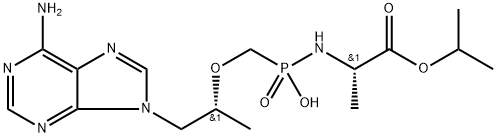
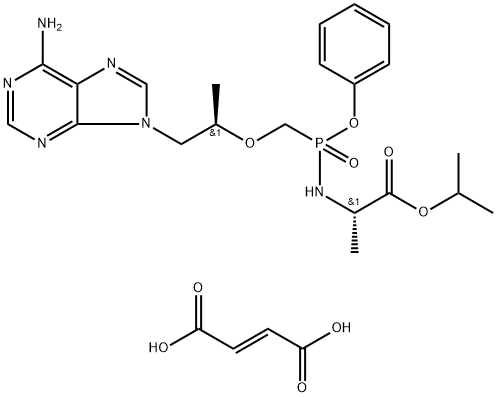
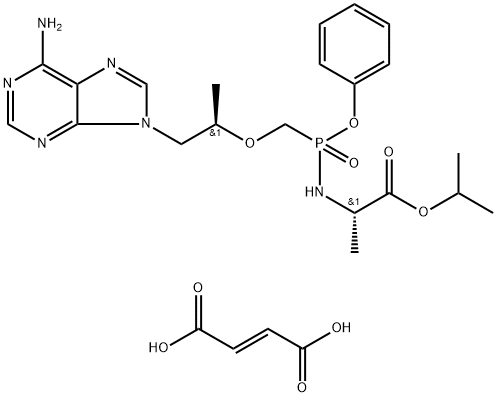
![[[(1R)-2-(6-aMino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-Methylethoxy]Methyl]-, Monophenylester](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20200611/GIF/379270-35-6.gif)
You may like
-
 379270-37-8 99%View Details
379270-37-8 99%View Details
379270-37-8 -
 Tenofovir alafenamide 99%View Details
Tenofovir alafenamide 99%View Details
379270-37-8 -
 Tenofovir alafenamide 379270-37-8 98%View Details
Tenofovir alafenamide 379270-37-8 98%View Details
379270-37-8 -
 379270-37-8 Tenofovir alafenamide 98%View Details
379270-37-8 Tenofovir alafenamide 98%View Details
379270-37-8 -
 379270-37-8 Tenofovir alafenamide 98%View Details
379270-37-8 Tenofovir alafenamide 98%View Details
379270-37-8 -
 Tenofovir Alafenamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 379270-37-8View Details
Tenofovir Alafenamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 379270-37-8View Details
379270-37-8 -
 Tenofovir alafenamide CAS 379270-37-8View Details
Tenofovir alafenamide CAS 379270-37-8View Details
379270-37-8 -
 Tenofovir AlafenamideView Details
Tenofovir AlafenamideView Details
379270-37-8
