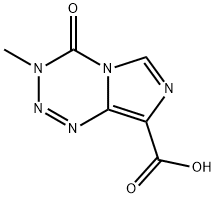
Temozolomide
Synonym(s):Temozolomide;3,4-Dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide;3-Methyl-4-oxo-8-imidazolo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazinecarboxamide;4-Methyl-5-oxo-2,3,4,6,8-pentazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-2,7,9-triene-9-carboxamide;8-Carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3H)-one
- CAS NO.:85622-93-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H6N6O2
- Molecular Weight: 194.15
- MDL number: MFCD00866492
- EINECS: 630-358-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-03 16:17:04

What is Temozolomide?
Absorption
Temozolomide is rapidly and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and is stable at both acidic and neutral pH. Therefore, temozolomide may be administered both orally and intravenously with a median Tmax of one hour. Following a single oral dose of 150 mg/m2, temozolomide and its active MTIC metabolite had Cmax values of 7.5 μg/mL and 282 ng/mL and AUC values of 23.4 μg*hr/mL and 864 ng*hr/mL, respectively. Similarly, following a single 90-minute IV infusion of 150 mg/m2, temozolide and its active MTIC metabolite had Cmax values of 7.3 μg/mL and 276 ng/mL and AUC values of 24.6 μg*hr/mL and 891 ng*hr/mL, respectively. Temozolomide kinetics are linear over the range of 75-250 mg/m2/day. The median Tmax is 1 hour
Oral temozolomide absorption is affected by food. Administration following a high-fat breakfast of 587 calories caused the mean Cmax and AUC to decrease by 32% and 9%, respectively, and the median Tmax to increase by 2-fold (from 1-2.25 hours).
Toxicity
The primary dose-limiting toxicity of temozolomide is myelosuppression, which can occur with any dose but is more severe at higher doses. Patients taking high doses experienced adverse reactions, including severe and prolonged myelosuppression, infections, and death. One patient who took 2000 mg/day for five days experienced pancytopenia, pyrexia, and multi-organ failure, which resulted in death. Patients experiencing an overdose should have complete blood counts monitored and provided with supportive care as necessary.
Description
Temozolomide was launched for the first time in the UK for the
treatment of patients with glioblastoma multiforme showing recurrence or
progression after standard therapy. It can be considered as a cyclic variant of
highly reactive triazenes producing a cascade of ionic or radical antitumoral
species. Temozolamide is a 3-methyl analog of mitozolomide and was shown to
be converted to cytotoxic triazene MCTIC. It can be prepared in 2 steps from 5-
aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide by diazotization then cyclization with
methylisocyanate. Mechanistically, the depletion of O6-alkylguanine-DNA
alkyltransferase (OGAT) in cells or tumors was shown to be correlated with the
cytotoxicity of temozolomide which is a potent inhibitor of this enzyme involved
in DNA repair activity.
Further approval applications for the treatment of other malignant gliomas such
as relapsed anaplastic astrocytoma, advanced metastatic melanoma were
submitted.
Description
Temozolomide (TMZ) is a chemotherapy drug often used to treat glioblastoma, the most aggressive form of cancer that begins in the brain. This cancer is extremely difficult to treat because it usually recurs even after extensive surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
TMZ was developed at Aston University (Birmingham, UK) more than 20 years ago. In 1999, the US Food and Drug Administration granted approval to Merck to market it under the trade name Temodar for treating glioblastoma and refractory anaplastic astrocytoma. It is available in capsule and injectable forms.
TMZ’s mode of action is alkylation, which causes serious side effects such as reduction in blood cells, weakening of the immune system, and secondary cancers. Only a small portion of administered TMZ enters the brain, making most of it free to cause problems in other parts of the body.
Now, Paul J. Hergenrother and colleagues at the University of Illinois (Urbana–Champaign) report that a modification to TMZ’s structure makes it easier for the drug to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. When the team replaced the molecule’s amide group with a methyl ketone group, the percentage of the drug that entered the central nervous system in mice increased from 8% to 69%.
In a mouse model of glioblastoma, treatment with the modified drug (K-TMZ) increased survival indefinitely. The researchers’ next step is to test K-TMZ on larger glioblastoma-affected animals.
Chemical properties
Off-white to light-pink crystalline solid, crystallized from dichloromethane, melting point 212℃ (decomposition). Maximum UV absorption (in 95% ethanol): 327nm.
Originator
CRC Technology (UK)
The Uses of Temozolomide
Temozolomide has been used for analyzing drug resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma cell lines15,16.
The Uses of Temozolomide
Temozolomide is an antineoplastic drug and an Imidazotetrazine alkylating agent. It induces apoptosis and causes cell cycle arrest at the G2/M checkpoint. It rapidly degrades in the body, producing the active metabolite MTIC, which exerts an anti-tumor effect. Moreover, temozolomide has shown effectiveness against paclitaxel-resistant tumors and has been utilized in the study of drug resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma cell lines.
Indications
Temozolomide is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma concomitantly with radiotherapy and for use as maintenance treatment thereafter. It is also indicated for the treatment of refractory anaplastic astrocytoma in adult patients or adjuvant therapy for adults with newly diagnosed anaplastic astrocytoma.
Background
Refractory anaplastic astrocytoma (WHO grade III) and Glioblastoma multiforme (WHO grade IV) are primary malignant brain tumours with poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Despite considerable genetic heterogeneity, these tumours often have impaired DNA repair systems, rendering them initially sensitive to alkylating agents, although they invariably develop resistance to these agents over time. Temozolomide is an imidazotetrazine prodrug that is stable at acidic pH but undergoes spontaneous nonenzymatic hydrolysis at neutral or slightly basic pH; these properties allow for both oral and intravenous administration. Following initial hydrolysis, further reactions liberate a highly reactive methyl diazonium cation capable of methylating various residues on adenosine and guanine bases leading to DNA lesions and eventual apoptosis. Temozomolide as an adjunct to radiotherapy followed by maintenance dosing remains the standard of care for both Glioblastoma and refractory anaplastic astrocytoma.
Temozolomide was granted FDA approval on August 11, 1999, as an oral capsule and subsequently on February 27, 2009, as an intravenous injection. It is currently marketed under the trademark TEMODAR? by Merck.
What are the applications of Application
Temozolomide is an apoptosis inducer which causes arrest at the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint
Definition
ChEBI: An imidazotetrazine that is 3,4-dihydroimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine which is substituted at positions 3, 4, and 8 by methyl, oxo, and carboxamide groups, respectively. A prodrug for MTIC (5-(3-methyltriaz-1-en-1-yl)-1H-i idazole-4-carboxamide, formed by spontaneous hydrolysis of temozolomide in the body), it is used as an oral alkylating agent for the treatment of newly diagnosed malignant glioblastoma multiforme (concomitantly with radiotherapy) and malignant melanoma.
Preparation
The synthesis of temozolomide involves several steps. First, 5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide is diazotized using nitrite. Then, the diazotized compound is reacted with methyl isocyanate in dichloromethane. This reaction leads to the cyclization of the compound, ultimately resulting in the formation of temozolomide.
Manufacturing Process
Reaction of 1H-imidazole-4-carboxilic acid amide with nitrous acid leads to the diazonium salt (5-diazenyl-1-H-imidazole-4-carboxilic acid amide). Condensation of the diazonium salt with methylisocyanate leads to initial formation of unstable urea which cyclizes under the reaction condition to give 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo(5,1-d)-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide (temozolomide).
brand name
Temodar (Schering);Temodal.
Therapeutic Function
Antineoplastic
General Description
Temozolomide can be called as an oral alkylating agent and antitumour drug, which may show potent activity in the treatment of recurrent gliomas or glioblastoma, a kind of tumour that affects the brain or spine.
Biological Activity
DNA methylating, chemotherapeutic agent. Displays antitumor activity against a board spectrum of tumors, including leukemias, lymphomas and solid tumors (IC 50 = 5.0 μ M for cytotoxicity against mouse TLX5 lymphoma cells).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Temozolomide is a DNA methylating agent and drug resistance-modifying agent; anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic. Temozolomide induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis through adduction of a methyl group to O6 position of guanine in genomic DNA and functional inactivation of DNA repair protein O(6)-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferase (AGT) in base excision repair (BER) pathway.
Pharmacokinetics
Temozolomide is a prodrug of the imidazotetrazine class that requires nonenzymatic hydrolysis at physiological pH in vivo to perform alkylation of adenine/guanine residues, leading to DNA damage through futile repair cycles and eventual cell death. Temozolomide treatment is associated with myelosuppression, which is likely to be more severe in females and geriatric patients. Patients must have an ANC of ≥1.5 x 109/L and a platelet count of ≥100 x 109/L before starting therapy and must be monitored weekly during the concomitant radiotherapy phase, on days one and 22 of maintenance cycles, and weekly at any point where the ANC/platelet count falls below the specified values until recovery. Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies, including myeloid leukemia, have been observed following temozolomide administration. Pneumocystis pneumonia may occur in patients undergoing treatment, and prophylaxis should be provided for patients in the concomitant phase of therapy with monitoring at all stages. Severe hepatotoxicity has also been reported, and liver testing should be performed at baseline, midway through the first cycle, before each subsequent cycle, and approximately two to four weeks after the last dose. Animal studies suggest that temozolomide has significant embryo-fetal toxicity; male and female patients should practice contraception up to three and six months following the last dose of temozolomide, respectively.
Clinical Use
This imidazolotetrazine derivative is administered orally in capsule form for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme or in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma who have not responded to procarbazine or the nitrosoureas.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine, increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Metabolism
After absorption, temozolomide undergoes nonenzymatic chemical conversion to the active metabolite 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl) imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC) plus carbon dioxide and to a temozolomide acid metabolite, which occurs at physiological pH but is enhanced with increasing alkalinity. MTIC subsequently reacts with water to produce 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC) and a highly reactive methyl diazonium cation, the active alkylating species. The cytochrome P450 system plays only a minor role in temozolomide metabolism. Relative to the AUC of temozolomide, the exposure to MTIC and AIC is 2.4% and 23%, respectively.
Metabolism
Oral absorption is rapid and complete. The CYP450 enzymes are not extensively involved in temozolomide metabolism, and less than 6% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. Women clear the drug less effectively than men and have a higher incidence of severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in the initial therapy cycle. Food decreases temozolomide absorption, and myelosuppression is the most significant adverse effect.
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Kurzen et al. (2003), Inhibition of angiogenesis by non-toxic doses of temozolomide; Anticancer Drugs, 14 515
2) Gunther et al. (2003), Temozolomide induces apoptosis and senescence in glioma cells cultured as multicellular spheroids; Br. J. Cancer, 88 463
3) Danson et al. (2001), Temozolomide: a novel oral alkylating agent; Curr. Opin. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther., 10 13
4) Natsumeda et al. (2011), Induction of autophagy in temozolomide treated malignant gliomas; Neuropathology, 31 486
Properties of Temozolomide
| Melting point: | 212°C dec. |
| Boiling point: | 526.6±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.97±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble10mg/mL, clear |
| appearance | white to light tan or light pink powder |
| form | powder |
| pka | 14.77±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | white to light brown |
| Merck | 14,9139 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 85622-93-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Temozolomide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Temozolomide
| InChIKey | BPEGJWRSRHCHSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Temozolomide manufacturer
Shilpa Medicare Limited (SML)
Vannsh Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Basil Drugs AND Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
ALS INDIA LIFE SCIENCES
Besil Chem LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Temozolomide 99%View Details
Temozolomide 99%View Details -
 Temozolomide 85622-93-1 98%View Details
Temozolomide 85622-93-1 98%View Details
85622-93-1 -
 Temozolomide, ≥98% CAS 85622-93-1View Details
Temozolomide, ≥98% CAS 85622-93-1View Details
85622-93-1 -
 Temozolomide CAS 85622-93-1View Details
Temozolomide CAS 85622-93-1View Details
85622-93-1 -
 Temozolomide 99%View Details
Temozolomide 99%View Details
85622-93-1 -
 85622-93-1 98%View Details
85622-93-1 98%View Details
85622-93-1 -
 Temozolomide 98% CAS 85622-93-1View Details
Temozolomide 98% CAS 85622-93-1View Details
85622-93-1 -
 Temozolomide CAS 85622-93-1View Details
Temozolomide CAS 85622-93-1View Details
85622-93-1