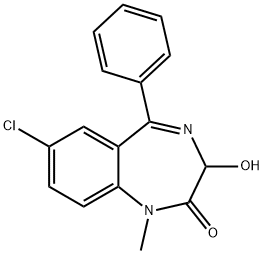
TEMAZEPAM
- CAS NO.:846-50-4
- Empirical Formula: C16H13ClN2O2
- Molecular Weight: 300.74
- MDL number: MFCD00057904
- EINECS: 212-688-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
What is TEMAZEPAM?
Absorption
Studies demonstrate that between 90 to 100% of an orally administered temazepam dose is absorbed, making the medication very well absorbed . The oral administration of 15 to 45 mg temazepam resulted in rapid absorption with significant blood levels achieved in 30 minutes and peak levels at 2-3 hours . In particular, direct studies following the oral ingestion of 30 mg of temazepam revealed measurable plasma concentrations were obtained 10-20 minutes after dosing with peak plasma levels ranging between 666-982 ng/mL (with a mean of 865 ng/mL) presenting approximately 1.2-1.6 hours (with a mean of 1.5 hours) after the dosing . Finally, a dose-proportional relationship was established for the area under the plasma concentration/time curve over the 15 to 30 mg dose range .
Toxicity
Manifestations of acute overdosage of temazepam, as with other benzodiazepines, can be expected to reflect the increasing CNS effects of the drug and include somnolence, confusion, and coma, with reduced or absent reflexes . With large overdoses, respiratory depression, hypotension, and finally coma can occur .
Benzodiazepines like temazepam might cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Transplacental distribution has in the past resulted in neonatal CNS depression following the ingestion of therapeutic doses of related benzodiazepine hypnotics like diazepam during the last weeks of pregnancy .
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk . Caution should, therefore, be exercised when temazepam is administered to a nursing woman .
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established .
Lower doses of temazepam, like 7.5 mg is recommended as the initial dosage for patients aged 65 and over since the risk of the development of oversedation, dizziness, confusion, ataxia and/or falls increases substantially with larger doses of benzodiazepines in elderly and debilitated patients .
No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in animal studies although hyperplastic liver nodules were observed in female mice exposed to the highest doses of temazepam . The clinical significance of this finding is not known .
Fertility in male and female rats was not adversely affected by temazepam toxicity studies .
No mutagenicity tests have been done with temazepam .
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Levanxol,Carlo Erba,Italy,1970
The Uses of TEMAZEPAM
Temazepam, is pharmacologically active metabolite of Diazepam (D416855). It is Sedative, and hypnotic. Controlled substance (depressant).
The Uses of TEMAZEPAM
Pharmacologically active metabolite of Diazepam. Controlled substance (depressant). Sedative, hypnotic
The Uses of TEMAZEPAM
Pharmacologically active labelled metabolite of Diazepam. Controlled substance (depressant). Sedative, hypnotic
Background
Temazepam, like many other similar and related benzodiazepines, acts as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) modulator and is capable of eliciting a variety of actions including sedation, hypnosis, skeletal muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, and anxiolytic action .
Although the chemical synthesis of temazepam was established by 1965 , mainstream contemporary use of the medication did not occur until it's legitimate use as treatment for insomnia was accepted and approved later on. In particular, before temazepam saw regular prescription use in civilians it was - and still is - employed by the US military as a sedative-hypnotic medication to be taken by soldiers, pilots, etc. to obtain the necessary rest required for medical recovery or scheduled maneuvers and operations . Regardless, temazepam has become one of the most frequently prescribed medications internationally and sees millions of prescriptions every year. Unfortunately, however, given its frequent use and the inherent nature of its pharmacological effects, temazepam - like many other benzodiazepines - possesses a high potential for misuse and is genuinely capable of developing drug tolerance, physical dependence, and addiction in users.
Indications
Temazepam is specifically indicated only for the short-term management of insomnia , . Furthermore, such management is generally predominantly associated with the symptomatic relief of transient and short-term insomnia characterized by difficulty in falling asleep, frequent nocturnal awakenings and/or early morning awakenings . In particular, the official prescribing information for temazepam typically specifies that the instructions issued for dispensed prescriptions of the medication should indicate specifically that patients are only expected to use the therapy for short periods of time - usually 7-10 days in general . Subsequently, treatment with temazepam should usually not exceed 7 to 10 consecutive days and nor should it be prescribed in quantities exceeding a one-month supply .
Some regional prescribing information also notes that temazepam may be used for premedication prior to minor surgery or other related procedures .
Definition
ChEBI: Temazepam is a benzodiazepine.
Manufacturing Process
According to British Patent 1,022,645 3.4 g of 3-acetoxy-7-chloro-1-methyl-5- phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one suspended in 80 ml alcohol was treated with 6 ml of 4 N NaOH. After complete solution had taken place, a solid precipitated; this solid was redissolved by the addition of 80 ml of water. The solution was acidified with acetic acid to give white crystals which were recrystallized from alcohol to yield 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1- methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, MP 119° to 121°C.
brand name
Restoril (Tyco); Temaz (Quantum Pharmics).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
World Health Organization (WHO)
Temazepam is a widely used benzodiazepine derivative. As with other drugs in this class, cases of misuse and drug dependence are known.
General Description
Temazepam, 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl -2H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-one(Restoril), also occurs as a minor metabolite of diazepam.It can be visualized as N-methyl oxazepam, and indeed, asmall amount of N-demethylation occurs slowly. However,metabolism proceeds mainly through glucuronidationof the 3-hydroxyl group, thus, it is intermediate acting andmarketed as a hypnotic said to have little or no residualeffect.
Pharmacokinetics
Temazepam is a benzodiazepine used as a hypnotic agent in the management of insomnia . Temazepam produces CNS depression at limbic, thalamic, and hypothalamic levels of the CNS . Temazepam increases the affinity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) for GABA receptors by binding to benzodiazepine receptors . Results are sedation, hypnosis, skeletal muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, and anxiolytic action .
In sleep laboratory studies, the effect of temazepam was compared to placebo during a two week period . The studies demonstrated a linear dose-response improvement in total sleep time and sleep latency with substantial drug-placebo differences apparent for total sleep time and for sleep latency at higher doses of temazepam . Regardless, REM sleep was ultimately unchanged but slow wave sleep was decreased .
Moreover, a transient syndrome, known as "rebound insomnia", wherein the symptoms that led to treatment with temazepam in the first place recur in an enhanced form, may happen on withdrawal of temazepam treatment . The possibility of this occurrence is in part why long term use of temazepam is not recommended due to worries over tolerance and dependence wherein patients' bodies become physiologically accustomed to the regular presence and pharmacological effect of higher and higher doses of the benzodiazepine used .
The duration of hypnotic effect and the profile of unwanted adverse effects may be influenced by the distribution and elimination half-lives of the administered temazepam and any active metabolites that may be formed . When such half-lives are long, the drug or its metabolite(s) may accumulate during periods of nightly administration and be associated with impairments of cognitive and motor performance during waking hours . Conversely, if half-lives are short, the drug and metabolites would be cleared before the next dose is ingested, and carry-over effects related to sedation or CNS depression should be minimal or not present at all . However, during nightly use and for an extended period, pharmacodynamic tolerance or adaptation to some effects of benzodiazepine hypnotics may develop - which may also contribute to the possibility of 'rebound insomnia' .
Consequently, if the drug has a very short elimination half-life, it is possible that a relative deficiency (for example, in relation to benzodiazepine GABA(a) receptor sites) may occur at some point in the interval between each night's use . This sequence of events may account for certain clinical findings reported happening after several weeks of nightly use of rapidly eliminated benzodiazepine hypnotics, including increased wakefulness during the last third of the night and the appearance of increased daytime anxiety .
Clinical Use
Benzodiazepine:
Insomnia (short-term use)
Pre-med anxiolytic prior to minor procedures
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: metabolism possibly increased by
rifampicin.
Antipsychotics: increased sedative effects; risk of
serious adverse effects in combination with clozapine.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Disulfiram: metabolism of temazepam inhibited
(increased toxicity).
Sodium oxybate: enhanced effects of sodium oxybate
- avoid.
Metabolism
First-pass metabolism of temazepam is minimal at approximately 5-8% of an administered dose . Nevertheless, temazepam is principally metabolized in the liver where most of the unchanged drug is directly conjugated to glucuronide and excreted in the urine . In particular, the primary metabolite present in the blood is the O-conjugate of temazepam . Less than 5% of the drug is demethylated to oxazepam and subsequently eliminated as the glucuronide . Regardless, the glucuronides of temazepam have no demonstrable CNS activity and it is believed that no active metabolites are formed in general . Since temazepam mainly undergoes Phase II conjugation reactions, it is proposed that it is devoid of CYP450 interactions.
Metabolism
Temazepam is metabolised mainly in the liver. It is excreted mainly in the urine in the form of its inactive glucuronide conjugate together with small amounts of the demethylated derivative, oxazepam, also in conjugated form.
Properties of TEMAZEPAM
| Melting point: | 119-121°C |
| Boiling point: | 211°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2682 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| pka | pKa 1.6 (Uncertain) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 846-50-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 66) 1996 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Temazepam (846-50-4) |
Safety information for TEMAZEPAM
Computed Descriptors for TEMAZEPAM
TEMAZEPAM manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
