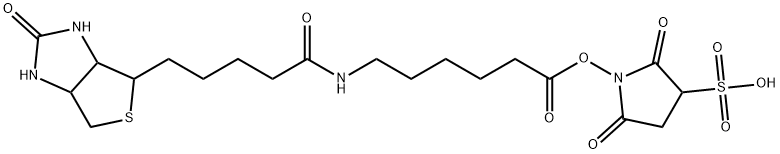
Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
Synonym(s):(+)-Biotinamidocaproate N-hydroxysuccinimidyl ester;Biotin-X-NHS, Water-Soluble;N-(+)-Biotinyl-6-aminocaproic acid N-succinimidyl ester;N-(+)-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid NHS ester;N-Succinimidyl N-biotinyl-6-aminocaproate
- CAS NO.:72040-63-2
- Empirical Formula: C20H30N4O6S
- Molecular Weight: 454.54
- MDL number: MFCD00065502
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
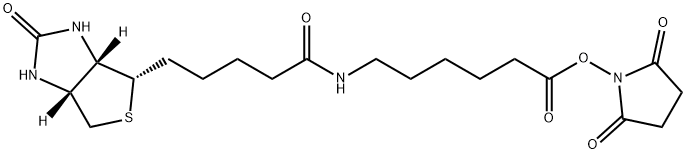
What is Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate?
Description
Biotin-LC-NHS Ester has an extended spacer arm which helps to minimize steric hindrance. The membrane permeability of this reagent allows it to be used for intracellular labeling. It can react efficiently with primary amino (-NH2) to form stable, irreversible amide bonds.
Chemical properties
Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate is White Solid
The Uses of Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate is a biotinylation reagent incorporating an aminocaproyl “spacer”. This can reduce the steric hindrance in binding avidin to some biotinylated compounds when used to biotinylate both the antibody and the carrier in the Protein Avidin-Biotin Capture System. This system avoids the direct interaction of a captured antibody with solid surfaces, such as plastics, which may reduce antigenicity. It has also been used to enhance the detection of DNA on nitrocellulose. Has also been used as a cell surface labelling reagent
The Uses of Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
Has been used to biotinylate both the antibody and the carrier in the Protein Avidin-Biotin solid surfaces, such as plastics, which may reduce antigenicity. It has also been used to enhance the detection of DNA on nitrocellulose. Spacer Arm:
The Uses of Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
A biotinylation reagent incorporating an aminocaproyl pacer? This can reduce the steric hindrance in binding avidin to some biotinylated compounds when used to biotinylate both the antibody and the carrier in the Protein Avidin-Biotin Capture Sy
What are the applications of Application
Succinimidyl-6-(biotinamido) Hexanoate is a biotinylation reagent
Biological Activity
nhs-lc-biotin (succinimidyl-6-(biotinamindo)hexanoate), also known as nhs-x-biotin is a derivative of d-biotin, a amine-reactive biotinylation agent, that contains a spacer arm off the valeric acid side chain of d-biotin with an nhs ester group at its end. the nhs ester group at the end of nhs-lc-biotin covalently binds to amine groups in proteins and other molecules forming a stable amide linkage and releasing the nhs group. the 6-aminocaproic acid spacer of nhs-lc-biotin greatly increases the length between a covalently modified molecule and the bicyclic biotin rings leading to a better binding potential for avidin or streptavidin probes. nhs-lc-biotin is insoluble in aqueous environments requiring the dissolution of organic solvents prior to the addition to a buffered reaction.bioconjugate techniques , 2nd ed. by greg t.hermanson (pierce biotechnology, thermo fisher scientific, rockford, il). academic press (an imprint of elsevier): london, amsterdam, burlington, san diego . 2008. isbn 978-0-12-370501-3.
storage
Store at -20°C
Purification Methods
Dissolve ~400mg of the ester in dry propan-2-ol (~25mL) with gentle heating. Reduce the volume to ~10mL by gentle boiling and allow the solution to cool. Decant the supernatant carefully from the white crystals, dry the crystals in a vacuum over P2O5 at 60o overnight. This material gives one spot on TLC. [Costello et al. Clin Chem 25 1572 1979, Kincaid et al. Methods Enzymol 159 619 1988.]
Properties of Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
| Melting point: | 169-171 °C |
| Density | 1.35±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: ≤2 mg/mL with sonication |
| form | powder |
| pka | 13.90±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| BRN | 3577403 |
| Stability: | Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72040-63-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate
| InChIKey | UVGHPGOONBRLCX-NJSLBKSFSA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate 95% CAS 72040-63-2View Details
Succinimidyl 6-(biotinamido)hexanoate 95% CAS 72040-63-2View Details
72040-63-2 -
 N-Succinimidyl 6-Biotinamidohexanoate CAS 72040-63-2View Details
N-Succinimidyl 6-Biotinamidohexanoate CAS 72040-63-2View Details
72040-63-2 -
 Biotin-X-NHS, Water-Soluble CASView Details
Biotin-X-NHS, Water-Soluble CASView Details -
 Biotinamidohexanoic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester CAS 72040-63-2View Details
Biotinamidohexanoic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester CAS 72040-63-2View Details
72040-63-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1