Stugeron
Synonym(s):1-trans-Cinnamyl-4-diphenylmethylpiperazine;Cinnarizine
- CAS NO.:298-57-7
- Empirical Formula: C26H28N2
- Molecular Weight: 368.51
- MDL number: MFCD00056037
- EINECS: 206-064-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
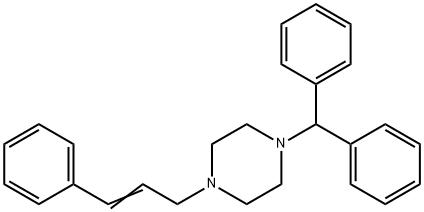
What is Stugeron?
Chemical properties
White or almost white powder.
Originator
Stugeron,Janssen,UK,1961
The Uses of Stugeron
Calcium channel blocker with antiallergic and anti-vasoconstricting activity. Antihistaminic
The Uses of Stugeron
glucocorticoid, antiinflammatory
The Uses of Stugeron
Histamine H1 receptor antagonist; antihistamine.
The Uses of Stugeron
For the treatment of vertigo/meniere's disease, nausea and vomiting, motion sickness and also useful for vestibular symptoms of other origins.
What are the applications of Application
Cinnarizine is a calcium channel protein inhibitor
Background
First synthesized by Janssen Pharmaceuticals in 1955, cinnarizine is an anti-histaminic drug mainly used for the control of vestibular disorders and motion sickness. Cinnarizine is a specific calcium channel blocker that primarily works on the central vestibular system to interfere with the signal transmission between vestibular apparatus of the inner ear and the vomiting centre of the hypothalamus. Cinnarizine could be also viewed as a nootropic drug because of its vasorelaxating abilities (due to calcium channel blockage), which happen mostly in brain. Combination use of cinnarizine with other nootropics, such as piracetam resulted in enhanced effect of boosting brain oxygen supply.
Indications
For the treatment of vertigo/meniere's disease, nausea and vomiting, motion sickness and also useful for vestibular symptoms of other origins.
Definition
ChEBI: Cinnarizine is a N-alkylpiperazine, a diarylmethane and an olefinic compound. It has a role as an antiemetic, a histamine antagonist, a calcium channel blocker, a muscarinic antagonist, an anti-allergic agent, a H1-receptor antagonist and a geroprotector.
Manufacturing Process
This compound can be prepared by the reaction of cinnamoyl chloride with
benzhydryl piperazine. The reaction is carried out in dry benzene under reflux.
The benzene is then evaporated, the residue taken up in chloroform, washed
with dilute HCl and then made alkaline.
The chloroform layer is washed with a dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide
solution, thereafter with water, and is finally dried over potassium carbonate.
The residue, which is obtained after evaporation of the chloroform, is
dissolved by heating in a mixture of 25% of toluene and 75% of heptane. On
cooling this solution to about 20°C the product precipitates. That compound is
reduced with LiAlH4, to give cinnarizine.
brand name
Rinomar.
Therapeutic Function
Antihistaminic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Cinnarizine, an antihistaminic and vasodilator agent, was introduced into medicine in 1962. It is indicated for the treatment of labyrinthine disturbances and vascular disorders, although its effectiveness in the latter indication has not been convincingly demonstrated.
General Description
Cinnarizine is a piperazine derivative, which is extracted from wood reed roots. It exhibits antihistaminic and calcium antagonist property. Cinnarizine is used to treat vertigo, unsteadiness and cognitive disorders. Cinnarizine has anticholinergic, antiserotonergic and antidopaminergic effects. It enhances cerebral blood flow. Cinnarizine blocks the contraction of smooth muscles cells and also acts as a skin whitening agent.
Biological Activity
cinnarizine is a calcium channel blocker.blockers of calcium channel are drugs disrupting the calcium movement via calcium channels, which are usually used as antihypertensive therapies to decrease blood pressure in hypertension patients.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cinnarizine is a piperazine and a specific anti-vertigo agent. It is used to treat and prevent vertigo and motion sickness. In addition, cinnarizine is also used as an anti-histamine agent. Chronic use of this drug leads to side effects such as extrapyramidal reactions (Parkinson, tremor and akathisia) and depression.
Mechanism of action
In addition to its antihistaminic activity, cinnarizine possesses Ca2+ channel blocking activity. Its vasodilator effect probably results from blocking the Ca2+ channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells.
Pharmacokinetics
Cinnarizine is an antihistamine and a calcium channel blocker. Histamines mediate a number of activities such as contraction of smooth muscle of the airways and gastrointestinal tract, vasodilatation, cardiac stimulation, secretion of gastric acid, promotion of interleukin release and chemotaxis of eosinophils and mast cells. Competitive antagonists at histamine H1 receptors may be divided into first (sedating) and second (non-sedating) generation agents. Some, such as Cinnarizine also block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and are used as anti-emetic agents. Cinnarizine through its calcium channel blocking ability also inhibits stimulation of the vestibular system.
Clinical Use
Vestibular disorders
Motion sickness
Synthesis
Cinnarinzine is prepared by alkylation of 1-diphenylmethyl piperazine with 3-phenyl-2-propenyl chloride .
in vitro
previous study found that cinnarizine could inhibit the phosphorylation of both arterial myosin p-light chain and arterial actomyosin superprecipitation. moreover, the concomitant inhibition of arterial superprecipitation and phosphorylation by perhexiline and cinnarizine was found to be similar to that of w-7. such inhibitary effect was then characterized by a rightward shift in the pca superprecipitation, depressed maximum activity as well as attenuation by exogenous calmodulin [1].
in vivo
previous animal study showed that augmented effects were obtained in mes seizure model when cinnarizine was combined with sodium valproate. whereas, in ptz-induced seizures, augmented effects were obtained when nifedipine was combined with sodium valproate [2].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: possibly increased sedative effects with
opioid analgesics.
Metabolism
Metabolism
Cinnarizine is extensively metabolised mainly via CYP2D6, but there is considerable inter-individual variation in the extent of metabolism. The elimination of metabolites occurs as follows: one third in the urine (unchanged as metabolites and glucuronide conjugates) and two thirds in the faeces.
References
[1] silver pj,dachiw j,ambrose jm,pinto pb. effects of the calcium antagonists perhexiline and cinnarizine on vascular and cardiac contractile protein function. j pharmacol exp ther.1985 sep;234(3):629-35.
[2] brahmane ri,wanmali vv,pathak ss,salwe kj. role of cinnarizine and nifedipine on anticonvulsant effect of sodium valproate and carbamazepine in maximal electroshock and pentylenetetrazole model of seizures in mice. j pharmacol pharmacother.2010 jul;1(2):78-81.
[3] hausler r,sabani e,rohr m. effect of cinnarizine on various types of vertigo. clinical and electronystagmographic results of a double-blind study. acta otorhinolaryngol belg.1989;43(2):177-85.
Properties of Stugeron
| Melting point: | 117-120°C |
| Boiling point: | 488.83°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1818 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7620 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in chloroform at 50mg/ml |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 7.47(H2O t=25.0 ) (Uncertain) |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 0.75g/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 14,2305 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 298-57-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cinnarizine(298-57-7) |
Safety information for Stugeron
Computed Descriptors for Stugeron
| InChIKey | DERZBLKQOCDDDZ-JLHYYAGUSA-N |
Stugeron manufacturer
PSN Medicare Private Limited
Fleming Laboratories Ltd
Rakshit Group of Companies (Rakshit Drugs Pvt Ltd)
Sibram Pharmaceutical
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
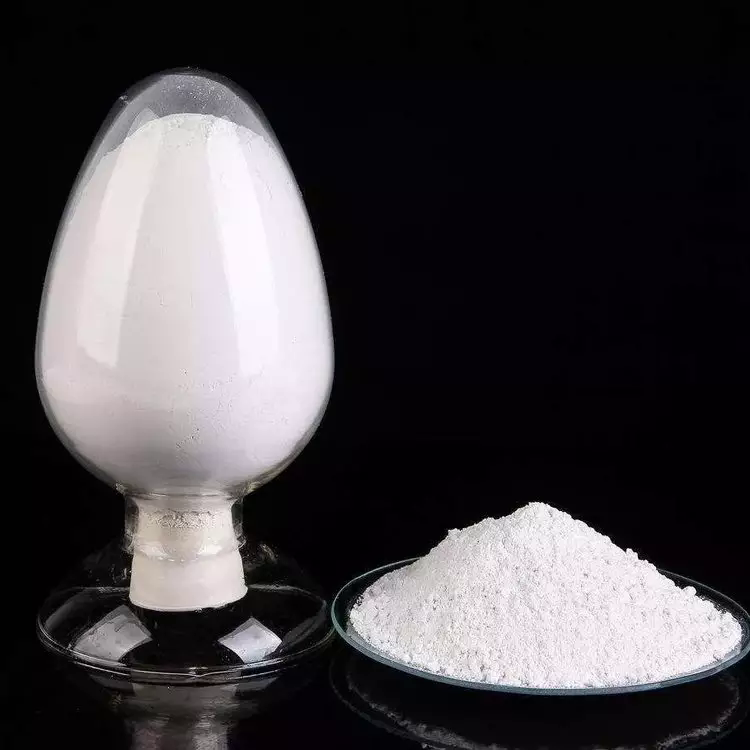 298-57-7 Cinnarizine 99%View Details
298-57-7 Cinnarizine 99%View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine 298-57-7 99%View Details
Cinnarizine 298-57-7 99%View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine 98% CAS 298-57-7View Details
Cinnarizine 98% CAS 298-57-7View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine 99%View Details
Cinnarizine 99%View Details -
 Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
298-57-7 -
 Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
Cinnarizine CAS 298-57-7View Details
298-57-7