STRONTIUM CHLORATE
- CAS NO.:7791-10-8
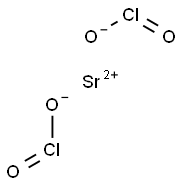
- Empirical Formula: Cl2O6Sr
- Molecular Weight: 254.52
- MDL number: MFCD00054051
- EINECS: 232-239-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
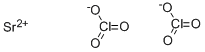
What is STRONTIUM CHLORATE?
Description
Strontium chlorate, Sr(ClO3)2, has a molecular weight of 254.52 g/mol. It is a white solid with a melting point of 120°C and a density of 3.152 g/cm3. It is soluble in water (174 g/100 ml at 20°C). Its CAS number is 7791-10-8. Sr(ClO3)2 is shock sensitive, and is highly flammable if allowed to sit in air. These white, water-soluble crystals decompose at 120°C. It is used in pyrotechnics and tracer bullets. There are two coexisting crystal hydrates that undergo interconversion, the dihydrate and the hexahydrate. These compounds are not as shock sensitive as the anhydrate.
Chemical properties
White, crystalline powder. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol.
Physical properties
Strontium chlorate is a strong oxidizing agent. It
forms a flammable mixture with combustible materials
(can be ignited by friction). Such mixtures may be explosive.
Contact with concentrated sulfuric acid can cause
fires or explosions. When mixed with ammonium salts,
spontaneous decomposition and ignition may result.
This compound liberates explosive chlorine dioxide
gas in the presence of strong acid; heating with a dibasic
organic acid in the presence of moisture liberates chlorine
dioxide and carbon dioxide. Mixtures with ammonium
salts, powdered metals, silicon, sulfur, or sulfides
are readily ignited and potentially explosive.
The Uses of STRONTIUM CHLORATE
In pyrotechnics to produce red fire.
Preparation
Strontium chlorate can be produced by the Liebig
method which consists of passing chlorine gas through
a solid such as Sr(OH)2:
6Sr(OH)2+ 6Cl2→5SrCl2+ Sr(CIO3)2+ H2O.
However, separating the two salts remains problematic
since both are soluble in water. Strontium chloride
solubility is 42.9 g/100 ml of water at 20°C while that
of strontium chlorate is 174.9 g/100 ml of water at 20°C.
General Description
A moist solid or semi-solid slurry of white crystals. May explode under exposure to heat or fire. Used in pyrotechnics.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
STRONTIUM CHLORATE is a strong oxidizing agent. Forms a flammable mixture with combustible materials (can be ignited by friction). Such mixtures may be explosive Contact with concentrated sulfuric acid can cause fires or explosions. When mixed with ammonium salts, spontaneous decomposition and ignition may result. Liberates explosive chlorine dioxide gas in the presence of strong acid; heating with a dibasic organic acid in the presence of moisture liberates chlorine dioxide and carbon dioxide [Bretherick 1979 p. 100]. Mixtures with ammonium salts, powdered metals, silicon, sulfur, or sulfides are readily ignited and potentially explosive [Bretherick 1979 p. 806].
Hazard
Dangerous explosion risk in contact with organic materials; highly sensitive to shock, heat, and friction; strong oxidizing agent.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Toxic fumes or dust may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars, etc.). Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
May explode from friction, heat or contamination. These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Safety Profile
A powerful oxidizer. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHLORATES.
Properties of STRONTIUM CHLORATE
| Melting point: | 120° with decomposition and evolution of O2 |
| Density | 3.15 |
| solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol |
| color | colorless crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | g/100g solution H2O: 61.40 (0°C), 63.78 (25°C), 67.08 (95°C); solid phase, Sr(ClO3)2 ·3H2O (0°C), Sr(ClO3)2 (25°C, 95°C) [KRU93]; slightly soluble alcohol [MER06] |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chloric acid, strontium salt (2:1) (7791-10-8) |
Safety information for STRONTIUM CHLORATE
Computed Descriptors for STRONTIUM CHLORATE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8