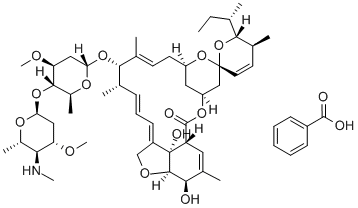
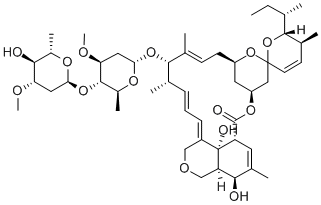
SPINOSAD
Synonym(s):Mixture of Spinosyn A and Spinosyn D
- CAS NO.:131929-60-7
- Empirical Formula: C41H65NO10
- Molecular Weight: 731.96
- MDL number: MFCD01753923
- EINECS: 620-162-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-23 17:25:30
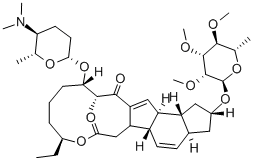
What is SPINOSAD?
Description
Spinosyn A, along with its almost identical isomer, spinosyn D, is a component of spinosad, a US Environmental Protection Agency–registered insecticide and Food and Drug Administration–registered topical treatment for head lice. The active ingredients are produced by the bacterium?Saccharopolyspora spinosa. An enzyme in genes extracted from in this bacterium is the?first natural product shown to catalyze the Diels–Alder reaction, a step in spinosyn biosynthesis.
The Uses of SPINOSAD
Spinosyn A is the major component of a complex of unusual, hydrophobic macrocyclic lactones isolated from Saccharopolyspora spinosa in 1991. The 12-membered macrocyclic lactone is fused to form a rare 12-5-6-5 tetracyclic ring system, with the macrocycle and the terminal cyclopentane bearing glycosides. Spinosyn A is a potent insecticide for crop pathogens and ectoparasite control on animals. The spinosyns have a unique mechanism of action involving disruption of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
What are the applications of Application
Spinosyn A is a potent insecticide for pathogens of crops and disruptor of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Definition
ChEBI: A spinosyn in which the sugar amino and hydroxy groups are globally methylated. One of the two active ingredients of spinosad.
Biological Activity
spinosyn a is an insect nicotinic acetylcholinesterase receptors (nachrs) agonist and potent insecticide.the spinosyns are a family of macrolide natural products produced by the soil microorganism saccharopolyspora spinosa. spinosyn a is identified as a naturally-occurring macrocyclic lactone that is a potent insecticide.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
For the prevention and treatment of fleas for one month on dogs 14 weeks of age and older.
Spinosad is a group 5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, that causes involuntary muscle contractions and tremors secondary
to motor neuron activation. Prolonged exposure causes paralysis and flea death. Flea death begins within 30 minutes of dosing and in 4
hours is complete. Spinosad does not interact with bindings sites of other insecticidal agents (GABA-ergic or nicotinic).
in vitro
the mixture of spinosyns a and d, a commercial insecticide tracertm (dowagrosciences), is useful against various crop pests such as tobacco budworm. it was found that the deoxy analogs of spinosyns a were more potent insecticides than their respective parent factor. moreover, the 2’-desmethoxy analogs of spinosyns a showed insecticidal potency against h. virescens greater than that of spinosyns a and d, suggesting that polarity was not well tolerated. furthermore, the activity of 3'-deoxy spinosyn j was about the same as spinosyn a, and the activity of 2'-deoxy spinosyn h was found to be slightly greater than that of spinosyn a [1].
Metabolic pathway
Spinosad consists of two major components, namely psinosyns A (ca 85%) and D (ca 15%). When either 14C-spinosyn A or -spinosyn D is applied in the soil under aerobic conditions, the major degradation product of spinosyn A is spinosyn B, resulting from demethylation on the forosamine sugar. Other degradation products are hydroxylation products of psinosyns A and B, probably on the aglycone portion of the molecule.
Degradation
Spinosad is relatively stable in water with no observed decomposition between pH 5 and 7. Measured DT50 values at pH 9 were 200 and 259 days, respectively, for spinosyns A and D (Saunders and Bret, 1997). Aqueous photolysis was very rapid with a DT50 of < 1 day in pH 7 buffered water at 25 °C (DowElanco, 1996). Spinosad was rapidly dissipated and degraded in an outdoor mesocosm study and on plant surfaces (Saunders and Bret, 1997).
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for rats: 2,000-5,000 mg/kg
References
[1] l. c. creemer, h. a. kirst, j. w. paschal, et al. synthesis and insecticidal activity of spinosyn analogs functionally altered at the 2'-,3'- and 4'-positions of the rhamnose moiety. j.antibiot.(tokyo) 53(2), 171-178 (2000).
Properties of SPINOSAD
| Boiling point: | 801.5±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.16±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | Spinosyn A: 3.2 x 10-8 Pa Spinosyn D: 2.1 x 10-8 Pa |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | solid |
| pka | Spinosyn A: 8.1 (base);
Spinosyn D: 7.8 (base) |
| Water Solubility | Spinosyn A: 290 mg l-1 (pH 5);
Spinosyn D: 29 mg l-1 (pH 5) |
| color | White to off-white |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Spinosyn A (131929-60-7) |
Safety information for SPINOSAD
Computed Descriptors for SPINOSAD
| InChIKey | SRJQTHAZUNRMPR-XOBNMGJWNA-N |
SPINOSAD manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Spinosad 45% SC, 1 L, BottleView Details
Spinosad 45% SC, 1 L, BottleView Details
131929-60-7 -
 Liquid Spinosad 45% SC (Hitter), 1000 mlView Details
Liquid Spinosad 45% SC (Hitter), 1000 mlView Details
131929-60-7 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
