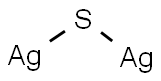
Silver fluoride
- CAS NO.:7775-41-9
- Empirical Formula: AgF
- Molecular Weight: 126.87
- MDL number: MFCD00003410
- EINECS: 231-895-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
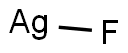
What is Silver fluoride?
Chemical properties
orange to brown solid
The Uses of Silver fluoride
- Silver fluoride is applied to convert organic Br and Cl Compounds to their fluoro analogs; as antiseptic.
- Preparation of bromoacetylenes from bulky, trialkylsilylacetylenes.
- Also used in a palladium-catalyzed cross coupling of acetanilides with trialkoxysilanes.
- Silver(I) fluoride is used as a fluorination and desilylation reagent in organic synthesis. In medical filed, it is used as topical caries in aqueous form in dentistry. It is employed in organofluorine chemistry for addition of fluoride across multiple bonds, especially to prepare perfluoroalkylsilver(I) by reacting with alkenes.
- Further, it is involved in the preparation of tetralkylammonium fluorides by the reaction with tetralkylammonium bromide. In addition to this, it is used as a desulfuration-fluorination reagent on thiourea derived substrates.
The Uses of Silver fluoride
The Uses of Silver fluoride
Silver(I) fluoride is used as a fluorination and desilylation reagent in organic synthesis. In medical filed, it is used as topical caries in aqueous form in dentistry. It is employed in organofluorine chemistry for addition of fluoride across multiple bonds, especially to prepare perfluoroalkylsilver(I) by reacting with alkenes. Further, it is involved in the preparation of tetralkylammonium fluorides by the reaction with tetralkylammonium bromide. In addition to this, it is used as a desulfuration-fluorination reagent on thiourea derived substrates.
Preparation
Silver(I) fluoride was prepared by reacting hydrogen fluoride with the carbonate and with the oxide.
Definition
ChEBI: Silver monofluoride is a silver salt and a fluoride salt.
General Description
Odorless yellow to gray solid. Sinks and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Boron reacts explosively when ground with Silver fluoride; silicon reacts violently [Bretherick 1979 p, 197]. Dimethyl sulfoxide is violently reactive with fluorinating agents such as Silver fluoride [Chem. Eng. News 44(24):7 1956]. When Silver fluoride is ground with calcium hydride the mass becomes incandescent [Mellor 3:389 1946-1947]. CaH2 reacts incandescently with AgF if subject to friction. (Mellor, 1941, Vol. 3, 389, 651).
Hazard
Strong irritant.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion may cause vomiting, salty taste, abdominal pain, diarrhea, convulsions, collapse, thirst, disturbed color vision, and acute toxic nephritis. Contact with eyes causes irritation. Skin may be blackened on prolonged exposure.
Purification Methods
The fluoride is a hygroscopic solid with a solubility of 135g/100mL of H2O at 15o, and forms an insoluble basic fluoride in moist air. Purify it by washing with AcOH and dry *C6H6, then keep it in a vacuum desiccator at room temperature to remove *C6H6, and store it in opaque glass bottles. The flaky hygroscopic crystals darken on exposure to light. It attacks bone and teeth. [Sharpe J Chem Soc 4538 1952, Kwasnik in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 240 1963.]
Properties of Silver fluoride
| Melting point: | ≥300 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1150 °C |
| Density | 5.852 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point: | 1150°C |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| color | orange to brown |
| Specific Gravity | 5.852 |
| Water Solubility | 182 g/100 mL (15.5 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8514 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3; TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 10 mg/m3; IDLH 250 mg/m3; TWA 0.01 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, reducing agents. Light sensitive. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7775-41-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silver monofluoride(7775-41-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silver fluoride (7775-41-9) |
Safety information for Silver fluoride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Silver fluoride
| InChIKey | REYHXKZHIMGNSE-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 Silver fluoride, GR 98%+ CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver fluoride, GR 98%+ CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 Silver(I) fluoride 99% CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver(I) fluoride 99% CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
Silver(I) fluoride CAS 7775-41-9View Details
7775-41-9 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1