Silver chloride
Synonym(s):AgCl (Silver monochloride);Chlorosilver;Silver chloride 99+;Silver(I) chloride
- CAS NO.:7783-90-6
- Empirical Formula: AgCl
- Molecular Weight: 143.32
- MDL number: MFCD00003399
- EINECS: 232-033-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:37
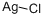
What is Silver chloride?
Chemical properties
Silver chloride, AgCl, is a white,granular powder that darkens on exposure to light,finally turning black.It exists in several modifications differing in behavior toward light and solubility in various solvents. Soluble in ammonium hydroxide, concentrated sulfuric acid, and sodium thiosulfate and potassium bromide solutions, very slightly soluble in water, can be melted, cast, and fabricated like a metal. Derived by heating a silver nitrate solution and adding hydrochloric acid or salt solution. The whole is boiled, then filtered. This must take place in the dark or under a ruby-red light. Used in photography,photometry and optics, batteries, photochromic glass,silver plating,production of pure silver, and as an antiseptic. Single crystals are used for infrared absorption cells and lens elements and as a lab reagent
The Uses of Silver chloride
Employed in Silver plating. Owing to its characteristic of reversible reduction to silver metal, it is used in photochromic lenses. Used as a cathode in sea water activated batteries. In electrochemistry, silver chloride electrode is used for potentiometric measurements. It serves as an antidote for mercury poisoning, and eliminates mercury from body. It is used in glass manufacturing industry. It is useful in the production of bandages, wound healing products and inglaze lustre, personal deodorant products, as well as for long term preservation of drinking water in water tanks; its pharmaceutical composition finds use as an antibacterial agent.
The Uses of Silver chloride
In silver plating, in making antiseptic silver preparations.
The Uses of Silver chloride
Found in nature as horn silver, this white powder is made by the combination of a soluble chloride and silver nitrate. Silver bromide could also be formed by exposing metallic silver to the fumes of bromine as in the daguerreotype process. It is soluble in sodium thiosulfate, potassium bromide solutions, and strong ammonia. This silver halide was the first to be observed to darken spontaneously by exposure to light. Silver chloride formed the basis of the photogenic drawing, salted paper print, albumen print, collodion-chloride POP, gelatin chloride POP, and gaslight paper.
The Uses of Silver chloride
Used in photographic films, to coat and silver glass, as an antiseptic, and to absorb infrared light in lenses.
Definition
T3DB: Silver chloride is a chloride of silver that occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite. It is used to make photographic paper and pottery glazes. It is also found in stained glass colorants, bandages, and other wound healing products, and may be used as an antidote to mercury poisoning. Silver is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It occurs naturally in its pure, free form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite.
What are the applications of Application
?AgCl is very important as a linear polarizer in the infrared region (λ: 2–23 mm). The refractive index is almost constant in the infrared region and the polarization angle is almost independent of wavelength. The polarization angles are 63°43' (3 mm), 63°20' (10 mm), and 63°33' (20 mm), showing the difference of angle below 18 for λ: 2–23 mm. The polariscope is fabricated typically by arranging the six sheets of plates with the thickness of 0.5 mm in the shape of roof type. Bakelite or plastic is good for the material of the holder case.
Hazard
As for silver.
Health effects
Silver itself is not toxic to humans, but most silver salts are. In large doses, silver and compounds containing it can be absorbed into the circulatory system and become deposited in various body tissues, leading to argyria, which results in a blue-grayish pigmentation of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Argyria is rare, and although, so far as known, this condition does not otherwise harm a person's health, it is disfiguring and usually permanent. Mild forms of argyria are sometimes mistaken for cyanosis. Exposure to high levels of silver in the air has resulted in breathing problems, lung and throat irritation, and stomach pains. Skin contact with silver can cause mild allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, and inflammation in some people.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Toxicology
Metallic silver is oxidized and may deposit in the tissues, causing arygria. The silver ion is known to inhibit glutathione peroxidase and NA+,K+-ATPase activity, disrupting selenium-catalyzed sulfhydryl oxidation-reduction reactions and intracellular ion concentrations, respectively. Silver nanoparticles are believed to disrupt the mitochondrial respiratory chain, causing oxidative stress, reduced ATP synthesis, and DNA damage.
Purification Methods
Recrystallise it from conc NH3 solution by acidifying with HCl, filtering off the solid, washing it with H2O and drying it in a vacuum. It is soluble in NH3 and should be kept in the dark.
Properties of Silver chloride
| Melting point: | 455 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1550 °C |
| Density | 5.56 |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 912 °C) |
| refractive index | 2.071 |
| Flash point: | 1550°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.00188g/l |
| form | beads |
| color | Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 5.56 |
| Water Solubility | 1.93 mg/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8509 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 9.75 |
| Dielectric constant | 11.2(0.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable, but discolours in light. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-90-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silver chloride(7783-90-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silver chloride (7783-90-6) |
Safety information for Silver chloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P390:Absorb spillage to prevent material damage. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Silver chloride
| InChIKey | HKZLPVFGJNLROG-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Silver chloride manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Silver Chloride 98%View Details
Silver Chloride 98%View Details -
 Silver chloride 99%View Details
Silver chloride 99%View Details -
 Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6 -
 Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6 -
 Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6 -
 Silver chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6 -
 Silver chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6 -
 Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
Silver chloride CAS 7783-90-6View Details
7783-90-6
