Ruthenium
Synonym(s):Ru/Al2O3;Ru/C;Ruthenium;Ruthenium black;Ruthenium element
- CAS NO.:7440-18-8
- Empirical Formula: Ru
- Molecular Weight: 101.07
- MDL number: MFCD00011207
- EINECS: 231-127-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30

What is Ruthenium?
Chemical properties
Ruthenium, a transition element, belongs to group VIII
(iron) of the periodic classification and to the light platinum
metals triad. It is a hard and brittle metal that resembles
platinum. It crystallizes in hexagonal form and occurs in the
form of seven stable isotopes: 96 (5.46%), 98 (1.87%), 99
(12.63%), 100 (12.53%), 101 (17.02%), 102 (31.6%), and
104 (18.87%). There are also several radioactive isotopes—93, 94, 95, 97, 103, 105, 106, 107, and 108—of which the
106 isotope characterized by strong β radiation and has a
half-life of 368 days; since it is produced in large quantities
in the nuclear reactors, it deserves special attention. Ruthenium
is the rarest of the platinum group elements (abundance
in the Earth’s crust ~0.0004 ppm). In chemical
compounds, it occurs at oxidation states from +2 to +8;
the most frequent is +3 in ruthenium compounds. Rutheniumis
resistant to acids and aqua regia, it is not oxidized in
the air at room temperature, and in the form of powder it
reacts with oxygen at elevated temperatures. It is dissolved
in molten strong alkalis and reacts with alkaline metal
peroxides and perchlorides. Ruthenium powder reacts
with chlorine above 200°C and with bromine at 300–
700°C.
Ruthenium compounds are usually dark brown (ranging
from yellow to black). Ruthenium forms alloys with platinum,
palladium, cobalt, nickel, and tungsten.
Chemical properties
Elemental ruthenium has a close-packed hexagonal crystal structure. The seven stable isotopes are 96Ru, 98Ru through 102Ru, and 104Ru.
Physical properties
Ruthenium is a rare, hard, silvery-white metallic element located in group 8, just aboveosmium and below iron, with which it shares some chemical and physical properties.Both ruthenium and osmium are heavier and harder than pure iron, making them morebrittle and difficult to refine. Both ruthenium and osmium are less tractable and malleable than iron. Although there are some similar characteristics between ruthenium and iron,ruthenium’s properties are more like those of osmium. Even so, ruthenium is less stablethan osmium. They are both rare and difficult to separate from minerals and ores that containother elements. These factors make it more difficult to determine ruthenium’s accurateatomic weight.
The oxidation state of +8 for ruthenium and its “mate” osmium is the highest oxidationstate of all elements in the transition series. Ruthenium’s melting point is 2,310°C, its boilingpoint is 3,900°C, and its density is 12.45 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 37 isotopes for ruthenium, ranging in atomic mass numbers from87 to 120. Seven of these are stable isotopes. The atomic masses and percentage ofcontribution to the natural occurrence of the element on Earth are as follows: Ru-96 =5.54%, Ru-98 = 1.87%, Ru-99 = 12.76%, Ru-100 = 12.60%, Ru-101 = 17.06%, Ru-102 = 31.55%, and Ru-104 = 18.62%.
Origin of Name
“Ruthenium” is derived from the Latin word Ruthenia meaning “Russia,” where it is found in the Ural Mountains.
Occurrence
Ruthenium is a rare element that makes up about 0.01 ppm in the Earth’s crust. Even so, itis considered the 74th most abundant element found on Earth. It is usually found in amountsup to 2% in platinum ores and is recovered when the ore is refined. It is difficult to separatefrom the leftover residue of refined platinum ore.
Ruthenium is found in South America and the Ural Mountains of Russia. There are someminor platinum and ruthenium ores found in the western United States and Canada. All ofthe radioactive isotopes of ruthenium are produced in nuclear reactors.
History
Berzelius and Osann in 1827 examined the residues left after dissolving crude platinum from the Ural mountains in aqua regia. While Berzelius found no unusual metals, Osann thought he found three new metals, one of which he named ruthenium. In 1844 Klaus, generally recognized as the discoverer, showed that Osann’s ruthenium oxide was very impure and that it contained a new metal. Klaus obtained 6 g of ruthenium from the portion of crude platinum that is insoluble in aqua regia. A member of the platinum group, ruthenium occurs native with other members of the group of ores found in the Ural mountains and in North and South America. It is also found along with other platinum metals in small but commercial quantities in pentlandite of the Sudbury, Ontario, nickel-mining region, and in pyroxinite deposits of South Africa. Natural ruthenium contains seven isotopes. Twenty-eight other isotopes and isomers are known, all of which are radioactive. The metal is isolated commercially by a complex chemical process, the final stage of which is the hydrogen reduction of ammonium ruthenium chloride, which yields a powder. The powder is consolidated by powder metallurgy techniques or by argon-arc welding. Ruthenium is a hard, white metal and has four crystal modifications. It does not tarnish at room temperatures, but oxidizes in air at about 800°C. The metal is not attacked by hot or cold acids or aqua regia, but when potassium chlorate is added to the solution, it oxidizes explosively. It is attacked by halogens, hydroxides, etc. Ruthenium can be plated by electrodeposition or by thermal decomposition methods. The metal is one of the most effective hardeners for platinum and palladium, and is alloyed with these metals to make electrical contacts for severe wear resistance. A ruthenium–molybdenum alloy is said to be superconductive at 10.6 K. The corrosion resistance of titanium is improved a hundredfold by addition of 0.1% ruthenium. It is a versatile catalyst. Hydrogen sulfide can be split catalytically by light using an aqueous suspension of CdS particles loaded with ruthenium dioxide. It is thought this may have application to removal of H2S in oil refining and other industrial processes. Compounds in at least eight oxidation states have been found, but of these, the +2. +3. and +4 states are the most common. Ruthenium tetroxide, like osmium tetroxide, is highly toxic. In addition, it may explode. Ruthenium compounds show a marked resemblance to those of osmium. The metal is priced at about $25/g (99.95% pure).
Characteristics
Ruthenium also belongs to the platinum group, which includes six elements with similarchemical characteristics. They are located in the middle of the second and third series of thetransition elements. The platinum group consists of ruthenium, rhodium,palladium, osmium, iridium, and platinum.
Ruthenium is a hard brittle metal that resists corrosion from all acids but is vulnerable tostrong alkalis (bases). Small amounts, when alloyed with other metals, will prevent corrosionof that metal.
The Uses of Ruthenium
Since ruthenium is rare and difficult to isolate in pure form, there are few uses for it. Itsmain uses are as an alloy to produce noncorrosive steel and as an additive to jewelry metalssuch as platinum, palladium, and gold, making them more durable.
It is also used as an alloy to make electrical contacts harder and wear longer, for medicalinstruments, and more recently, as an experimental metal for direct conversion of solar cellmaterial to electrical energy.
Ruthenium is used as a catalyst to affect the speed of chemical reactions, but is not alteredby the chemical process. It is also used as a drug to treat eye diseases.
The Uses of Ruthenium
As substitute for platinum in jewelry; for pen nibs; as hardener in electrical contact alloys, electrical filaments; in ceramic colors; catalyst in synthesis of long chain hydrocarbons.
The Uses of Ruthenium
Ruthenium is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and the production of thick-film resistors. Its use in some platinum alloys, and as a catalyst. It is a most effective hardeners for platinum and palladium. It is also used in some advanced high-temperature single-crystal super alloys, with applications including the turbine blades in jet engines and fountain pen nibs.
What are the applications of Application
Ruthenium, powder 20 Mesh is one of the most effective hardeners for platinum and palladium, and is alloyed with these metals to make electrical contacts for severe wear resistance. It is also a versatile catalyst, used to split hydrogen sulfide for example.
Definition
A transition metal that occurs naturally with platinum. It forms alloys with platinum that are used in electrical contacts. Ruthenium is also used in jewelry alloyed with palladium.Symbol: Ru; m.p. 2310°C; b.p. 3900°C; r.d. 12.37 (20°C); p.n. 44; r.a.m. 101.07.
Definition
ruthenium: Symbol Ru. A hardwhite metallic transition element;a.n. 44; r.a.m. 101.07; r.d. 12.3; m.p.2310°C; b.p. 3900°C. It is found associatedwith platinum and is used as acatalyst and in certain platinum alloys.Chemically, it dissolves in fusedalkalis but is not attacked by acids. Itreacts with oxygen and halogens at high temperatures. It also formscomplexes with a range of oxidationstates. The element was isolated byK. K. Klaus in 1844.
Production Methods
Elemental ruthenium occurs in native alloys of iridium and
osmium (irridosmine, siskerite) and in sulfide and other ores
(pentlandite, laurite, etc.) in very small quantities that are
commercially recovered.
The element is separated from the other platinum metals
by a sequence involving treatment with aqua regia (separation
of insoluble osmium, rhodium, ruthenium, and iridium),
fusion with sodium bisulfate (with which rhodium reacts),
and fusion with sodium peroxide (dissolution of osmium and
ruthenium). The resulting solution of ruthenate and osmate is
treated with ethanol to precipitate ruthenium dioxide. The
ruthenium dioxide is purified by treatment with hydrochloric
acid and chlorine and reduced with hydrogen gas to pure
metal.
Ruthenium is recovered from exhausted catalytic converters
or, in a similar manner, from the waste produced during
platinum and nickel ore processing.
General Description
This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency.
Hazard
The main hazard is the explosiveness of ruthenium fine power or dust. The metal willrapidly oxidize (explode) when exposed to oxidizer-type chemicals such as potassium chlorideat room temperature. Most of its few compounds are toxic and their fumes should beavoided.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmaceutical Applications
Ruthenium is the chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It occurs as a minor side product in the mining of platinum. Ruthenium is relatively inert to most chemicals. Its main applications are in the area of specialised electrical parts. The success of cisplatin, together with the occurrence of dose-limiting resistances and severe side effects such as nausea and nephrotoxicity, encouraged the research into other metal-based anticancer agents. Ruthenium is one of those metals under intense research, and first results look very promising, with two candidates – NAMI-A and KP1019 – having entered clinical trials.
Safety Profile
Most ruthenium compounds are poisons. Ruthenium is retained in the bones for a long time. Flammable in the form of dust when exposed to heat or flame. Violent reaction with ruthenium oxide. Explosive reaction with aqua rega + potassium chlorate. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of RuO, and Ru, which are hghly injurious to the eyes and lung and can produce nasal ulcerations. See also RUTHENIUM COMPOUNDS.
Properties of Ruthenium
| Melting point: | 2310 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 3900 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 12.45 g/cm3 (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in acid solutions, aqua regia |
| form | sponge |
| color | Grayish-white |
| Specific Gravity | 12.3 |
| Resistivity | 7.1 μΩ-cm, 0°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Sensitive | Lachrymatory |
| Merck | 14,8299 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: Ceiling 2 ppm OSHA: Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 50 ppm; Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) |
| Stability: | Stable. Powder is highly flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-18-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ruthenium(7440-18-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ruthenium (7440-18-8) |
Safety information for Ruthenium
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. |
Computed Descriptors for Ruthenium
Ruthenium manufacturer
Vineeth Precious Catalysts Pvt Ltd
Arora Matthey Limited
Vineeth Precious Catalysts Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

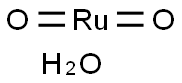
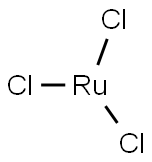
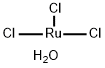

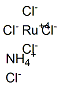
You may like
-
 Ruthenium 99%View Details
Ruthenium 99%View Details -
 Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details
Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details -
 Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details
Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details -
 Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details
Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details -
 Ruthenium standard for AAS CASView Details
Ruthenium standard for AAS CASView Details -
 Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details
Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details -
 Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details
Ruthenium on carbon CASView Details -
 Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details
Ruthenium on alumina CASView Details