PUROMYCIN
- CAS NO.:53-79-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H29N7O5
- Molecular Weight: 471.51
- MDL number: MFCD00866328
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 09:00:29
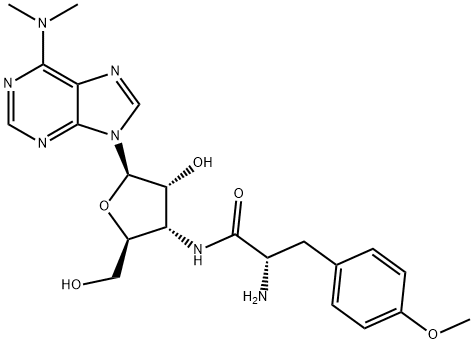
What is PUROMYCIN?
Description
Puromycin is an aminonucleoside antibiotic produced by
Streptomyces alboniger. It is a very common antibiotic routinely
used by scientists in biomedical research to select cells modified
by genetic engineering. It specifically inhibits peptidyl transfer
on both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. The antibiotic
inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and various
animal and insect cells. Fungi and Gram-negative bacteria are
resistant due to the low permeability of the antibiotic. For more
than 30 years, puromycin has been widely used as a basic tool
for studying protein synthesis. Now, puromycin hydrochloride
is particularly useful for the selection of cell types harboring
plasmids carrying puromycin resistance genes. Puromycinresistant
cells express pac gene, which encodes an N-acetyl
puromycin transferase. The pac gene can be mobilized on
a plasmid and used to transfect a host cell in an attempt to
provide resistance; therefore, puromycin can be used in gene
selections for mammalian host cells.
This aminonucleoside antibiotic causes premature chain
termination during translation in the ribosomes. Part of the
molecule resembles the 30 end of the aminoacylated tRNA. It
enters the A site and transfers to the growing chain, causing
premature chain release. The exact mechanism of action is
unknown, but the 30 position contains an amide linkage
instead of the normal ester linkage of tRNA; the amide bond
makes the molecule much more resistant to hydrolysis and
thus causes the ribosome to become stopped. It is not selective
for either prokaryotes or eukaryotes.
Also of note, puromycin is critical in mRNA display as it
allows the growing peptide chain to be covalently bonded to its
own mRNA template. Additionally, puromycin is a reversible
inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase II (serine peptidase) and
cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase (metallopeptidase). The mechanism
of inhibition is not well understood; however, puromycin
can be used to distinguish between aminopeptidase M
(active) and cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase (inhibited by
puromycin) and therefore extremely useful in biochemistry
and nephrology research.
Chemical properties
Crystals.
The Uses of PUROMYCIN
Puromycin is a nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces alboniger in the 1950s as an anti-trypansomal agent with antibiotic activity. Puromycin is non-selective, inhibiting RNA by blocking ribosomal translation. Puromycin is used in cell biology to select mammalian cell lines that have been transformed by vectors that express puromycin-N-acetyl-transferase.
The Uses of PUROMYCIN
Puromycin has been widely used as a basic tool in research for studying protein synthesis. It is an antibiotic used by scientists in bioresearch to select cells modified by genetic engineering. It inhibits protein synthesis by binding to RNA. It is also an antineoplastic and antitrypanosomal agent.
The Uses of PUROMYCIN
Puromycin is an aminonuclease antibiotic produced by the soil actinomycete?Streptomyces alboniger; which induces apoptosis.
What are the applications of Application
Puromycin? is an aminonuclease antibiotic produced by the soil actinomycete Streptomyces alboniger; which induces apoptosis.
Definition
ChEBI: An aminonucleoside antibiotic, derived from the Streptomyces alboniger bacterium, that causes premature chain termination during translation taking place in the ribosome.
Hazard
Toxic to living cells of all kinds.
Toxicity evaluation
Puromycin is a specific metabolic inhibitor of protein synthesis and acts as an aminoacyl-tRNA analog and peptidyl acceptor. The latter causes premature chain termination of the protein and the release of nascent or growing polypeptide chains. In liver, it has been shown to cause fat accumulation without causing death of the hepatocytes. Puromycin causes focal glomerular sclerosis and alters the morphology, localization of anionic sites, and metabolism of renal epithelial cells. This injury is attributable to the production of reactive oxygen species.
Properties of PUROMYCIN
| Melting point: | 175.5-177° |
| Boiling point: | 572.65°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 -11° (ethanol) |
| Density | 1.3119 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7010 (estimate) |
| RTECS | AU7350000 |
| pka | 6.8, 7.2(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (50 mg/ml at 20°C). |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Adenosine, 3'-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-oxopropyl]amino]-3'-deoxy-N,N-dimethyl- (53-79-2) |
Safety information for PUROMYCIN
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P330:Rinse mouth. |
Computed Descriptors for PUROMYCIN
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

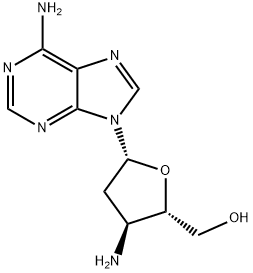

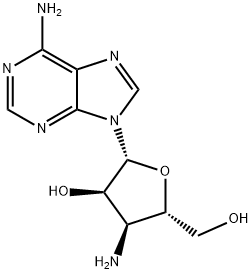
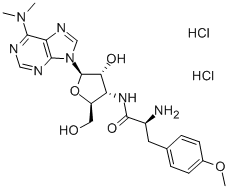
You may like
-
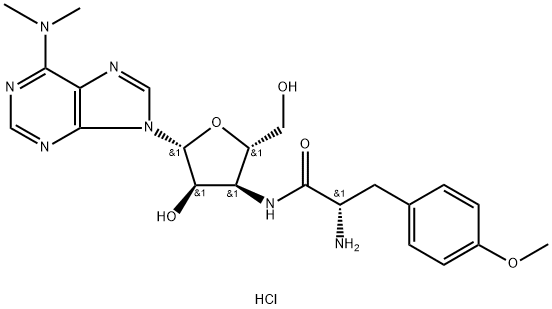
 Puromycin dihydrochloride 95% CAS 53-79-2View Details
Puromycin dihydrochloride 95% CAS 53-79-2View Details
53-79-2 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
