Propionitrile
- CAS NO.:107-12-0
- Empirical Formula: C3H5N
- Molecular Weight: 55.08
- MDL number: MFCD00001948
- EINECS: 203-464-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32

What is Propionitrile?
Chemical properties
Clear liquid
Chemical properties
Propionitrile is a colorless liquid with a pleasant, sweetish, ethereal odor. Propionitrile [107-12-0], ethyl cyanide, CH3CH2CN, is a colorless liquid which is miscible with water, ethanol, dimethylformamide, and diethyl ether. The physical properties are listed in Table 1. Propionitrile is obtained either by hydrogenation of acrylonitrile or by the gas-phase reaction of propanal or propanol with ammonia. It is also obtained as a byproduct in the electrohydrodimerization of acrylonitrile to adiponitrile (EHD process).
The Uses of Propionitrile
Propionitrile is an intermediate for organic syntheses, e.g. Houben-Hoesch reaction, as well as for pharmaceuticals, e.g. ketoprofen and fragrances.
The Uses of Propionitrile
Propionitrile is used as a chemical intermediate. It is formed as a by-product of the electrodimerization of acrylonitrile to adiponitrile.
The Uses of Propionitrile
Propionitrile, act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including, Extraction solvent for fatty acids, oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons, Solvent for spinning and casting, removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic alcohols, Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic salts, Recrystallization of steroids, Parent compound for organic synthesis, chemical intermediate in biochemistry, Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex catalysts, Stabilizer for chlorinated solvents, Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and pharmaceuticals. It is used as a dielectric fluid.
Definition
ChEBI: A nitrile that is acrylonitrile in which the carbon-carbon double bond has been reduced to a single bond.
Production Methods
Propionitnle may be prepared by dehydration of propionamide (or propionic acid plus ammonia) or by distilling ethyl sulfate and concentrated aqueous KCN. It also is formed as a byproduct of the electrohydrodimerization of acrylonitrile or by the hydrogenation of acrylonitrile with the use of copper, rhodium or nickle catalysts . U.S. production is estimated for 1980 to range between 10-15 million pounds.
General Description
A colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. Density 0.683 g / cm3. Flash point 61°F. Toxic by inhalation, skin absorption, and ingestion. Vapors are heavier than air. Used as a solvent, and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Propionitrile is incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents and strong reducing agents. After refluxing for 24 hours at 221°F, a mixture of Propionitrile with N-bromosuccinimide exploded.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
Propionitrile is highly toxic. This super toxic compound has a probable oral lethal dose in humans of less than 5 mg/kg or a taste (less than 7 drops) for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person. It is a mild to moderate skin and eye irritant.
Health Hazard
Reports of human toxicity data for propionitrile have not been found in the literature. However, Deichman indicated that propionitrile is rapidly absorbed through the skin and that it is one of the most toxic organic cyanides known. Clinical symptoms are characterized as loss of conciousness, salivation, nausea and vomiting. Hypopnea and dyspnea with bitter almond odor in breath and vomitus also were observed. Due to high concentrations of oxy- and cyanohemoglobin in venous blood, pink coloration of the skin was observed .
Health Hazard
Propionitrile is a moderate to highly toxic compound, an eye irritant, and a teratomer. The toxic symptoms are similar to acetonitrile. However, the acute inhalation toxicity is greater than that associate with acetonitrile. Willhite (1981) reported a median lethal concentration of 163 ppm in male mice exposed for 60 minutes. By comparison, acetonitrile and butyronitrile exhibited median lethal concentrations of 2693 and 249 ppm, respectively.
The toxic routes are inhalation, ingestion, and absorption through skin. The target organs are kidney, liver, central nervous system, lungs, and eyes. Inhalation of 500 ppm for 4 hours was lethal to rats. When administered intraperitoneally to mice, it caused corneal damage, ataxia, and dyspnea. The acute oral toxicity of this compound was found to be moderately high in rodents.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 36 mg/kg
Scolnick et al. (1994) have reported two cases of human intoxication from propionitrile. In the more severe case, the victim was comatose, acidotic, and hypotensive. Sodium nitrite/sodium thiosulfate therapy followed by treatment with hyperbaric oxygen at 2 atm was effective. In the second case, the symptoms were nausea, dizziness, and headache. The measured blood cyanide concentration in this case was 3.5μg/ml and the concentration of propionitrile at work site shortly after the exposure was found to be 77.5 mg/m3 in the air. The authors have suggested the use of hyperbaric oxygen as a valuable adjunct therapy in addition to the cyanide antidote kit for all nitrile poisoning. Propionitrile exhibited teratogenic effects in hamsters. Intraperitoneal administration of 238 mg/kg caused cytological changes in embryo and developmental abnormalities in the central nervous system. There is no report of any cancer-causing effects of this compound in animals or humans.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, Propionitrile emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and cyanide. Propionitrile is a flammable/combustible material and may be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and flash back. Container may explode in heat of fire. Vapor explosion and poison hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Generates cyanide ions. Poisonous on contact with acids. stable, but may become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures.
Industrial uses
Propionitnle is used as a selective solvent in the chemical industry and in petroleum refining and as a dielectric fluid . It has also been used experimentally as an ulcerogen .
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by inhalation. Experimental teratogenic effects. Other experimental reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame (sparks), oxidners. Mixture with N- bromosuccinimide may explode when heated. To fight fire, use water spray, foam, mist, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx and CN-. Used as a solvent in petroleum refining, and as a raw material for drug manufacture. See also NITRILES.
Potential Exposure
Used as a solvent in petroleum refin- ing, as a chemical intermediate; a raw material for drug manufacture; and a setting agent.
Shipping
UN2404 Propionitrile, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, 6.1-Poisonous material. UN1992 Flammable liquids, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Shake the nitrile with dilute HCl (20%), or with conc HCl until the odour of isonitrile has gone, then wash it with water, and aqueous K2CO3. After a preliminary drying with silica gel or Linde type 4A molecular sieves, it is stirred with CaH2 until hydrogen evolution ceases, then decant and distil from P2O5 (not more than 5g/L, to minimise gel formation). Finally, it is refluxed with, and slowly distilled from CaH2 (5g/L), taking precautions to exclude moisture. [Beilstein 2 IV 728.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlo- rine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides., reducing agents. Hydrogen cyanide is produced when propionitrile is heated to decomposition. Reacts with acids, steam, warm water; producing toxic and flammable hydrogen cyanide fumes. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompati- ble with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids .
Waste Disposal
Alcoholic NaOH followed by calcium hypochlorite may be used, as may incineration . Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guid- ance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Propionitrile
| Melting point: | -93 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 97 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.772 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 53.33-63.195hPa at 22.05-25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 43 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | soluble in water at 40°C is 11.9 g/100 g H20; miscible with alcohol,
ether, dimethylformamide |
| form | Oil |
| color | Clear Colourless |
| Water Solubility | decomposes. 5-10 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| FreezingPoint | -93℃ |
| Merck | 14,7827 |
| BRN | 773680 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 14 mg/m3 (6 ppm) (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 27.7(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Note low flash point. Incompatible with strong oxidising agents, strong bases, strong acids, strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 107-12-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanenitrile(107-12-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propanenitrile (107-12-0) |
Safety information for Propionitrile
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H300:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Propionitrile
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
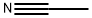


You may like
-
 Propionitrile CAS 107-12-0View Details
Propionitrile CAS 107-12-0View Details
107-12-0 -
 PROPIONITRILE For Synthesis CAS 107-12-0View Details
PROPIONITRILE For Synthesis CAS 107-12-0View Details
107-12-0 -
 Propionitrile CAS 107-12-0View Details
Propionitrile CAS 107-12-0View Details
107-12-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1