Propanil
Synonym(s):3′,4′-Dichloropropionanilide;Anti-STAM1;DKFZp686J2352;STAM;STAM1
- CAS NO.:709-98-8
- Empirical Formula: C9H9Cl2NO
- Molecular Weight: 218.08
- MDL number: MFCD00018149
- EINECS: 211-914-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
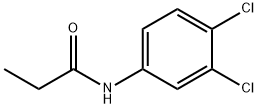
What is Propanil ?
Description
propanil is used as a rice herbicide. The resistance of rice plants toward propanil has been found in an enzyme aryl-acylamidase that rapidly hydrolyzes the herbicide. This enzyme can be inhibited by carbamate insecticides, and this can lead to an increased propanil phytotoxicity (38).
Chemical properties
(Pure) Light-brown solid.
Chemical properties
Propanil is a colorless solid. The technical product is a brown crystalline solid.
The Uses of Propanil
Selective preemergence and postemergence herbicide used to control many grasses and broad-leaved weeds in potatoes, rice and wheat.
The Uses of Propanil
Postemergence herbicide, especially for rice culture; nematocide.
The Uses of Propanil
Propanil is a a widely used herbicide. Propanil is used mainly to control weed growth in rice fields.
Definition
ChEBI: Propanil is an anilide resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of propanoic acid with the amino group of 3,4-dichloroaniline. It is a herbicide used for the treatment of numerous grasses and broad-leaved weeds in rice, potatoes, and wheat. It has a role as a herbicide. It is an anilide and a dichlorobenzene. It is functionally related to a 3,4-dichloroaniline.
General Description
Colorless to brown crystals. Non corrosive. Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed by acid and alkaline media.
Reactivity Profile
Propanil is incompatible with carbamates and organophosphates.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: Propanil is a post-emergence herbicide with no residual effect. It is used against numerous grasses and broadleaved weeds in rice, potatoes, and wheat. Mixing with carbamates or organophosphorus compounds is not recommended. It is also used on wheat in a mixture with MCPA. With carbaryl, it is used in citrus crops grown in sod culture. Not approved for use in EU countries (re-submitted). Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
Cekupropanil; DCPA; N-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl) propanamide; 3',4'-Dichlorophenyl propionanilide; 3,4-Dichloropropionanilide; 3',4'-Dichloropropionanilide; Dichloropropionanilide; Dipram; DPA; NSC 31312; Propanamide, N-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-; Propanide; Propionanilide, 3',4'-Dichloro-; Propionic acid, 3,4-dichloroanilide
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by an unspecified route. Mildly toxic by skin contact. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl and NOx.
Potential Exposure
Propanil is used as a postemergent herbicide for rice and spring wheat. A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this contact herbicide.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In the presence of suspended natural populations from unpolluted aquatic
systems, the second-order microbial transformation rate constant determined in the laboratory was reported to be 5 × 10–10 L/organisms-hour (Steen, 1991).
Soil. Propanil degrades in soil forming 3,4-dichloroaniline (Bartha, 1968; Bartha and
Pramer, 1970; Chisaka and Kearney, 1970; Bartha, 1971; Duke et al., 1991; Pothuluri et
al., 1991) which is further degraded by microbial peroxidases to 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazobenzene (Bartha and Pramer, 1967; Bartha et al., 1968; Chisaka and Kearney, 1970),
3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazooxybenzene (Bartha and Pramer, 1970), 4-(3,4-dichloroanilo)-
3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazobenzene (Linke and Bartha, 1970) and 1,3-bis(3,4-dichlorophenyl)triazine (Plimmer et al., 1970a), propanoic acid, carbon dioxide and unidentified
products (Chisaka and Kearney, 1970). Evidence suggests that 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazobenzene reacted with 3,4-dichloroaniline forming a new reaction product, namely 4-(3,4-
dichloroanilo)-3,3′,4′-trichloroazobenzene (Chisaka and Kearney, 1970). Under aerobic
conditions, propanil in a biologically active, organic-rich pond sediment underwent dechlorination at the para- position forming N-(3-chlorophenyl)propanamide (Stepp et al., 1985).
Residual activity in soil is limited to approximately 3–4 months (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Plant. In rice plants, propanil is rapidly hydrolyzed via an aryl acylamidase enzyme
isolated by Frear and Still (1968) forming the nonphototoxic compounds (Ashton and
Monaco, 1991) 3,4-dichloroaniline, propionic acid (Matsunaka, 1969; Menn and Still,
1977; Hatzios, 1991) and a 3′,4′-dichloroaniline-lignin complex. This complex was identified as a metabolite of N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)glucosylamine, a 3,4-dichloroaniline saccharide conjugate and a 3,4-dichloroaniline sugar derivative (Yi et al., 1968). In a rice
field soil under anaerobic conditions, however, propanil underwent amide hydrolysis and
dechlorination at the para position forming 3,4-dichloroaniline and m-chloroaniline (Pettigrew et al., 1985). In addition, propanil may degrade indirectly via an initial oxidation
step resulting in the formation of 3,4-dichlorolacetanilide which is further hydrolyzed to
3,4-dichloroaniline and lactic acid (Hatzios, 1991). In an earlier study, four metabolites
were identified in rice plants, two of which were positively identified as 3,4-dichloroaniline
and N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)glucosylamine (Still, 1968).
Photolytic. Photoproducts reported from the sunlight irradiation of propanil (200 mg/L)
in distilled water were 3′-hydroxy-4′-chloropropionanilide, 3′-chloro-4′-hydroxypropionanilide, 3′,4′-dihydroxypropionanilide, 3′-chloropropionanilide, 4′-chloropropionanilide,
propionanilide, 3,4-dichloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, propionic acid, propionamide,
3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazobenzene and a dark polymeric humic substance. The photolysis
products resulted from the reductive dechlorination, replacement of chlorine substituents
by hydroxyl groups, formation of propionamide, hydrolysis of the amide group and
azobenzene formation (Moilanen and Crosby, 1972). Tanaka et al. (1985) studied the
photolysis of propanil (100 mg/L) in aqueous solution using UV light (λ = 300 nm) or
sunlight. After 26 days of exposure to sunlight, propanil degraded forming a trichlorinated
biphenyl product (<1% yield) and hydrogen chloride (Tanaka et al., 1985).
Chemical/Physical. Hydrolyzes in acidic and alkaline media to propionic acid (Worthing and Hance, 1991) and 3,4-dichloroaniline (Sittig, 1985; Worthing and Hance, 1991).
The half-life of propanil in a 0.50 N sodium hydroxide solution at 20°C was determined
to be 6.6 days (El-Dib and Aly, 1976).
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Hydrolysis in acidic or basic media yields the more toxic substance, 3,4-dichloraniline, and is not recommended.
Properties of Propanil
| Melting point: | 92-93°C |
| Boiling point: | 369.9±32.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.25 |
| refractive index | 1.5680 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 13.58±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Dark brown, blue-black |
| Water Solubility | 225mg/L(room temperature) |
| Merck | 13,7896 |
| BRN | 2365645 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 709-98-8 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanil(709-98-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propanil (709-98-8) |
Safety information for Propanil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Propanil
| InChIKey | LFULEKSKNZEWOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Propanil manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 709-98-8 98%View Details
709-98-8 98%View Details
709-98-8 -
 Propanil CAS 709-98-8View Details
Propanil CAS 709-98-8View Details
709-98-8 -
 Propanil CAS 709-98-8View Details
Propanil CAS 709-98-8View Details
709-98-8 -
 Anti-Stam Antibody Produced In Rabbit CASView Details
Anti-Stam Antibody Produced In Rabbit CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1