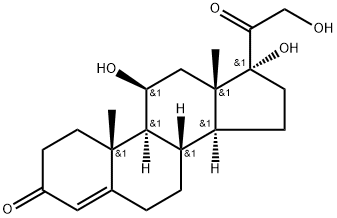
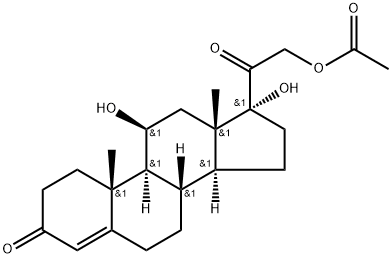
Prednisolone
Synonym(s):1,4-Pregnadiene-11β,17α,21-triol-3,20-dione;11β,17α,21-Trihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;1-Dehydrocortisol;1-Dehydrohydrocortisone;Prednisolone
- CAS NO.:50-24-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H28O5
- Molecular Weight: 360.45
- MDL number: MFCD00003649
- EINECS: 200-021-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-12 18:27:14
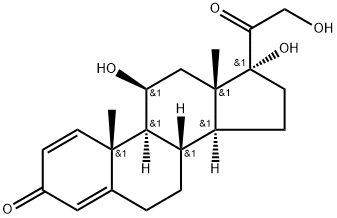
What is Prednisolone?
Absorption
Oral prednisolone reaches a Cmax of 113-1343ng/mL with a Tmax of 1.0-2.6 hours. Oral prednisolone is approximately 70% bioavailable.
Toxicity
The intraperitoneal LD50 in rats is 2g/kg and 65mg/kg in mice. The subcutaneous LD50 in rats is 147mg/kg and >3500mg/kg in mice. The oral LD50 in mice is 1680mg/kg. In humans, the oral TDLO in men is 9mg/kg/2W and in women is 14mg/kg/13D.
Patients experiencing an overdose of prednisolone may present with gastrointestinal disturbances, insomnia, and restlessness. Overdose of oral prednisolone may be treated by gastric lavage or inducing vomiting if the overdose was recent, as well as supportive and symptomatic therapy. Chronic overdosage may be treated by dose reduction or treating patients on alternate days. An overdose by the ophthalmic route is not expected to cause problems.
Description
Prednisolone is the active metabolite of the synthetic corticosteroid prednisone , which is used in the suppression of inflammation and autoimmunity, as well as in other conditions. It alters gene expression through both the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid. soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethyl formamide, which should be purged with an inert gas. The solubility of prednisone in these solvents is approximately 3, 30, and 25 mg/ml, respectively.
Originator
Sterane, Pfizer ,US ,1955
The Uses of Prednisolone
Prednisolone is used for the same indications as all corticosteroids: rheumatism, polyarthritis, bronchial asthma, neurodermatitis, and eczema.
Indications
Prednisolone is indicated to treat endocrine, rheumatic, and hematologic disorders; collagen, dermatologic, ophthalmic, respiratory, and gastrointestinal diseases; allergic and edematous states; and other conditions like tuberculous meningitis.
Background
Prednisolone is a glucocorticoid similar to cortisol used for its anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-neoplastic, and vasoconstrictive effects.
Prednisolone was granted FDA approval on 21 June 1955.
What are the applications of Application
Prednisolone-d6 is a synthetic corticosteroid that is metabolically interconvertible with prednisone
What are the applications of Application
Prednisolone is an antiinflammatory, immunosuppressive glucocorticoid
Definition
ChEBI: Prednisolone is a glucocorticoid that is prednisone in which the oxo group at position 11 has been reduced to the corresponding beta-hydroxy group. It is a drug metabolite of prednisone. It has a role as an adrenergic agent, an anti-inflammatory drug, an antineoplastic agent, an immunosuppressive agent, a drug metabolite, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. It is a glucocorticoid, an 11beta-hydroxy steroid, a 21-hydroxy steroid, a 17alpha-hydroxy steroid, a 20-oxo steroid, a 3-oxo-Delta(1),Delta(4)-steroid, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone, a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a C21-steroid. It is functionally related to a Delta(1)-progesterone.
What are the applications of Application
Prednisolone is a synthetic corticosteroid with metabolically interconvertible with prednisone. It mediates its effect by acting on neurokinin 1 receptor. It is used to treat many conditions that cause inflammation, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
brand name
Cortalone(Halsey); Delta-Cortef (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Fernisolone(Ferndale); Meti-Derm (Schering); Prelone (Muro); Prelone(Teva); Sterane (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Glucocorticoid
General Description
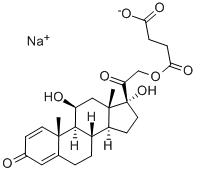
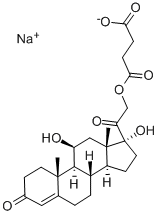
Prednisolone,Δ1-hydrocortisone,11β,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, hasless salt-retention activity than hydrocortisone, but some patients have more frequently experiencedcomplications such as gastric irritation and peptic ulcers.Because of low MC activity, it cannot be used alone for adrenalinsufficiency. Prednisolone is available in varioussalts and esters to maximize its therapeutic utility:
Prednisolone acetate, USP (21-acetate)
Prednisolone sodium phosphate, USP (21-sodiumphosphate)
Prednisolone sodium succinate, USP (21-sodiumsuccinate)
Prednisolone tebutate, USP (21-tebutate).
Hazard
Causes sodium retention; may have side effects similar to cortisone.
Mechanism of action
Prednisolone is hydrocortisone to which has been added a ?1 double bond. This places two double bonds in ring A, which flattens it and increases glucocorticoid action at the expense of mineralocorticoid activity. Prednisolone has fourfold the glucocorticoid activity of hydrocortisone while having approximately half its mineralocorticoid activity. In addition, prednisolone has an increased duration of action compared to hydrocortisone, because the extra double bond in ring A retards its metabolic reduction.
Pharmacokinetics
Corticosteroids bind to the glucocorticoid receptor, inhibiting pro-inflammatory signals, and promoting anti-inflammatory signals. Prednisolone has a short duration of action as the half life is 2.1-3.5 hours. Corticosteroids have a wide therapeutic window as patients make require doses that are multiples of what the body naturally produces. Patients taking corticosteroids should be counselled regarding the risk of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression and increased susceptibility to infections.
Clinical Use
Prednisolone can be used to treat severe asthmatic attacks that do not respond to conventional treatment, and it is available as the free alcohol for oral administration. The C-21 sodium phosphate (Hydeltrasol) ester is available for parenteral use.
Side Effects
A prodrug of prednisolone is prednisone. It is the 11-keto analogue of prednisolone and must be converted in vivo to the active 11β-hydroxy compound, which is necessary to hydrogen bond to Asn-564 in the glucocorticoid receptor. Prednisone should not be used in patients with hepatic dysfunction, because their ability to reduce the 11-keto group with 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to the active metabolite may be impaired.
Prednisolone is well tolerated by most people and can start to work very quickly. Side effects can be dependent on the dose and duration of treatment. Short courses of treatment often have fewer side effects than long term use. A Severe allergic reaction is a very rare side effect of prednisolone.
Safety Profile
A poison by intravenous and subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human teratogenic effects by an unspecified route: developmental abnormalities of the central nervous system; effects on embryo or fetus: fetal death, extra embryonic structures. Human reproductive effects by an unspecified route: stdlbirth. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Synthesis
Prednisolone is 11|?,17|á,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-dien-3,20-dione (27.1.33). Structurally, prednisolone differs from prednisone in that the keto-group at C11 of prednisone is replaced by a hydroxyl group. Prednisolone is synthesized either by microbiological dehydrogenation of C1¨CC2 bond in hydrocortisone [16¨C19], or from 21-acetoxy- 11|?,17|á-dihydroxy-5|á-pregnan-3,20-dione, which undergoes dibromination by molecular bromine in acetic acid at positions C2 and C4, and then the resulting dibromide 27.1.32 is dehydrobrominated by heating it in collidine, which gives prednisolone as an acetate at position C21. Hydrolyzing this compound leads to formation of prednisolone (27.1.33).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifamycins
and rifampicin; metabolism possibly inhibited by
erythromycin; concentration of isoniazid possibly
reduced.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and
phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital,
phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin - avoid; metabolism possibly inhibited
by itraconazole and ketoconazole.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: rare reports of convulsions in patients
on ciclosporin and high-dose corticosteroids;
increased levels of prednisolone; increased
ciclosporin levels reported with prednisolone.
Cobicistat: concentration possibly increased by
cobicistat - increased risk of adrenal suppression.
Diuretics: enhanced hypokalaemic effects of
acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazide diuretics.
Vaccines: high-dose corticosteroids can impair
immune response to vaccines - avoid with live
vaccines.
Metabolism
Prednisolone can be reversibly metabolized to prednisone which is then metabolized to 17α,21-dihydroxy-pregnan-1,4,6-trien-3,11,30-trione (M-XVII), 20α-dihydro-prednisone (M-V), 6βhydroxy-prednisone (M-XII), 6α-hydroxy-prednisone (M-XIII), or 20β-dihydro-prednisone (M-IV). 20β-dihydro-prednisone is metabolized to 17α,20ξ,21-trihydroxy-5ξ-pregn-1-en-3,11-dione(M-XVIII). Prednisolone is metabolized to Δ6-prednisolone (M-XI), 20α-dihydro-prednisolone (M-III), 20β-dihydro-prednisolone (M-II), 6αhydroxy-prednisolone (M-VII), or 6βhydroxy-prednisolone(M-VI). 6αhydroxy-prednisolone is metabolized to 6α,11β,17α,20β,21-pentahydroxypregnan-1,4-diene-3-one (M-X). 6βhydroxy-prednisolone is metabolized to 6β,11β,17α,20β,21-pentahydroxypregnan-1,4-diene-3-one (M-VIII), 6β,11β,17α,20α,21-pentahydroxypregnan-1,4-diene-3-one (M-IX), and 6β,11β,17α,21-tetrahydroxy-5ξ-pregn-1-en-3,20-dione (M-XIV). MVIII is metabolized to 6β,11β,17α,20β,21-pentahydroxy-5ξ-pregn-1-en-3-one (M-XV) and then to MXIV, while MIX is metabolized to 6β,11β,17α,20α,21-pentahydroxy-5ξ-pregn-1-en-3-one (M-XVI) and then to MXIV. These metabolites and their glucuronide conjugates are excreted predominantly in the urine.
Metabolism
Prednisolone is hepatically metabolised and excreted in the urine as sulphate and glucuronide conjugates, with an appreciable proportion of unchanged prednisolone.
Properties of Prednisolone
| Melting point: | 240 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 412.46°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +102° (dioxane) |
| Density | 1.0963 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 100 ° (C=1, Dioxane) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methanol, sparingly soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in methylene chloride. It shows polymorphism (5.9). |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.46±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 2.225g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,7721 |
| BRN | 1354103 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-24-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Prednisolone (50-24-8) |
Safety information for Prednisolone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Prednisolone
| InChIKey | OIGNJSKKLXVSLS-VWUMJDOOSA-N |
Prednisolone manufacturer
Allmpus Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 50-24-8 Prednisolone 98%View Details
50-24-8 Prednisolone 98%View Details
50-24-8 -
 Prednisolone 99%View Details
Prednisolone 99%View Details -
 Prednisolone 98% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
Prednisolone 98% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
50-24-8 -
 Prednisolone >98% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
Prednisolone >98% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
50-24-8 -
 Prednisolone 50-24-8 98%View Details
Prednisolone 50-24-8 98%View Details
50-24-8 -
 Prednisolone 99%View Details
Prednisolone 99%View Details -
 Prednisolone 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
Prednisolone 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-24-8View Details
50-24-8 -
 Prednisolone CAS 50-24-8View Details
Prednisolone CAS 50-24-8View Details
50-24-8
