Polyisobutylene
- CAS NO.:9003-27-4
- Empirical Formula: C4H8
- Molecular Weight: 56.10632
- MDL number: MFCD00084436
- EINECS: 618-360-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:07
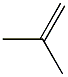
What is Polyisobutylene?
Chemical properties
Polyisobutylene is composed of long-chain hydrocarbon formed by polymerization of isobutene, and is extremely stable under normal conditions. It is transparent non-noxious high-consistency semi-solid polymer free of impurities.
Chemical properties
The physical properties of polyisobutene are very dependent on molecular
weight. Polymers with average molecular weight (Mw) of about 15 000 are sticky viscous liquids whilst those with molecular weight of 100000-200000
are rubber-like, resembling unmilled crepe rubber.
Polyisobutene is non-crystalline when unstretched and is therefore soluble
at room temperature in hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons. The
material is resistant to most acids, alkalis and aqueous solutions, as would be
expected from its saturated hydrocarbon structure and absence of tertiary
hydrogen atoms. The lack of tertiary hydrogen atoms renders polyisobutene
more resistant to oxidation than polypropylene; also, the less numerous and
partially shielded methylene groups in polyisobutene are less reactive than
those in polyethylene. However, polyisobutene is rather susceptible to thermal degradation since chain scission is favoured by the greater stability of the
resultant tertiary free radical: Polyisobutene may be chlorinated but the reaction is accompanied by
severe degradation.
Polyisobutene may be chlorinated but the reaction is accompanied by
severe degradation.
A limitation of polyisobutene is its tendency to cold flow and, as a result,
the polymer finds little use in self-supporting form. Applications are restricted
mainly to adhesives, fabric and paper coatings, and blends with other polymers. Low molecular weight polyisobutene is also used in caulking compounds.
The Uses of Polyisobutylene
polyisobutene (hydrogenated) is an emollient.
Polyisobutylene, sometimes called butyl rubber, and other times PIB, is a vinyl polymer. It's very similar to polyethylene and polypropylene in structure, except that every other carbon is substituted with two methyl groups. It is made from the monomer isobutylene, by cationic vinyl polymerization.
Polyisobutylene is a synthetic rubber, or elastomer. It's special because it's the only rubber that's gas impermeable. That is, it's the only rubber that can hold air for long periods of time. You may have noticed that balloons will go flat after a few days. This is because they are made of polyisoprene, which is not gas impermeable. Because polyisobutylene will hold air, it is used to make things like the inner tubes, liner layers of tires, and the inner liners of basketballs.
Definition
ChEBI: A polymer composed of repeating 1,1-dimethylethylene units.
Preparation
Silicone rubbers are prepared as follows:

Other groups may replace the methyl groups. Silicone rubbers have excellent ozone and weathering resistance, good electrical properties, and good adhesion to metal.
Properties of Polyisobutylene
| Melting point: | 54-56 °C |
| Boiling point: | 300 °C |
| Density | 0.92 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| form | slab/chunk |
| Stability: | Stability Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C4H8/c1-4(2)3/h1H2,2-3H3 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Polyisobutylene (9003-27-4) |
Safety information for Polyisobutylene
Computed Descriptors for Polyisobutylene
| InChIKey | VQTUBCCKSQIDNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C(C)C |
Polyisobutylene manufacturer
Thirthraj Consolidated Company
Dev Industries
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 9003-27-4 Polyisobutene 99%View Details
9003-27-4 Polyisobutene 99%View Details
9003-27-4 -
 Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
9003-27-4 -
 Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
9003-27-4 -
 Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
Polyisobutylene CAS 9003-27-4View Details
9003-27-4 -
 Loose Technical Grade Polyisobutylene (PIB 1300 Mol.)View Details
Loose Technical Grade Polyisobutylene (PIB 1300 Mol.)View Details
9003-27-4 -
 Polyisobutylene Viscous LiquidView Details
Polyisobutylene Viscous LiquidView Details
9003-27-4 -
 Barrel of 50 L itre Barrel of 50 L Polyisobutene Liquid ChemicalView Details
Barrel of 50 L itre Barrel of 50 L Polyisobutene Liquid ChemicalView Details
9003-27-4 -
 50 Kg PIB 200 Polyisobutylene (2400 Molecular Weight), For Adhesives and SealantsView Details
50 Kg PIB 200 Polyisobutylene (2400 Molecular Weight), For Adhesives and SealantsView Details
9003-27-4
