Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer
- CAS NO.:29154-49-2
- Empirical Formula: C16H26O9
- Molecular Weight: 362.37224
- MDL number: MFCD00084422
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
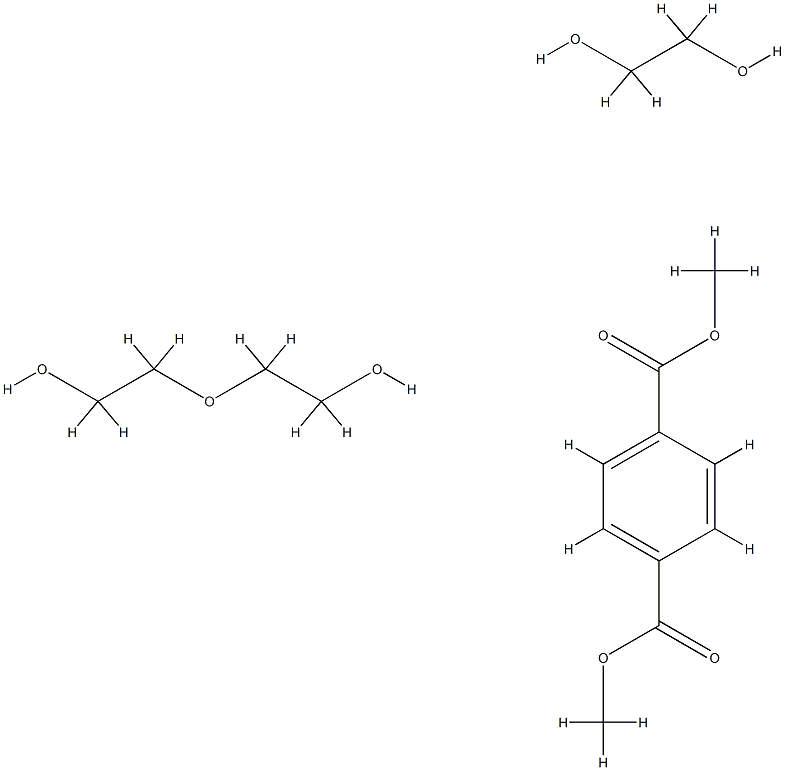
What is Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer?
Chemical properties
Poly(ethylene terephthalate) is a colourless rigid substance. Because of its structural regularity, the polymer readily crystallizes and the physical properties of the bulk material are greatly affected by the extent of crystallinity, which, in turn, is largely determined by the previous history of the material. In the production of fibre, the molten polymer is extruded through spinnerets into air at normal temperature. The filaments are thus rapidly cooled and are largely amorphous and are weak. The filaments are then drawn at a temperature above the glass-transition temperature (80°C), whereby molecular orientation and crystallinity are induced. Finally, the filaments are heated at about 200°C under tension to give a dimensionally-stable material of maximum crystallinity. The manufacture of poly(ethylene terephthalate) film closely resembles that of fibre and also involves extrusion, orientation and stabilization.
The Uses of Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer
Poly(butylene terephthalate) is used as an engineering material in a variety of applications which include automotive parts, electrical components and domestic appliance assemblies.
Preparation
It is prepared from 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid or dimethylterephthalate by processes which are essentially the same as those used for poly(ethylene terephthalate) and described in the preceding section. Due to the longer sequence of methylene groups, the polymer chains are more flexible and less polar than in poly(ethylene terephthalate). This results in a lower crystalline melting point (225°C) and glass-transition point (22-43°C). The low glass-transition temperature facilitates rapid crystallization in the mould and most poly(butylene terephthalate) is processed by injection moulding.
Industrial uses
Polyethylene terephthalate is a useful materialthat has good resistance to acids and alkalisprovided that they are diluted. It is insoluble inmany common solvents, although it does dissolvein aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons,especially when warm. It softens above250°C.
Properties of Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer
| Melting point: | 250-255 °C |
| Density | 1.68 g/mL at 25 °C |
| form | pellets |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester, polymer with 1,2-ethanediol and 2,2'-oxybis[ethanol] (29154-49-2) |
Safety information for Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer
Computed Descriptors for Diethyleneglycol,ethyleneglycol,dimethylterephthalatepolymer
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![DEUTERATED POLY[ETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE(D4)]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
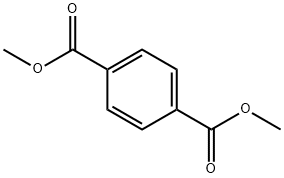
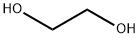
You may like
-
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details -
 Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
Polyethylene Terephthalate CASView Details
