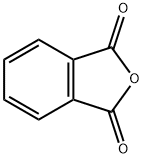
Phthalonitrile
Synonym(s):1,2-Benzenedicarbonitrile;Phthalonitrile
- CAS NO.:91-15-6
- Empirical Formula: C8H4N2
- Molecular Weight: 128.13
- MDL number: MFCD00001771
- EINECS: 202-044-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
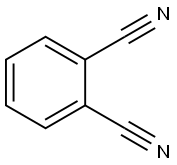
What is Phthalonitrile?
Chemical properties
Phthalonitrile is a crystalline powder having a faint grayish yellow color and a slighty aromatic odor, similar to benzonitrile. Phthalonitrile was first described in 1896 when it was isolated during the diazotization of 2-aminobenzonitrile. The compound is sparingly soluble in water (ca. 1 g/L) and soluble in acetone, nitrobenzene, and benzonitrile. It cannot be distilled and polymerizes if heated above the melting point. It is not explosive and is difficult to ignite, but the dust can explode.
The Uses of Phthalonitrile
Phthalonitrile is used as a starting material for producing phthalocyanine pigments (→ Phthalocyanines), fluorescent brightners, and photographic sensitizers.
The Uses of Phthalonitrile
Phthalonitrile is used as an intermediate for chemical synthesis in the production of building blocks for colorants and coatings, life science and agricultural chemicals. It is also used as a precursor to phthalocyanine pigments (which are precursors to the blue dye in jeans), fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
The Uses of Phthalonitrile
Phthalodinitrile monomers can be polymerized thermally in the presence of small amounts of curing agents into thermosetting polymers. Phthalodinitrile is a precursor to phthalocyanine which is used as a dye or pigment.
Preparation
Phthalonitrile can be produced from phthalic acid, phthalic anhydride, phthalamide, or phthalimide by reaction with ammonia and elimination of water at 300–500°C in the gas phase in the presence of a catalyst.

In a single-stage continuous process, o-xylene is converted to phthalonitrile by reaction with ammonia and oxygen in the gas phase in a fluidized-bed reactor. Generally, metal oxide mixtures containing vanadium, antimony, chromium, and molybdenum, with further active components such as iron, tungsten, and alkali-metal oxides, on an alumina or silica support are used as catalysts.
Reactions
The route from o-phthalodinitrile can be represented 4C8H4N2 +M → MPc, where M is a bivalent metal, metal halide, metal alcoholate, or an equivalent amount of metal of valence other than two in a 4:1 molar ratio.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of CN- and NOx. See also NITRILES.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the nitrile from EtOH, toluene or *benzene. It has also been distilled under high vacuum. It is steam volatile. [Beilstein 9 H 815, 9 II 602, 9 III 4199, 9 IV 3268.]
Properties of Phthalonitrile
| Melting point: | 137-139 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 227.54°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.24 |
| vapor pressure | <1 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6231 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 162°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | benzene: 50 mg/mL, clear |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to beige |
| PH | 7 (H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 0.56 g/L (25 ºC) |
| BRN | 775028 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91-15-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phthalonitrile(91-15-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,2-Benzenedicarbonitrile (91-15-6) |
Safety information for Phthalonitrile
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Phthalonitrile
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium iodide (3,3-DIFLUOROCYCLOBUTYL)METHANOL 4,4-DIFLUOROCYCLOHEXANAMINE Cyclobutylamine (S)-3-Fluoro-pyrrolidine hydrochloride 3-Oxocyclobutanecarboxylic acid N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide L-tert-Leucine,97% 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% Aluminum oxide, basic Calcium hydroxide, 95% Diallylamine, 99% 2-Iodobenzoic Acid 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Pentachlorobenzonitrile Chloral Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide O-Benzylhydroxylamine Hydrochloride 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde 2-Picolylamine (2-Aminomethylpyridine) 2-Venylpyridine Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 4-Dimethylamine PyridineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Phthalonitrile CAS 91-15-6View Details
Phthalonitrile CAS 91-15-6View Details
91-15-6 -
 Phthalonitrile CAS 91-15-6View Details
Phthalonitrile CAS 91-15-6View Details
91-15-6 -
 1,2-Dicyanobenzene CAS 91-15-6View Details
1,2-Dicyanobenzene CAS 91-15-6View Details
91-15-6 -
 1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 -
 tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
870-46-2 -
 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 -
 19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2