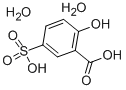
PHENOLSULFONIC ACID
- CAS NO.:1333-39-7
- Empirical Formula: C6H6O4S
- Molecular Weight: 174.17
- MDL number: MFCD00007506
- EINECS: 215-587-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
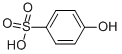
What is PHENOLSULFONIC ACID?
Description
Phorate is a stable, clear, pale yellow mobile liquid. Phorate is soluble and miscible with carbon
tetrachloride, dioxane, vegetable oils, xylene, alcohols, ethers, and esters. Phorate get hydrolysed
in the presence of moisture and by alkalis, toxic oxides of carbon, sulphur, and phosphorus.
Phorate may be used in foliar or soil treatments on alfalfa, barley, beans, brassicas, coffee,
corn, cotton, grapes, hops, lettuce, oats, peanuts, potatoes, rice, sorghum, soybeans, sugarcane,
sugar beets, tomatoes, watermelon, wheat, and on ornamentals and pine nursery stock. Phorate
has applications for the control of a wide variety of crop pests such as mites, aphids, greenbugs,
thrips, leafhoppers, sorghum shoot fly, leaf miners, corn rootworms, psyllids, cutworms,
Hessian fly, foliar nematodes, wireworms, flea beetles, whiteflies, pine tip moth, and others.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid is an arenesulfonic acid that is phenol substituted by a sulfo group at C-2. It has a role as a metabolite. It is functionally related to a phenol.
General Description
A yellowish liquid that becomes brown on exposure to air. Soluble in alcohol. Irritating to mucous membranes, skin, and eyes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Used as a laboratory reagent, in water analysis and in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. A mixture of ortho and para isomers.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
PHENOLSULFONIC ACID is a strong acid. Reacts exothermically with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. Dissolution in water or the dilution of a concentrated solutions with water may generate significant amounts of heat. Can serve as an oxidizing agent, but has a much weaker oxidizing action than sulfuric acid [Noller]. Can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases may be generated by reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Can catalyze (increase the rate) of chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Properties of PHENOLSULFONIC ACID
| Boiling point: | 275.14°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.384 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenolsulfonic acid (1333-39-7) |
Safety information for PHENOLSULFONIC ACID
Computed Descriptors for PHENOLSULFONIC ACID
PHENOLSULFONIC ACID manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1333-39-7 98%View Details
1333-39-7 98%View Details
1333-39-7 -
 Phenol Disulphonic Acid (SQ) CAS 1333-39-7View Details
Phenol Disulphonic Acid (SQ) CAS 1333-39-7View Details
1333-39-7 -
 phenolsulfonic acid CASView Details
phenolsulfonic acid CASView Details -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
