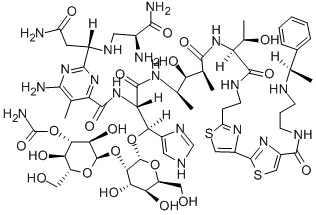
PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
- CAS NO.:70384-29-1
- Empirical Formula: C61H90N18O25S3
- Molecular Weight: 1571.67
- MDL number: MFCD01708900
- EINECS: 274-588-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-16 16:35:19
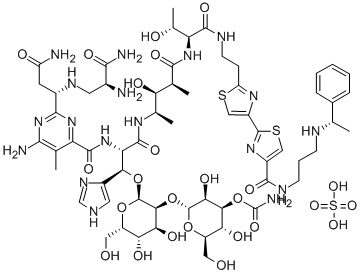
What is PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE?
Description
Peplomycin was derived biosynthetically from Streptomyces verticillus, the bleomycinproducing organism, in the course of efforts to obtain bleomycin derivatives with high activity and low toxicity. This antibiotic was found by Nippon Kayaku Co. and the Institute of Microbial Chemistry, Japan, in 1974. Its anticancer effects appear earlier than those of bleomycin; consequently, the period of therapy is shortened. Peplomycin is also active against metastatic cancer of the lymph nodes and shows less pneumotoxicity than bleomycin.
Chemical properties
Pale Yellow Amorphous Powder
Originator
Pepleo, Nippon Kayaku, Co., Japan ,1981
The Uses of PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
A derivative of Bleomycin with cytostatic activity and less pulmonary toxicity than the natural Bleomycin mixture
The Uses of PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
A derivative of Bleomycin with cytostatic activity and less pulmonary toxicity than the natural Bleomycin mixture.
Manufacturing Process
In 400 ml of dimethylformamide was dissolved 15.0 g of bleomycinic acid (copper-containing form). To the solution kept at 0°C by cooling were added 1.1 ml of N-methylmorpholine and 10.3 g of 6-chloro-1-pchlorobenzenesulfonyloxybenzotriazole (CCBT) as an activating compound. The mixture was stirred for 5 minutes at 0°C, then admixed with 5.3 g of N[(S)-1'-phenylethyl]-1,3-diaminopropane and further stirred for 1 hour.
After termination of the reaction by adding 200 ml of a 25% aqueous acetic acid solution, the reaction mixture was mixed with 5 liters of cold acetone to precipitate the reaction product. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with acetone, and dissolved in 500 ml of distilled water. The resulting aqueous solution was immediately adjusted to pH 6.0 and poured into a column containing 2 liters of CM-Sephadex C-25 (NH4+type) packed in 0.05 M aqueous ammonium chloride solution to adsorb bleomycins.
Using aqueous ammonium chloride solution, elution was performed by passing through the column 20 liters of eluent in which the concentration of ammonium chloride was continually increased from 0.05 to 1.0 M. The unreacted bleomycinic acid was found in the effluent at the ammonium chloride concentration of about 0.05 M and NK631 at the ammonium chloride concentration of about 0.45 M. Both fractions, which showed UV absorption at 292 nm;, were separately collected.
The NK631-containing fraction was poured into a resin column containing 2.6 liters of Amberlite XAD-2. The column was then washed thoroughly with water and eluted with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid in methanol-water (4:1 v/v). A total of 2.5 liters of the blue fraction, which showed UV absorption at 292 mμ, was collected. After evaporating off the methanol from the eluent fraction, the concentrate was adjusted to pH 6.0 with Dowex 44 (OH- type, an anionexchange resin composed of a copolymer of epichlorohydrin and ammonia) and was freeze-dried to obtain 16.1 g (92% yield) of NK631 dihydrochloride (copper-containing form) in the form of blue amorphous powder.
By similar treatment, 280 mg of the unreacted bleomycinic acid (coppercontaining form) were recovered.
In 200 ml of distilled water was dissolved 10.0 g of the NK631 dihydrochloride (copper-containing form). The solution was poured into a column containing 600 ml of Amberlite XAD-2 packed in distilled water. The column was washed successively with 2 liters of an aqueous solution containing 5% of EDTA-Na2, 2.5 liters of a 5% aqueous sodium sulfate solution, and 630 ml of distilled water.
The column was then eluted with 0.0025 N sulfuric acid in methanol-water mixture (1:1 v/v). A total of 900 ml of fractions containing a substance which showed UV absorption at 290 mμ was collected. After removal of methanol by distillation, the residual liquid was adjusted to pH 6.0 with Dowex 44 (OHtype) and freeze-dried to obtain 9.3 g (95% yield) of NK631 monosulfate (copper-free form) in the form of pale yellowish-white amorphous powder.
Therapeutic Function
Antineoplastic
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Properties of PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
| Melting point: | 196-198°C |
| alpha | 25436 -2.0° (c = 1 in water) |
| solubility | DMSO, DMF, Methanol, Water |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 2.9, 4.8, 7.4, 9.0(at 25℃) |
| color | Pale Yellow Amorphous |
Safety information for PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
Computed Descriptors for PEPLOMYCIN SULFATE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4