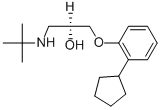
Penbutolol
- CAS NO.:38363-40-5
- Empirical Formula: C18H29NO2
- Molecular Weight: 291.43
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
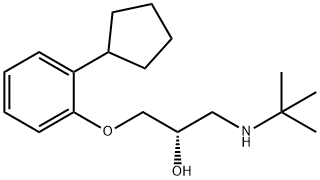
What is Penbutolol?
Absorption
>90%.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include drowsiness, vertigo, headache, and atriventricular block.
Originator
Betapressin, Hoechst , W. Germany ,1980
The Uses of Penbutolol
Anti-adrenergic (β-receptor).
Background
Penbutolol is a drug in the beta-blocker class used to treat hypertension. Penbutolol binds both beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, rendering it a non-selective beta-blocker. Penbutolol can act as a partial agonist at beta adrenergic receptors, since it is a sympathomimetric drug. Penbutolol also demonstrates high binding affinity to the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A with antagonistic effects. This binding characteristic of penbutolol is being investigated for its implications in Antidepressant Therapy. Penbutolol is contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock, sinus bradycardia, second and third degree atrioventricular conduction block, bronchial asthma, and those with known hypersensitivity.
Indications
Penbutolol is indicated in the treatment of mild to moderate arterial hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, especially thiazide-type diuretics.Penbutolol is contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock, sinus bradycardia, second and third degree atrioventricular conduction block, bronchial asthma, and those with known hypersensitivity.
Definition
ChEBI: Penbutolol is a member of ethanolamines.
Manufacturing Process
21.8 g (0.1 mol) of 1,2-epoxy-3-(2'-cyclopentylphenoxy)propane, boiling at 113°C to 115°C/0.2 mm Hg (prepared from 2-cyclopentylphenol and epichlorhydrin in the presence of alkali) were dissolved in 250 ml of ethanol; to this solution, there were added dropwise, while stirring.8.9 g (0.15 mol) of t-butylamine. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours at 60°C and then the solvent and the excess t-butylamine were removed by distillation. The residue which had been purified via the aqueous hydrochloride, crystallized, after removal of the ether by evaporation, upon rubbing or inoculation and yielded, after recrystallization from n-heptane, the 1-t-butylamino-2-hydroxy3-(2'-cyclopentylphenoxy)propane which was found to melt at 69°C to 70°C.
brand name
Levatol(Schwarz Pharma).
Therapeutic Function
Beta-adrenergic blocker
Pharmacokinetics
Penbutolol is a ?-1, ?-2 (nonselective) adrenergic receptor antagonist. Experimental studies showed a dose-dependent increase in heart rate in reserpinized (norepinephrine-depleted) rats given penbutolol intravenously at doses of 0.25 to 1.0 mg/kg, suggesting that penbutolol has some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. In human studies, however, heart rate decreases have been similar to those seen with propranolol.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation and glucuroconjugation forming a glucuronide metabolite and a semi-active 4-hydroxy metabolite.
Properties of Penbutolol
| Melting point: | 68-72° |
| Boiling point: | 433.43°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 20D -11.5° (c = 1 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.0344 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| pka | 9.3 (1.5 mmol/l in 25% ethanol) |
| color | Crystals |
| Water Solubility | 7g/L(room temperature) |
Safety information for Penbutolol
Computed Descriptors for Penbutolol
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![PENBUTOLOL IMPURITY A(2S)-1-[2-(CYCLOPENT-1-ENYL)PHENOXY]-3-[(1,1-DIMETHYLETHYL)AMINO]PROPAN-2-OL EPP(CRM STANDARD)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure22/GIF/CB6976910.gif)


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8