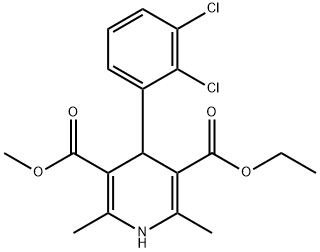
Felodipine
Synonym(s):4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinecarboxylic acid ethyl methyl ester;Plendil
- CAS NO.:72509-76-3
- Empirical Formula: C18H19Cl2NO4
- Molecular Weight: 384.25
- MDL number: MFCD08235033
- EINECS: 620-472-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
What is Felodipine?
Absorption
Is completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; however, extensive first-pass metabolism through the portal circulation results in a low systemic availability of 15%. Bioavailability is unaffected by food.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly bradycardia. Oral rat LD50 is 1050 mg/kg.
Description
Felodipine is a vasodilatory calcium antagonist with a high degree of vascular selectivity. It is currently indicated for use only in hypertension, either as monotherapy or in conjunction with diuretics or beta blockers.
Chemical properties
White or Light Yellow Crystalline Powder
Originator
Astra (Sweden)
The Uses of Felodipine
Felodipine is used as a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It displays high vascular selectivity; lowers arterial blood pressure without altering cardiac contractility. Antihypertensive.
The Uses of Felodipine
vasodilator, Ca channel blocker
The Uses of Felodipine
Zanarnivir influenza prophylaxis and therapy
What are the applications of Application
Felodipine is a 1,4-dihydropyridine antagonist and calcium channel protein inhibitor
Background
Felodipine is a long-acting 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (CCB)b. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, felodipine prevents calcium-dependent myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. Felodipine is the most potent CCB in use and is unique in that it exhibits fluorescent activity. In addition to binding to L-type calcium channels, felodipine binds to a number of calcium-binding proteins, exhibits competitive antagonism of the mineralcorticoid receptor, inhibits the activity of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, and blocks calcium influx through voltage-gated T-type calcium channels. Felodipine is used to treat mild to moderate essential hypertension.
Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension.
Definition
ChEBI: The mixed (methyl, ethyl) diester of 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid. A calcium-channel blocker, it lowers blood pressure by reducing peripheral vascular resistance through a highly selective action on smooth m scle in arteriolar resistance vessels. It is used in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of 2,3-dichlorobenzylideneacetylacetic acid-methylester.
2,3-Dichlorobenzaldehyde is reacted with methyl acetoacetate in a suitable
solvent in the presence of a catalytic amount of acetic acid and piperidine.
Water is azeotropically separated off during the reaction. The reaction mixture
is extracted in order to remove the catalysts. The solvent is evaporated and
methanol is added. The product is crystallized by cooling the solution, isolated
by filtration and finally washed with methanol.
brand name
Plendil (AstraZeneca).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
General Description
Felodipine, 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid ethylmethyl ester (Plendil), is a second-generation dihydropyridinechannel blocker of the nifedipine type. It is more selectivefor vascular smooth muscle than for myocardial tissueand serves as an effective vasodilator.
Biological Activity
L-type Ca 2+ channel blocker that is selective over N-, R-, P/Q- and T-type channels. Displays high vascular selectivity; lowers arterial blood pressure without altering cardiac contractility. Antihypertensive.
Pharmacokinetics
Felodipine belongs to the dihydropyridine (DHP) class of calcium channel blockers (CCBs), the most widely used class of CCBs. There are at least five different types of calcium channels in Homo sapiens: L-, N-, P/Q-, R- and T-type. It was widely accepted that CCBs target L-type calcium channels, the major channel in muscle cells that mediates contraction; however, some studies have shown that felodipine also binds to and inhibits T-type calcium channels. T-type calcium channels are most commonly found on neurons, cells with pacemaker activity and on osteocytes. The pharmacologic significance of T-type calcium channel blockade is unknown. Felodipine also binds to calmodulin and inhibits calmodulin-dependent calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The effect of this interaction appears to be minor. Another study demonstrated that felodipine attenuates the activity of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (CaMPDE) by binding to the PDE-1B1 and PDE-1A2 enzyme subunits. CaMPDE is one of the key enzymes involved in cyclic nucleotides and calcium second messenger systems. Felodipine also acts as an antagonist to the mineralcorticoid receptor by competing with aldosterone for binding and blocking aldosterone-induced coactivator recruitment of the mineralcorticoid receptor. Felodipine is able to bind to skeletal and cardiac muscle isoforms of troponin C, one of the key regulatory proteins in muscle contraction. Though felodipine exhibits binding to many endogenous molecules, its vasodilatory effects are still thought to be brought about primarily through inhibition of voltage-gated L-type calcium channels. Similar to other DHP CCBs, felodipine binds directly to inactive calcium channels stabilizing their inactive conformation. Since arterial smooth muscle depolarizations are longer in duration than cardiac muscle depolarizations, inactive channels are more prevalent in smooth muscle cells. Alternative splicing of the alpha-1 subunit of the channel gives felodipine additional arterial selectivity. At therapeutic sub-toxic concentrations, felodipine has little effect on cardiac myocytes and conduction cells.
Clinical Use
Felodipine is used inthe treatment of angina and mild-to-moderate essential hypertension.Felodipine, like most of the dihydropyridines,exhibits a high degree of protein binding and has a half-liferanging from 10 to 18 hours.
Metabolism
Hepatic metabolism primarily via cytochrome P450 3A4. Six metabolites with no appreciable vasodilatory effects have been identified.
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Todd and Faulds, (1992)?Felodipine. A review of the pharmacology and therapeutic use of the extended release formulation in cardiovascular disorders; Drugs?44?251 2) Furukawa?et al. (1999)?Selectivities of Dihydropyridine Derivatives in Blocking Ca2+ Channel Subtypes Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.?291?464
Properties of Felodipine
| Melting point: | 142-145°C |
| Boiling point: | 471.5±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.3506 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 28 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 2.73±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | light yellow |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19Cl2NO4/c1-5-25-18(23)14-10(3)21-9(2)13(17(22)24-4)15(14)11-7-6-8-12(19)16(11)20/h6-8,15,21H,5H2,1-4H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72509-76-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Felodipine(72509-76-3) |
Safety information for Felodipine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Felodipine
| InChIKey | RZTAMFZIAATZDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C)NC(C)=C(C(OC)=O)C(C2=CC=CC(Cl)=C2Cl)C=1C(OCC)=O |
Felodipine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


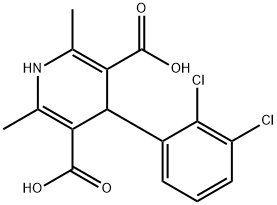
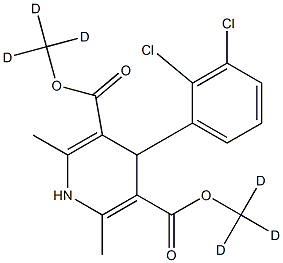
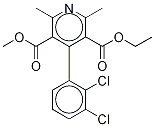
You may like
-
 72509-76-3 Felodipine 99%View Details
72509-76-3 Felodipine 99%View Details
72509-76-3 -
 Felodipine 98%View Details
Felodipine 98%View Details
72509-76-3 / 86189-69-7 -
 Felodipine 72509-76-3 / 86189-69-7 99%View Details
Felodipine 72509-76-3 / 86189-69-7 99%View Details
72509-76-3 / 86189-69-7 -
 Felodipine 98%View Details
Felodipine 98%View Details
72509-76-3 / 86189-69-7 -
 Felodipine CAS 72509-76-3View Details
Felodipine CAS 72509-76-3View Details
72509-76-3 -
 Felodipine 98% CAS 72509-76-3View Details
Felodipine 98% CAS 72509-76-3View Details
72509-76-3 -
 Felodipine CAS 72509-76-3View Details
Felodipine CAS 72509-76-3View Details
72509-76-3 -
 Felodipine Api PowderView Details
Felodipine Api PowderView Details
72509-76-3
