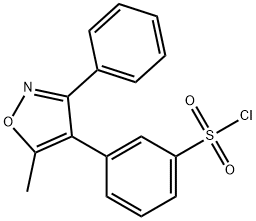
Parecoxib
Synonym(s):N-[[4-(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)phenyl]sulfonyl]propanamide;N-{[4-(5-Methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl]sulfonyl}propionamide
- CAS NO.:1709956-95-5
- Empirical Formula: C16H12ClNO3S
- Molecular Weight: 333.79
- Update Date: 2024-03-19 15:37:50
What is Parecoxib?
The Uses of Parecoxib
3-(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonyl Chloride is an Impurity of Parecoxib Sodium (P193275), an anti-inflammatory, analgesic.
The Uses of Parecoxib
Anti-inflammatory; analgesic (cyclooxygenase COX-2 inhibitor).
Clinical Use
Parecoxib is a pro-drug of valdecoxib administered IM or IV for perioperative analgesic and anti-inflammatory use. As a pro-drug, it undergoes rapid in vivo hydrolysis to valdecoxib.Parecoxib at greater than 20 mg has analgesic activity superior to that of placebo and similar to that of parenteral 30 or 60 mg of ketorolac in patients with postoperative dental pain. A significant adverse effect is drug hypersensitivity. Parecoxib is currently marketed worldwide but has not been approved for use in the United States.
Synthesis
The acylation of 4-(5-methyl- 3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide (valdecoxib), with propionic anhydride in a solution of triethanolamine (TEA) and 4-dimethylaminophenol (DMAP) in tetrahydrofuran gives N-propionamide, which is treated with NaOH in ethanol to give the sodium salt of parecoxib .
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possible increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparin, dabigatran and edoxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlafaxine.
Antidiabetics: possibly enhanced effect of
sulphonylureas.
Antiepileptics: possibly enhanced effect of phenytoin.
Antifungals: if used with fluconazole reduce the dose
of parecoxib.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: potential for increased risk of
nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate,
(possible increased risk of toxicity); increased risk of
bleeding with erlotinib.
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity; possible
antagonism of diuretic effect; increased risk of
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: reduced excretion of lithium (risk of
toxicity).
Pentoxifylline: possibly increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Parecoxib is rapidly and almost completely converted to
valdecoxib and propionic acid.
Elimination of valdecoxib
is by extensive hepatic metabolism involving multiple
pathways, including cytochrome P 450 (CYP) 3A4 and
CYP2C9 isoenzymes and glucuronidation (about 20%) of
the sulphonamide moiety.
Excretion is mainly via the urine with about 70% of a dose
appearing as inactive metabolites. No unchanged parecoxib is
found in the urine with only trace amounts in the faeces.
Properties of Parecoxib
| Melting point: | 165-167°C |
| Boiling point: | 459.4±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.340±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | -3.44±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Parecoxib
Computed Descriptors for Parecoxib
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
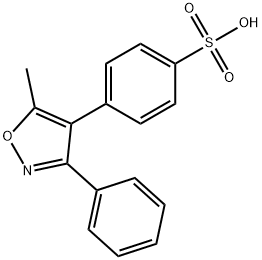
![4-[(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)methyl]benzenesulfonamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/1391052-01-9.gif)

You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
