p-Cresol
Synonym(s):p-Cresol;4-Methylphenol;4-Methylphenol solution;p-Cresol;p-Cresol solution
- CAS NO.:106-44-5
- Empirical Formula: C7H8O
- Molecular Weight: 108.14
- MDL number: MFCD00002376
- EINECS: 203-398-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:52
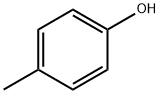
What is p-Cresol?
Chemical properties
Cresol is a mixture of three isomeric forms: o-, m-, and p-cresol. These compounds are slightly soluble in water. The m-isomer is a colorless or yellow liquid with characteristic odor. The p-cresol is a colorless to pink crystals with a characteristics phenol-like odor. The concentration at which the odor becomes detectable in water is 55 parts per billion (Buttery et al., 1988). Another study by Leonardos et al. (1969) reported an experimental odor threshold concentration of 1 parts per billion, which is higher than the 0.054 parts per billion reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
Occurrence
Has been found in a score of essential oils including ylang ylang and oil of jasmine (Gildemeister & Hoffman, 1966).
The Uses of p-Cresol
p-Cresol is used in the synthesis of Bupranolol (B689650), a non-selective beta blocker.
The Uses of p-Cresol
p-Cresol is utilized in the production of artificial resins, liquid crystal intermediates, disinfectants, fumigants, and as an industrial solvent. It is also involved in the manufacturing of Bupranolol, a non-selective beta blocker.
Definition
ChEBI: P-cresol is a cresol that consists of toluene substituted by a hydroxy group at position 4. It is a metabolite of aromatic amino acid metabolism produced by intestinal microflora in humans and animals. It has a role as a uremic toxin, a human metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite.
Preparation
It can be prepared by fractional distillation of coal tar where it occurs together with the ortho- and para- isomers.
Production Methods
The cresols (cresylic acids) are methyl phenols and generally appear as a mixture of isomers. p-Cresol is a 4-methyl derivative of phenol and is prepared from m-toluic acid or obtained from coal tar or petroleum. Crude cresol is obtained by distilling “gray phenic acid” at a temperature of ~180–201°C. p-Cresol may be separated from the crude or purified mixture by repeated fractional distillation in vacuo. It can also be prepared synthetically by diazotization of the specific toluene or by fusion of the corresponding toluenesulfonic acid with sodium hydroxide.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 55 to 100 ppb.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 81, p. 4230, 1959 DOI: 10.1021/ja01525a028
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31, p. 749, 1983 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.31.749
Tetrahedron Letters, 21, p. 3731, 1980 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(80)80164-X
General Description
Colorless solid with a tar like odor. Sinks and mixes slowly with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
p-Cresol is sensitive to heat. p-Cresol is also sensitive to light. p-Cresol is incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong alkalis. p-Cresol will attack some forms of plastics, coatings and rubber.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: Irritation of nose or throat. EYES: Intense irritation and pain, swelling of conjunctiva and corneal damage may occur. SKIN: Intense burning, loss of feeling, white discoloration and softening. Gangrene may occur. INGESTION: Burning sensation in mouth and esophagus. Vomiting may result. Absorption by all routes may cause muscular weakness, gastroenteric disturbance, severe depression and collapse. Effects are primarily on central nervous system, edema of lungs, injury of spleen and pancreas may occur.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. A severe skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data by itself and with 7,12-dirnethyl benz(a)anthracene. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Moderately explosive in the form ofvapor when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical, alcohol foam. See also other cresol entries and PHENOL.
Potential Exposure
Cresol is used as a disinfectant and fumigant; as an ore flotation agent, and as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals, dyes, plastics, and antioxidants. A mixture of isomers is generally used; the concentrations of the components are determined by the source of the cresol.
Carcinogenicity
o-Cresol has been induced a few papillomas but no carcinomas in tumor studies.
Source
As 3+4-methylphenol, detected in distilled water-soluble fractions of 87 octane gasoline
(6.03 mg/L), 94 octane gasoline (0.60 mg/L), Gasohol (1.76 mg/L), No. 2 fuel oil (1.84 mg/L), jet
fuel A (0.43 mg/L), diesel fuel (1.318 mg/L), and military jet fuel JP-4 (0.92 mg/L) (Potter, 1996).
A high-temperature coal tar contained 4-methylphenol at an average concentration of 0.27 wt %
(McNeil, 1983).
Occurs naturally in brown juniper, Spanish cedar, peppermint (2 to 20 ppb), tarragon, asparagus
shoots, ylang-ylang, jasmine, tea leaves, coffee beans, Japanese privet, white mulberries,
raspberries, vanilla, blueberries, sour cherries, anise, and tamarind (Duke, 1992).
A liquid swine manure sample collected from a waste storage basin contained 4-methylphenol
at a concentration of 4.9 mg/L (Zahn et al., 1997).
Metabolism
p-Cresol is oxidized at the methyl group in both dogs and rabbits to yield ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid. In the rabbit up to 10% of oral doses of 0.25-0.5 g is excreted as free and conjugated p-hydroxybenzoic acid (Williams, 1959).
Shipping
UN2076 Cresols, liquid, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 8-Corrosive material. UN3455 Cresols, solid, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1- Poisonous materials, 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
It can be separated from m-cresol by fractional crystalisation of its melt. Purify it by distillation, by precipitation from *benzene solution with pet ether, and via its benzoate, as for phenol. Dry it under vacuum over P2O5. It has also been crystallised from pet ether (b 40-60o) and by conversion to sodium p-cresoxyacetate which, after crystallisation from water is decomposed by heating with HCl in an autoclave [Savard Ann Chim (Paris) 11 287 1929]. The 3,5-dinitrobenzoate (prepared with 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride in dry pyridine, and recrystallised from EtOH or aqueous Me2CO) has m 189o. [Beilstein 6 II 2093.]
Incompatibilities
Vapors may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with strong acids; oxidizers, alkalies, aliphatic amines; amides, chlorosulfonic acid; oleum. Decomposes on heating, producing strong acids and bases, causing fire and explosion hazard. Liquid attacks some plastics and rubber. Attacks many metals.
Waste Disposal
Wastewaters may be subjected to biological treatment. Concentrations may be further reduced by ozone treatment. High concentration wastes may be destroyed in special waste incinerators.
Properties of p-Cresol
| Melting point: | 32-34 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 202 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.034 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.72 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.5395 |
| FEMA | 2337 | P-CRESOL |
| Flash point: | 193 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 20g/l |
| form | Crystalline Solid or Liquid |
| pka | 10.17(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.0341 (20/4℃) |
| color | Colorless to light yellow, may darken on exposure to light |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in dipropylene glycol. phenolic narcissus animal mimosa |
| Odor Threshold | 0.000054ppm |
| explosive limit | 1%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 20 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2579 |
| JECFA Number | 693 |
| BRN | 1305151 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 6.17 at 20.00 °C, 9.31 at 25.00 °C (dynamic equilibrium system-GC, Feigenbrugel et al., 2004a) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 2.3 ppm (10 mg/m3), IDLH 250 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 5
ppm (22 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA for all isomers 5 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 5.6(21.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Air and light-sensitive. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 106-44-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol, 4-methyl-(106-44-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | p-Cresol (106-44-5) |
Safety information for p-Cresol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for p-Cresol
p-Cresol manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 p-Cresol supplierView Details
p-Cresol supplierView Details
106-44-5 -
 p-Cresol pure CAS 106-44-5View Details
p-Cresol pure CAS 106-44-5View Details
106-44-5 -
 Para Cresol CASView Details
Para Cresol CASView Details -
 p-Cresol 98% CAS 106-44-5View Details
p-Cresol 98% CAS 106-44-5View Details
106-44-5 -
 Crystals Paracresol (106-44-5), Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, 25 kgView Details
Crystals Paracresol (106-44-5), Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, 25 kgView Details
106-44-5 -
 Para-Cresol , (4-Methylphenol), Purity: 96% - 98%View Details
Para-Cresol , (4-Methylphenol), Purity: 96% - 98%View Details
106-44-5 -
 PARA CRESOL (CAS NO 106-44-5)View Details
PARA CRESOL (CAS NO 106-44-5)View Details
106-44-5 -
 Para CresolView Details
Para CresolView Details
106-44-5
