OLIGOMYCIN
Synonym(s):Oligomycin - CAS 1404-19-9 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:1404-19-9
- Empirical Formula: C135H220O33
- Molecular Weight: 2371.1715
- MDL number: MFCD01779388
- EINECS: 215-767-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 20:41:25
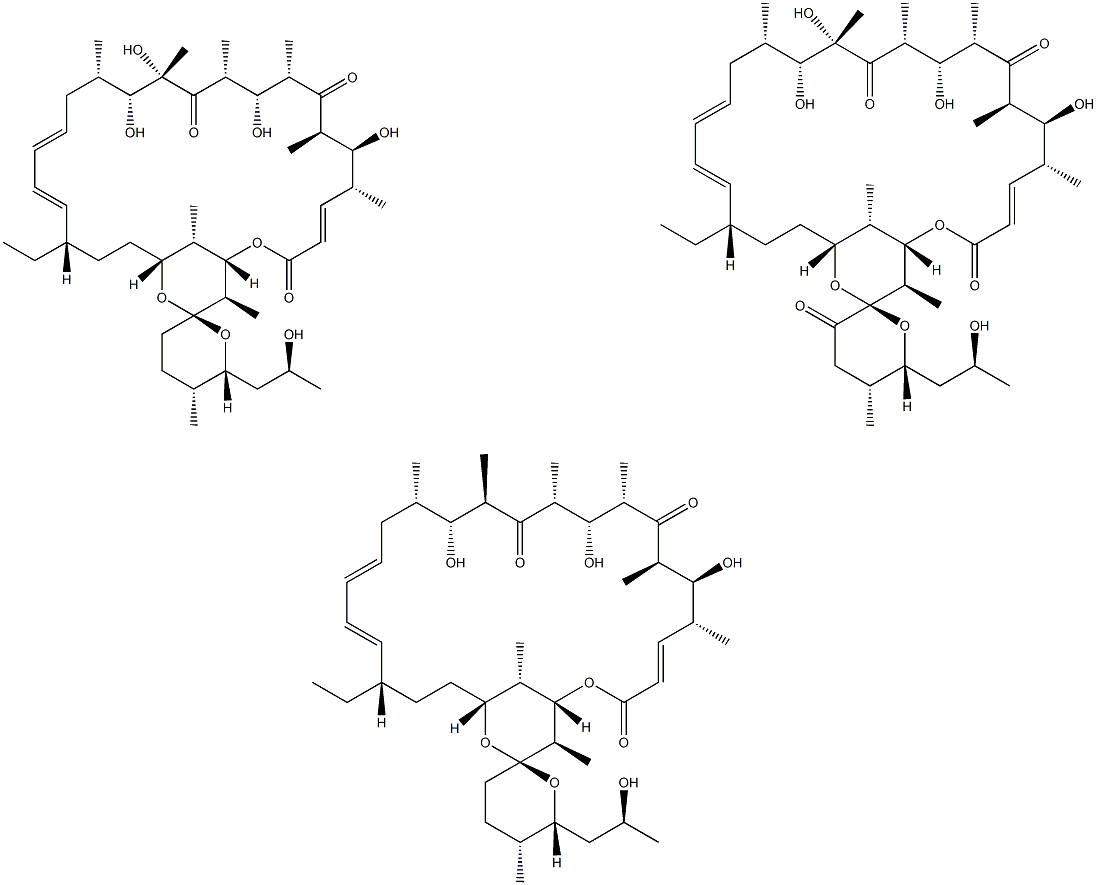
What is OLIGOMYCIN?
Description
Oligomycin (1404-19-9) inhibits mitochondrial F1F0?ATP synthase.1?A useful tool for decreasing cellular ATP levels.2?Induces autophagy.3?Stimulates lysosome acidification.4?Oligomycin protects against ischemic kidney in male rats.5
Chemical properties
White to pale yellow powder
The Uses of OLIGOMYCIN
Oligomycin is a specific inhibitor of the mitochondrial ATP-synthase.
What are the applications of Application
Oligomycin is an oxidative phosphorylation blocker and specific inhibitor of the mitochondrial ATP-synthase.
General Description
A mixture of A, B, and C isomers. A macrolide antibiotic that inhibits membrane-bound mitochondrial ATP synthase, preventing phosphoryl group transfer. Induces apoptosis in cultured human lymphoblastoid and other mammalian cells.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Product does not compete with ATP.
in vitro
in a549, h1299, h1975, h520, 786-0, h838, and u87mg cancer cell lines, 100 ng/ml oligomycin could completely inhibit oxphos phosphorylation activity and stimulate various levels of glycolysis gains [1]. besides, 5 μg/ml oligomycin could inhibit the f0 part of h+-atp-synthase, and strongly suppress cytochrome c release and apoptosis in hela cells induced by tnf [2]. furthermore, oligomycin could inhibit mitochondrial respiration, and sensitize melanoma cells to cisplatin treatment to inhibit cell invasion [3].
Enzyme inhibitor
These macrolide antibiotics from Streptomyces diastatochromogenes have three major members: Oligomycin A (FW = 791.08 g/mol; CAS 14104-19- 9), Oligomycin B (FW = 805.06 g/mol; CAS 11050-94-5), and Oligomycin C (FW = 775.08 g/mol; CAS 11052-72-5). Others include Oligomycin D (also known as rutamycin; FW = 777.05 g/mol; CAS 1404-59-7), Rutamycin B (isolated from Streptomyces aureofaciens (See also Rutamycin)), and Oligomycin E (FW = 822.07 g/mol; CAS 110231-34-0; isolated from Streptomyces sp. MCI-2225). Primary Mode of Inhibitory Action: The oligomycins inhibit the ATP synthesis activity of the mitochondrial FoF1 ATP synthase, defining the “o” (not 0) in the first subscript. The ATPase activity of the isolated F1 complex is unaffected by oligomycins, unlike the Fo portion. Oligomycin-sensitivity conferring ptrotein (OSCP) interacts with other components in the ATP synthase complex and facilitates oligomycin’s binding to the Fo unit. The Fo complex is, in fact, an integral membrane protein that functions as a proton channel. Other Actions: Oligomycins also inhibit Na+/K+-exchanging ATPases that transport sodium ions from the inside to the outside of animal cells while translocating potassium ions in the reverse direction with the concomitant hydrolysis of ATP. Oligomycin inhibits Na+ translocation in vivo (i.e., the enzyme activity is inhibited by stabilizing the Na+ occlusion but not the K+ occlusion). Other Properties: The oligomycins are slightly soluble in water (e.g., oligomycin A has a solubility of 2 μg per 100 mL at 25°C) and are considerable more soluble in water-miscible solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and glacial acetic acid. Target(s): aldehyde oxidase; ammonia kinase; apyrase, membrane-bound; ATP synthase, or FoF1 ATP synthase; calcidiol 1-monooxygenase; copper-exporting ATPase, partially inhibited; endopeptidase La, weakly inhibited; H+-transporting ATPase, lysosomal; Na+/K+-exchanging ATPase (24- 32); nucleoside triphosphatase; photophosphorylation in Rhodospirillum rubrum; xenobiotic-transporting ATPases.
References
1) Antoniel?et al. (2014),?The oligomycin-sensitivity conferring protein of mitochondrial ATP synthase: emerging new roles in mitochondrial pathophysiology;? J. Mol. Sci.,?15?7513 2) Ng et al. (2014),?Essential role of TID1 in maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential homogeneity and mitochondrial DNA integrity;? Mol. Cell Biol.,?34?1427 3) Tettamonti?et al. (2006),?Oligomycin A induces autophagy in the IPLB-LdFB insect cell line;? Cell Tissue Res.,?326?179 4) van Dyke?et al. (1993),?Acidification of rat liver lysosomes:quantification and comparison with endosomes;? Am. J. Physiol.,?265?C901 5) Tanaka?et al. (2013),?Oligomycin, an F1Fo-ATPase inhibitor, protects against ischemic acute kidney injury in male but not in female rats;? J. Pharmacol. Sci.,?123?227
Properties of OLIGOMYCIN
| Melting point: | 84-100 °C |
| Density | 1.143 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 300 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 200 mg/ml) |
| form | White solid |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water. Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) and ethanol (30mg/ml)
/n |
| BRN | 7615308 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for OLIGOMYCIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P330:Rinse mouth. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for OLIGOMYCIN
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Oligomycin from Streptomyces diastatochromogenes CAS 1404-19-9View Details
Oligomycin from Streptomyces diastatochromogenes CAS 1404-19-9View Details
1404-19-9 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4