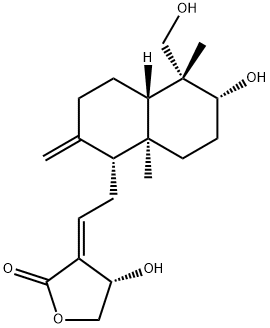
Neoandrographolide
Synonym(s):ent-19-Hydroxy-8(17),13-labdadien-16,15-olide 19-O-β-D -glucopyranoside;D -Glucopyranosyloxy)methyl]decahydro-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylene-1-naphthalenyl]ethyl]-2(5H)-furanone
- CAS NO.:27215-14-1
- Empirical Formula: C26H40O8
- Molecular Weight: 480.59
- MDL number: MFCD07779130
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
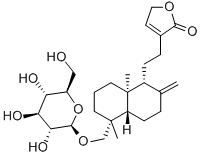
What is Neoandrographolide?
Description
Andrographic plants are derived from the aerial parts of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees and known by various vernacular names such as “chunlianqiuliu,” “yijianxi,” “lanhelian,” “kudancao,” “jinxiangcao,” “jinergou,” “India grass,” and “bitter grass.” Andrographis paniculata is planted in South and Southeast Asia, India, and Australia. This herb is also cultivated in Fujian, Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, Yunnan, Jiangsu, and Shaanxi provinces in China. Andrographis paniculata has been used to treat colds, sore throat, mouth sores, cough, diarrhea dysentery, and so on. Andrographis paniculata contains diterpene lactone compounds, and they have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. The main active ingredients include andrographolide, neoandrographolide, deoxy andrographolide, dehydrated andrographolide, and so on. Andrographis paniculata has been included by US Pharmacopeia.
Physical properties
Appearance: Neoandrographolide is a colorless column crystal that has been isolated from the stem and leaves of Andrographis paniculata. Melting point: 167– 168?°C. Specific optical rotation: ?48°(pyridine); ?45°(c?=?1, absolute ethanol). Solubility: Soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetone, and pyridine and slightly soluble in chloroform and water but insoluble in ether and petroleum ether.
History
The chemical constituents of Andrographis paniculata are mainly lactones and flavonoids, including the lactone compounds such as andrographolide and dehydrated andrographolide. In 1952, Kleipool first reported the separation of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata . In 1968 and 1971, W.?R. Chan et?al. identified the chemical structure and stereostructure of andrographolide. In the 1990s, a variety of diterpene lactones were isolated from the aerial part and the lotus leaf of Andrographis paniculata, such as andrographolide, neoandrographolide, dehydroandrographolide, deoxyandrographolid, deoxyandrographiside, 8-methylandrograpanin, 3-dehydrodeoxyandrographolide, andrograpanin, and 3-oxo-14-deoxy-andrographol,and also some flavonoids and sitosterol and daucosterol compounds . Until now, more than 40 diterpene lactone components and more than 70 flavonoids have been found from Andrographis paniculata. There are sterols, organic acids, diterpene alcohols, diterpene acid salts, and cycloalkene ether also found from Andrographis paniculata .Since the 1970s, pharmacists and organic chemists have done a lot of work on the modification of andrographolide, mainly in Michael addition of α, β-unsaturated lactone double bonds and three hydroxyl groups selective esterification, oxidation and substitution reactions, redox reduction of double bonds, intramolecular cyclization, and lactone ring replacement reactions , and the resulting andrographolide derivatives or analogues can improve the antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular system, immunomodulation, and antitumor activities.
The Uses of Neoandrographolide
Neoandrographolide is one of the principle diterpenoids isolated from A. paniculata, a well-recognized medicinal plant in Asia.
Indications
Neoandrographolide is available in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (1977).Neoandrographolide and andrographolide are the main active ingredients of a variety of pharmaceutical preparations containing the Andrographis herb, such as andrographolide capsules, andrographolide tablets, Andrographis injection, potassium dehydroandrographolide succinate injection, Andrographis tablets, Xiaoyan Lidan tablets, and Fufang chuan xin lian tablets. These drugs are mainly used for treating acute bacterial dysentery, acute gastroenteritis, upper respiratory tract infection, acute tonsillitis, pharyngitis, etc. In addition, they are also used to treat malignant hydatidiform mole and choriocarcinoma.
Pharmacology
Andrographis paniculata has detoxifying abilities, reduces swelling, and relieves pain. The four major diterpene lactones in Andrographis paniculata have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activities against 2,4-dinitrophenol or endotoxin-induced fever and egg white-induced edema or croton oil-induced inflammatory models.Animal experiments have shown that Andrographis paniculata has inhibited and delayed the body temperature elevation of persons with infections caused by pneumococcus and hemolytic streptococcus. It also can be used for treating cough and asthma and especially for treating acute bacterial dysentery, acute gastroenteritis, upper respiratory tract infection, acute tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and so on.The active ingredients andrographolide and neoandrographolide inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced NO production in the mouse peritoneal macrophages . Neoandrographolide at the high concentration can inhibit the macrophage outbreak caused by LPS and the proliferation of lymphocytes and can synergistically enhance the PMA stimulating effect on the respiratory outbreak. The possible mechanism is related to its ROS scavenging activity .
Clinical Use
Neoandrographolide is one of the main active ingredients of the natural plant Andrographis paniculata. But there is no formulation of neoandrographolide. Andrographis injection has been clinically used, but it has several side effects.
Properties of Neoandrographolide
| Melting point: | 167~168℃ |
| Boiling point: | 668.1±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.27±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 12.93±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| color | White |
Safety information for Neoandrographolide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Neoandrographolide
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Neoandrographolide CAS 27215-14-1View Details
Neoandrographolide CAS 27215-14-1View Details
27215-14-1 -
 Neoandrographolide CAS 27215-14-1View Details
Neoandrographolide CAS 27215-14-1View Details
27215-14-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8