Nalidixic acid
Synonym(s):1,4-Dihydro-1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one-3-carboxylic acid;1-Ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:389-08-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H12N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 232.24
- MDL number: MFCD00006884
- EINECS: 206-864-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
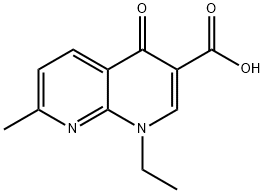
What is Nalidixic acid?
Absorption
Following oral administration, nalidixic acid is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is approximately 96%. Absorption may be delayed if taken with antacids.
Toxicity
ORAL (LD50): Acute: 1160 mg/kg [Rat]. 572 mg/kg [Mouse]. Toxic psychosis, convulsions, increased intracranial pressure, or metabolic acidosis may occur in patients taking more than the recommended dosage. Vomiting, nausea, and lethargy may also occur following overdosage.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Powder
Originator
Neggram,Winthrop,US,1964
The Uses of Nalidixic acid
Nalidixic acid(NegGram) is a synthetic 1,8-naphthyridine antimicrobial agent with a limited bacteriocidal spectrum. It is an inhibitor of the A subunit of bacterial DNA gyrase. Evidence exists that the active metabolite, hydroxynalidixic acid, binds stron
The Uses of Nalidixic acid
Quinolone antibacterial.
The Uses of Nalidixic acid
For the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms, including the majority of E. Coli, Enterobacter species, Klebsiella species, and Proteus species.
Indications
For the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms, including the majority of E. Coli, Enterobacter species, Klebsiella species, and Proteus species.
Background
Nalidixic acid is a synthetic 1,8-naphthyridine antimicrobial agent with a limited bacteriocidal spectrum. It is an inhibitor of the A subunit of bacterial DNA gyrase.
What are the applications of Application
Nalidixic acid is an inhibitor of bacterial DNA polymerase
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid comprising 1,8-naphthyridin-4-one substituted by carboxylic acid, ethyl and methyl groups at positions 3, 1, and 7, respectively.
Manufacturing Process
A warm solution containing 41 grams of 4-hydroxy-7-methyl-1,8-
naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid and 39 grams of potassium hydroxide in 1
liter of ethanol and 200 cc of water was treated with 50 cc of ethyl iodide and
the resulting mixture was refluxed gently overnight, acidified with hydrochloric
acid and cooled. The resulting precipitate was collected and recrystallized
twice from acetonitrile to yield 26 grams (56% yield) of 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-
oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid, MP 229° to 230°C.
The starting material is prepared by reacting 2-amino-6-methylpyridine with
ethoxymethylene-malonic acid diethyl ester and then reacting that product
with sodium hydroxide.
brand name
Neggram(Sanofi Aventis).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
It displays good activity in vitro against a wide range of Enterobacteriaceae.
General Description
Cream-colored powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Ingestion of Nalidixic acid may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, allergic reactions and possible liver damage.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Nalidixic acid are not available, but Nalidixic acid is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A 1,8 naphthyridone derivative available for oral administration.
Pharmacokinetics
Nalidixic acid is a quinolone antibacterial agent for oral administration. Nalidixic acid has marked antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria including Enterobacter species, Escherichia coli, Morganella Morganii; Proteus Mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Providencia rettgeri. Pseudomonas species are generally resistant to the drug. Nalidixic acid is bactericidal and is effective over the entire urinary pH range. Conventional chromosomal resistance to nalidixic acid taken in full dosage has been reported to emerge in approximately 2 to 14 percent of patients during treatment; however, bacterial resistance to nalidixic acid has not been shown to be transferable via R factor.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: >90%
Cmax 1 g oral: c. 25 mg/L
Plasma half-life:c.1.5h
Volume of distribution :0.4 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 93%
The plasma concentrations achieved after oral administration vary widely. In infants with acute shigellosis, absorption is much impaired by diarrhea. Administration with an alkaline compound leads to higher plasma concentrations, partly as the result of enhanced solubility (nalidixic acid is much more soluble at higher pH) and absorption and partly because of reduced tubular reabsorption.
It is rapidly metabolized, principally to the hydroxy acid, which is bacteriologically active, and glucuronide conjugates, which are not. The entire administered dose appears in the urine over a 24 h period. Elimination is reduced by probenecid. In the presence of renal impairment there is little accumulation of the active compound because it continues to be metabolized. However, elimination of metabolites is progressively delayed as renal function declines. About 4% of a dose appears in the feces.
Clinical Use
1-Ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid (NegGram) occurs as a pale buff crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and ether but solublein most polar organic solvents.Nalidixic acid is useful in the treatment of urinary tractinfections in which Gram-negative bacteria predominate.The activity against indole-positive Proteus spp. is particularlynoteworthy, and nalidixic acid and its congeners representimportant alternatives for the treatment of urinary tractinfections caused by strains of these bacteria resistant toother agents. Nalidixic acid is rapidly absorbed, extensivelymetabolized, and rapidly excreted after oral administration.The 7-hydroxymethyl metabolite is significantly more activethan the parent compound. Further metabolism of theactive metabolite to inactive glucuronide and 7-carboxylicacid metabolites also occurs. Nalidixic acid possesses at1/2elim of 6 to 7 hours. It is eliminated, in part, unchanged inthe urine and 80% as metabolites.
Side Effects
Adverse reactions are generally those common to all quinolones: gastrointestinal tract and CNS disturbances and skin rashes, including eruptions related to photosensitivity. About half of the reported CNS reactions involve visual disturbances, hallucinations or disordered sensory perception. Severe excitatory states, including acute psychoses and convulsions, are usually observed in patients receiving high dosages. The drug should be avoided in patients with psychiatric disorders or epilepsy.
Acute intracranial hypertension has been observed in children, some of whom have also manifested cranial nerve palsies. Hemorrhage has occurred in patients who were also receiving warfarin, presumably due to displacement of the anticoagulant from its protein binding sites by the nalidixic acid. Hemolytic anemia has been described several times in infants with or without glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; in adults, death has occurred from autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Arthralgia and severe metabolic acidosis have rarely been reported.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects: convulsions, hyperglycemia, sweating, and blood changes in children. Experimental reproductive effects.Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. Used as an antibacterial agent and urinary tract antiseptic. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Synthesis
Nalidixic acid, 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthiridin-3- carboxylic acid (33.2.4), is synthesized by the following scheme. In the first stage, the reaction of 2-amino-6-methylpyridine and diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate forms the substituted product (33.2.1), which when heated cyclizes to ethyl ester of 4-hydroxy -7-methyl-1,8-napthiridin-3-carboxylic acid (33.2.2). Hydrolyzing the resulting product with a base gives the corresponding acid (33.2.3). Alkylating this with ethyl iodide in the presence of potassium hydroxide gives nalidixic acid.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline and theophylline: possibly increased
risk of convulsions.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
NSAIDs.
Antibacterials: possibly antagonised by
nitrofurantoin.
Anticoagulants: anticoagulant effect of coumarins
enhanced.
Antimalarials: manufacturer of artemether with
lumefantrine advises avoid.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increases risk of melphalan toxicity
Metabolism
Hepatic. 30% of administered dose is metabolized to the active metabolite, hydroxynalidixic acid. Rapid conjugation of parent drug and active metabolite to inactive metabolites. Metabolism may vary widely among individuals. In the urine, hydroxynalidixic acid represents 80 to 85% of the antibacterial activity.
Metabolism
Nalidixic acid is partially metabolised in the liver to hydroxynalidixic acid, which has antibacterial activity similar to that of nalidixic acid and accounts for about 30% of active drug in the blood. Both nalidixic acid and hydroxynalidixic acid are rapidly metabolised to inactive glucuronide and dicarboxylic acid derivatives; the major inactive metabolite 7-carboxynalidixic acid is usually only detected in urine.
Purification Methods
Nalidixic acid crystallises from H2O or EtOH as a pale buff powder. It is soluble at 23o in CHCl3 (3.5%), toluene (0.16%), MeOH (0.13%), EtOH (0.09%), H2O (0.01%) and Et2O (0.01%). It inhibits nucleic acid and protein synthesis in yeast. [Lesher et al. J Med & Pharm Chem 5 1063 1962.]
Properties of Nalidixic acid
| Melting point: | 227-229 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 374.4°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2243 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6660 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | chloroform: 20 mg/mL, clear |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pKa 6.11± 0.02(Approximate) |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 0.1 G/L (23 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6359 |
| BRN | 750515 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 389-08-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nalidixic acid (389-08-2) |
Safety information for Nalidixic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Nalidixic acid
Nalidixic acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Nalidixic acid 98%View Details
Nalidixic acid 98%View Details -
 Nalidixic acid 389-08-2 98%View Details
Nalidixic acid 389-08-2 98%View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
Nalidixic acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic Acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
Nalidixic Acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic acid 95% CAS 389-08-2View Details
Nalidixic acid 95% CAS 389-08-2View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 389-08-2View Details
Nalidixic acid 99% (HPLC) CAS 389-08-2View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
Nalidixic acid CAS 389-08-2View Details
389-08-2 -
 Nalidixic Acid Powder, USPView Details
Nalidixic Acid Powder, USPView Details
389-08-2
