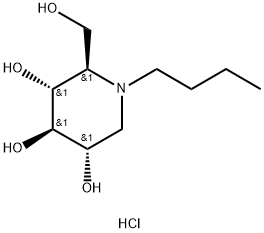
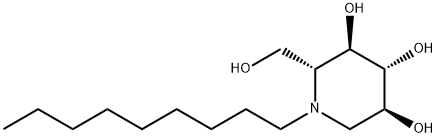
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
Synonym(s):Miglustat;NB-DNJ;NB-DNJ, HCl, N-Butyl-DNJ, HCl;N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin, Hydrochloride - CAS 72599-27-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:72599-27-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H21NO4
- Molecular Weight: 219.28
- MDL number: MFCD00272581
- EINECS: 207-526-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22

What is N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin ?
Absorption
Mean oral bioavailability is 97%.
Toxicity
Miglustat has been administered at doses of up to 3000 mg/day (approximately 10 times the recommended starting dose administered to Gaucher patients) for up to six months in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-positive patients. Adverse events observed in the HIV studies included granulocytopenia, dizziness, and paresthesia. Leukopenia and neutropenia have also been observed in a similar group of patients receiving 800 mg/day or above.
Description
Miglustat is an N-alkylated iminosugar, launched as an oral treatment for mild to moderate type 1 Gaucher’s disease in adult patients for whom enzyme replacement therapy is not a therapeutic option. It is readily synthesized from D-glucose in three steps by first converting to N-butylglucamine via reductive amination with butylamine, followed by a microbial oxidation to an aminofuranose intermediate and subsequent reductive cyclization. Type 1 Gaucher’s disease is a metabolic disorder caused by the lysosomal accumulation of certain glycosphingolipids (GSLs) as a result of deficiency in their degradation. Enlargement of the liver and spleen, low blood platelet and bone lesions are among the key symptoms of this disease. Miglustat acts by inhibiting glucosylceramide synthase, a glucosyl transferase enzyme in the biosynthesis of most GSLs, which results in the lowering of GSLs to a level that can be effectively cleared. Up to 50% reduction in liver and splenocyte GSL levels are achieved in mice by long-term administration of Miglustat (600– 1800 mg/kg/day for 118 days). Miglustat, dosed at 50 and 100 mg in Gaucher patients, exhibits dose proportionate pharmacokinetics (tmax=2.5 h, t1/2=6 to 7 h) and >90% oral bioavailability. Steady-state plasma levels are reached after 4–6 weeks of treatment. Miglustat is not significantly metabolized in humans and the major route of excretion is renal. In clinical trials, efficacy was demonstrated by significant reductions in liver and spleen volumes (12 and 19%, respectively) at 12 months and increase in hemoglobin and platelet count (0.91 g/dL and 13.6×109/l, respectively) at 24 months. Miglustat is generally well tolerated by patients and the most common side effects are diarrhea and weight loss.
Originator
G.D. Searle (Pfizer) (US)
The Uses of N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
Treatment of glycolipid storage diseases.
The Uses of N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
An alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor
Background
Miglustat, commonly marketed under the trade name Zavesca, is a drug used to treat Gaucher disease. It inhibits the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase, an essential enzyme for the synthesis of most glycosphingolipids. It is only used for patients who cannot be treated with enzyme replacement therapy with imiglucerase. Miglustat is now the first and only approved therapy for patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C). It has recently been approved for treatment of progressive neurological symptoms in adult and pediatric patients in the European Union, Brazil, and South Korea. Miglustat was first developed as an anti-HIV agent in the 1990s. However, clinical experience with miglustat showed that therapeutic levels of the drug could not be achieved in patients without a high incidence of adverse effect.
Indications
For the treatment of adult patients with mild to moderate type 1 (nonneuropathic) Gaucher's disease for whom enzyme replacement therapy is not a therapeutic option (e.g. due to constraints such as allergy, hypersensitivity, or poor venous access). Now approved in some countries for the treatment of progressive neurological symptoms in adult and pediatric patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C).
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxypiperidine that is deoxynojirimycin in which the amino hydrogen is replaced by a butyl group.
brand name
Zavesca(Actelion);Vevesca.
General Description
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin is an alkylated product of imino sugar deoxynojirimycin.
Biological Activity
Orally active α -glucosidase I and II and ceramide-specific glycosyltransferase inhibitor. Rescues trafficking-deficient F508del-CTFR in human airway epithelial cells via inhibition of ER α -glucosidases I and II. Also has broad spectrum antiviral activity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin is an inhibitor of glucosyltransferase and α-glucosidases. N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin, also known as misglustat, reduces glycolipid levels by substrate reduction therapy (SRT) and is effectively used for the treatment of glycosphingolipid lysosomal storage disorder, Gaucher disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Miglustat, an N-alkylated imino sugar, is a synthetic analogue of D-glucose. Miglustat is an inhibitor of the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase, which is a glucosyl transferase enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of glucosylceramide (glucocerebroside). Glucosylceramide is a substrate for the endogenous glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme that is deficient in Gaucher's disease. The accumulation of glucosylceramide due to the absence of glucocerebrosidase results in the storage of this material in the lysosomes of tissue macrophages, leading to widespread pathology due to infiltration of lipid-engorged macrophages in the viscera, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. This results in secondary hematologic consequences including sever anemia and thrombocytopenia, in addition to the characteristic progressive hepatosplenomegaly, as well as skeletal complications including osteonecrosis and osteopenia with secondary pathological fractures.
Metabolism
There is no evidence that miglustat is metabolized in humans.
Properties of N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
| Melting point: | 126-127℃ |
| Boiling point: | 394.7±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 -15.9° (c = 0.77 in water) |
| Density | 1.234 |
| RTECS | TN4350150 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO 44 mg/mL (200.66 mM) Ethanol 22 mg/mL (100.33 mM) Water 44 mg/mL (200.66 mM) |
| pka | 13.72±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water at 10mg/ml |
Safety information for N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin
| InChIKey | UQRORFVVSGFNRO-UTINFBMNSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd
Apothecon Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 72599-27-0 Miglustat 98%View Details
72599-27-0 Miglustat 98%View Details
72599-27-0 -
 72599-27-0 99%View Details
72599-27-0 99%View Details
72599-27-0 -
 Miglustat 98%View Details
Miglustat 98%View Details
72599-27-0 -
 Miglustat 72599-27-0 98%View Details
Miglustat 72599-27-0 98%View Details
72599-27-0 -
 72599-27-0 Miglustat 98%View Details
72599-27-0 Miglustat 98%View Details
72599-27-0 -
 N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin CAS 72599-27-0View Details
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin CAS 72599-27-0View Details
72599-27-0 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4