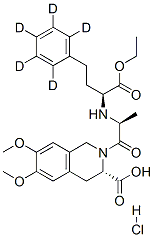
MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Synonym(s):(3S)-2-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-(Ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:82586-52-5
- Empirical Formula: C27H35ClN2O7
- Molecular Weight: 535.03
- MDL number: MFCD00940481
- EINECS: 617-363-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 14:33:46
What is MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE?
Description
Moexipril hydrochloride is a novel ACE inhibitor first marketed in the U.S.A. for the treatment of hypertension as a monotherapy and as a second-line therapy in combination with diuretics or calcium antagonists. Like other ACE inhibitors, moexipril is a prodrug that is converted in the liver to its diacid moexiprilat which is the active agent. Moexipril displays a higher in vitro inhibitory potency to ACE than enalapril although its effectiveness in reduction of blood pressure in hypertensive patients is similar to that seen with enalapril. It is orally active with a rapid onset and prolonged duration of action. Excellent tolerability has been reported. Moexipril is distinguished by its lower cost than other marketed ACE inhibitors.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Warner-Lambert (U.S.A.)
The Uses of MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor; dimethoxy analog of quinapril
The Uses of MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Moexipril HCl is a potent orally active non-sulfhydryl angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE) with IC50 of 0.041 μM, which is used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure
What are the applications of Application
Moexipril-d5 is a deuterated inhibitor of ACE
What are the applications of Application
Moexipril hydrochloride is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Moexipril hydrochloride is a dipeptide.
Manufacturing Process
1) A solution of 2.0 g of t-butyl alanine (S-form) and 3.78 g of ethyl 2-bromo-
4-phenylbutanoate in 25 ml of DMF was treated with 1.8 ml of triethylamine
and the solution was heated at 70°C for 18 hours. The solvent was removed
at reduced pressure and the residue was mixed with water and extracted with
ethyl ether. The organic layer was washed with water and dried over
magnesium sulfate. Concentration of the solvent at reduced pressure gave the
oily ethyl-α-[(1-carboxyethyl)amino]benzene-t-butanoate.
A solution of 143.7 g of this t-butyl ester in 630 ml of trifluoroacetic acid was
stirred at room temperature for one hour. The solvent was removed at
reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in ethyl ether and again
evaporated. This operation was repeated. Then the ether solution was treated
dropwise with a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in ethyl ether until
precipitation ceased. The solid, collected by filtration, was a mixture of
diastereoisomers of ethyl-α-[(1-carboxyethyl)amino]benzenebutanoate
hydrochloride, melting point 153-165°C; [α]D23 = +3.6° (1% MeOH).
The free amino acid (S,S-form) was prepared by treatment of an aqueous
solution of the hydrochloride with saturated sodium acetate. The product was
filtered, washed efficiently with cold water and recrystallized from ethyl
acetate; melting point 149-151°C; [α]D23 = +29.7°.
2) A stirred solution of 0.0158 mole of ethyl-α-[(1-carboxyethyl)amino]
benzenebutanoate hydrochloride in 200 ml of methylene chloride was treated
successively with 1.60 g (0.0158 mole) of triethylamine, 0.0158 mole of 1-
hydroxybenzotriazole, 0.0158 mole of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-
isoquinolinecarboxylic acid and then with 0.0158 mole of
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in 10 ml of methylene dichloride. Dicyclohexylurea
gradually separated. The mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature
overnight. Hexane (300 ml) was added and the urea was filtered. The filtrate
was washed with 250 ml of saturated sodium bicarbonate, dried over sodium
sulfate and concentrated to remove solvent. The viscous residue was
triturated with 50 ml of ether and filtered to remove insolubles. The filtrate
was concentrated to give 2-[2-[[1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-
oxopropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic acid.
After addition of hydrochloric acid was obtained 2-[2-[[1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-
phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-
isoquinolinecarboxylic acid, hydrochloride.
brand name
Univasc (Schwarz Pharma).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
Hazard
Moderately toxic by ingestion.
Biological Activity
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor that is hydrolyzed in the liver to the active metabolite moexiprilat (IC 50 values are 2.1 and 2700 nM for moexiprilat and moexipril respectively). Antihypertensive; decreases mean blood pressure in the spontaneous hypertensive rat (SHR). Also blocks degradation of bradykinin into inactive metabolites.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor:
Hypertension
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia,
hypotension and renal failure with ARB’S and
aliskiren.
Bee venom extract: possible severe anaphylactoid
reactions when used together.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of angioedema with
everolimus.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Gold: flushing and hypotension with sodium
aurothiomalate.
Lithium: reduced excretion (possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity).
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Moexipril is a prodrug that is converted to an active metabolite, moexiprilat in the gastrointestinal mucosa and liver. Moexipril is excreted mainly in the urine as moexiprilat, unchanged drug, and other metabolites; some moexiprilat may also be excreted in the faeces.
Properties of MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
| Melting point: | 141-1610C |
| alpha | D23 +34.2° (c = 1.1 in ethanol) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble32mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for MOEXIPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
82586-52-5 -
 Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
82586-52-5 -
 Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
Moexipril hydrochloride CAS 82586-52-5View Details
82586-52-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
