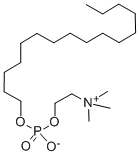
Miltefosine
Synonym(s):Choline hexadecyl phosphate;HePC;HePC, 1-Hexadecylphosphorylcholine;Hexadecyl phosphocholine;Miltefosine - CAS 58066-85-6 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:58066-85-6
- Empirical Formula: C21H46NO4P
- Molecular Weight: 407.57
- MDL number: MFCD00133396
- EINECS: 622-572-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is Miltefosine?
Absorption
After oral administration, miltefosine is slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with an absolute bioavailability of 82% in rats and 94% in dogs. Absolute bioavailability has not been assessed in humans, however GI absorption rate in a two-compartment model is estimated to be 0.416 hr-1.
Toxicity
Preclinical reproductive toxicity studies in animals showed fetal death and teratogenicity at doses lower than the recommended human dose. Use of miltefosine during pregnancy is therefore strictly contraindicated, and contraceptive use is mandatory for females of child-bearing age during therapy and for 5 months afterwards. Preclinical studies additionally showed impaired female and male fertility in animals. Stevens-Johnson syndrome has been reported, therefore therapy should be discontinued if an exfoliative or bullous rash occurs during treatment.
Description
Miltefosin, representing the prototype of a new phospholipid structure, was introduced for the palliative treatment of skin metastases in patients with breast cancer. It is highly active against the human leukemia tumor cells xenograft in nude mice, leading to growth inhibition and regression of large established tumors. Its mode of antitumor activity is not mediated by the host immune system but by its pharmacological effects at the level of the cancer cell membrane, distinctly different from that of the classical cytostatic drugs which interact with cell proliferation at the level of DNA replication. Protein kinase C inhibition has been suggested as a possible mechanism.
Originator
Asta Medica (Germany)
The Uses of Miltefosine
A phospholipid drug with antineoplastic and antiprotozoal/antifungal properties, also acts as an Akt inhibitor, and under investigation as a potential therapy against HIV infection.
Indications
For the treatment of mucosal (caused by Leishmania braziliensis), cutaneous (caused by L. braziliensis, L. guyanensis, and L. panamensis), and visceral leishmaniasis (caused by L. donovani). In comparing Leishmania drug susceptibility, it has been found that L. donovani is the most susceptible to miltefosine while L. major is the least susceptible. Off-label use includes treatment of free-living amebae (FLA) infections (unlabeled use; CDC, 2013).
Background
Miltefosine is a broad spectrum antimicrobial, anti-leishmanial, phospholipid drug that was originally developed in the 1980s as an anti-cancer agent. It is currently the only recognized oral agent used to treat visceral, cutaneous, and mucosal forms of leishmaniasis, a neglected tropical disease. It can be administered topically or orally and is only indicated in patients aged 12 years or older. The CDC has also recommended it as a first line treatment for free-living amebae (FLA) infections such as primary amebic meningoencephalitis and granulomatous amebic encephalitis.
What are the applications of Application
Miltefosine is a PI 3-kinase and Akt inhibitor that also inhibits anti-IgE induced histamine release
Definition
ChEBI: A phospholipid that is the hexadecyl monoester of phosphocholine.
brand name
Miltex
Antimicrobial activity
Concentrations of 1–5 μm inhibit the promastigotes and amastigotes of Leishmania spp. and the epimastigotes and amastigotes of T. cruzi. Inhibitory concentrations against T. brucei spp. and E. histolytica are closer to 50 μm. Acanthamoeba spp. are variably susceptible, depending on the experimental conditions.
Acquired resistance
There are no reports of clinical resistance in Leishmania so far. Experimental resistance has been induced in vitro against the promastigote stage of Leishmania and two plasma membrane proteins, LdMT and Ld Ros3, are necessary for miltefosine uptake. There is evidence that reduced sensitivity of promastigotes is passed on to intracellular amastigotes.
Pharmaceutical Applications
An alkylphospholipid, originally investigated as an anticancer compound, formulated for oral administration.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Inhibitor of protein kinase C and of phosphatidylcholine synthesis. Used for the treatment of visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Active against metronidazole-resistant and -susceptible strains of Trichomonas vaginalis
Pharmacokinetics
In rodent models the drug is almost completely absorbed after
oral administration. About 90% is bound to plasma proteins. It
is widely distributed in the body; studies in rats showed highest
uptake in kidney, liver and spleen. In rats and dogs bioavailability
was 82% and 94%, with maximum values reached after 4–48 h.
In adult human trials repeated oral dosing with 100 mg per
day achieved a peak plasma concentration of 70 mg/L after
8–24 h (day 23). The half-life is 6–8 days.
Pharmacokinetics
Little is known about the clinical pharmacodynamics of miltefosine and other antileishmanial drugs.
Clinical Use
Visceral leishmaniasis
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Side Effects
Mild to moderate gastrointestinal side effects are reported in 40–60% of patients. Moderate to severe nephrotoxicity was seen in 2% and 1% of patients, respectively; increases in creatinine levels were reversible. Miltefosine is contraindicated in pregnancy, based on findings of teratogenicity in rats. It causes hemolysis and cannot be given intravenously.
Metabolism
Miltefosine is metabolized mainly by phospholipase D, releasing choline, choline-containing metabolites, and hexadecanol, which are likely to enter the intermediary metabolism. The metabolites produced by this reaction are all endogenous and are likely used for bio-synthesis of acetylcholine, cell membranes, and long-chain fatty acids.
storage
-20°C
Properties of Miltefosine
| Melting point: | 232-234° (dec) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: soluble10mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystalline solid |
| color | White to Almost white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H46NO4P/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-20-25-27(23,24)26-21-19-22(2,3)4/h5-21H2,1-4H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58066-85-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Miltefosine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Miltefosine
| InChIKey | PQLXHQMOHUQAKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O(CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)P([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C |
Abamectin manufacturer
Zydus Lifesciences Ltd.
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 58066-85-6 Miltefosine 98%View Details
58066-85-6 Miltefosine 98%View Details
58066-85-6 -
 Miltefosine hydrate 95% CAS 58066-85-6View Details
Miltefosine hydrate 95% CAS 58066-85-6View Details
58066-85-6 -
 Miltefosine CAS 58066-85-6View Details
Miltefosine CAS 58066-85-6View Details
58066-85-6 -
 Miltefosine 95% CAS 58066-85-6View Details
Miltefosine 95% CAS 58066-85-6View Details
58066-85-6 -
 Miltefosine CAS 58066-85-6View Details
Miltefosine CAS 58066-85-6View Details
58066-85-6 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4